Memory Enhancing Effect of Ethanolic Extract of Stevia rebaudiana (Bert.)
Keywords:
Stevia rebaudiana, Memory, Alzheimer diseaseAbstract
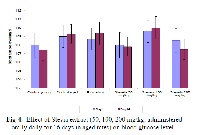
Suspension of ethanolic extract of leaves of Stevia rebaudiana bert. in gum acacia were administered orally to evaluate the memory enhancing activity in the aged rats. Memory enhancing effect was evaluated by using Morris water maze and elevated plus maze. Mean escape latency time (ELT) calculated each day during acquisition trial was used as an index of acquisition and mean time spent in target quadrant in search of missing platform provided an index of retrieval. Significant reduction in transfer latency (TL) value of retention indicated improvement of memory. Significant memory enhancing effect of ethanolic extract Stevia rebaudiana was observed in aged rats at 200 mg/kg p.o. dose.
References
Michelle CJ, Michael AM, Salvatore O,
Frank ML, Howard JF, William JB. Early
correlation of microgilal activation with
enhanced tumor necrosis factor-alpha and
monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
expression specifically with in the
entorhinal cortex of triple transgenic
Alzheimer disease mice. Journal of
neuroinflammation 2005; 2:23-26.
Tamar A, Yael AT, Moussa BHY, Silvia
M. Targeting multiple Alzheimer’s
Disease etiologies with multimodal
neuroprotective and neurorestorative iron
chelators. FASEB 2008;22:1296-1305.
McGeer PL, McGeer EG. Polymorphism
in inflammatory genes and the risk of
Alzheimer disease. Archives of
Neurology 2001;58:1790-1792.
Colin KC, Derrick EJ, Kario JC, Steven
BC, Gary EL. Inflammatory mechanism
in Alzheimer’s disease: Inhibition of beta
amyloid stimulated proinflammatory
responses and neuro toxicity by PPARgama agonist. The Journal of
Neuroscience 2000;20(2):558-567.
Mark AS, Catherine AR, Akihiko N,
Arun KR, George P. Oxidative stress in
Alzheimer’s disease. Biochimica et
Biophysica Acta 2000;1502:139-144.
Veurink G, Fullers SJ, Atwood CS,
Martins RN. Genetic, lifestyle and roles
of amyloid beta and oxidative stress in
Alzheimer’s disease. Annals of Human
Biology 2003;30(6) 639-667.
Sulkava R. Anti-inflammatory drug
therapy for prevention of Alzheimer’s
disease. Duodecim 1998;114:2025-2027.
Wood AJJ. Drug therapy : Alzheimer’s
disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;351:56-67.
Jan MC. Stevioside. Phytochemistry
;64:913-921.
Soni S, Kondalkar A, Tailang M, Pathak
AK. Pharmacognistic and phytochemical
investigation on Stevia rubadiana. Phcog
Mag. 2008; 4(13):89-94.
Kennelly EJ. Sweet and non-sweet
constitute of Stevia rubadiana (Bertoni)
bertoni. Kinghorn AD. Editor In the
genous of stevia Vol 19, Taylor and
Francis, London and NY 2002. pp 68-85
Starrat AN, Kirby CW, Pocs R, Brandle
JE. Rebaudioside F, a diterpene
glycoside from Stevia rubadiana.
Phytochemistry 2002;59:367-370.
Murali B, Upadhyaya UM, Goyal RK.
Effect of chronic treatment with
enicostemma littorale in non-insulindependent diabetic (NIDDM) rats. J.
Ethanopharmacol 2002;81:199-204.
Akiyma H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B,
Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR,
Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich
BL, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Griffin WS,
Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue L,
Mrak R, Mackenzie IR, McGeer PL.
Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease.
Neurobio. Aging 2000;21:383-421.
Berr C. Oxidative stress and cognitive
impairment in the elderly. J. Nutr.
Health Aging. 2002;6:261-266.
Floyd RA, Hensly K. Oxidative stress in
brain aging. Implication for
therapeutics of neurogenerative disease.
Neurobil. Aging 2002;23:795-807.
Harman D. Aging: A theory based on
free radical and radiation chemistry.
Journal of Gerontal 1956;11:298-300.
Harmanal. A hypothesis on the
pathogenesis of AD. Ann NY ACad
Science 1996;786: 152-168.
Takatsu H, Owada K, Abe L, Natano M,
Urans S. Effect of vitamin E on
learning and memory deficit in aged
rats. Journal of Nutration Science
Vitaminal 2009;55:389-393.
Gumieniczek A, Hopkala H, Roliñski J,
Bojarska-Junak A. Antioxidative and
anti-inflammatory effects of repaglinide
in plasma of diabetic animals.
Pharmacol Res 2005;52:162–6.
Tuttle HA, Davis-Gorman G, Goldman S,
Copeland JG, McDonagh PF.
Proinflammatory cytokines are increased
in type 2 diabetic women with
cardiovascular disease. J Diabet
Complications 2004;18:343–51.
Stephan A, Laroche S, Davis S.
Learning defects and dysfunctional
synaptic plasticity induced by
aggregated amyloid deposits in the
dentate gyrus are reduced by chronic
treatment with indomethacin. Eur. J.
Neurosci. 2003;17: 1921-1927.
Ibrahim NA, Motaw H, Riad SA.
Phytochemical and biological
investigation of Stevia rubadiana
(Bertoni). European Food Research and
Technology 2007;224 :483-488.
Brunet J, Farine JC, Garay RP, Hannaert
P. Invitro antioxidant properties of
calcium dobesilate. Clin. Pharmacol.
;12: 205-212.
Morris KA, Chang Q, Mohler, EG, Gold
PE. Age related memory Impairment
due to reduced blood glucose responses to
epinephrine Neurobilogy of Aging
;1-10..