Hepatoprotective effect of edible Oyster mushroom Pleurotus cornucopiae against Sodium Arsenite induced hepatotoxicity in rats
Keywords:
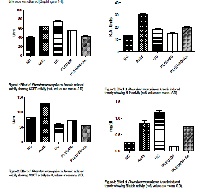
Pleurotus cornucopiae, Sodium Arsenite, SGPT, SGOT, ALP, BilirubinAbstract
Arsenic poisoning in ground water had been major challenge for the mankind in arsenic hit areas. In India, this problem is a big alarm in the entire Gangetic belt. The arsenic poisoning through drinking water has caused lots of health hazards to humans especially related hepato-biliary. This present study was carried out to investigate the therapeutic role of the ethanolic extract of Pleurotus cornucopiae on Sodium Arsenite induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Sodium Arsenite at the dose of 8mg/kg-1 body weight orally caused liver damage in rats as manifested by the significant rise in serum levels of Serum Glutamic Pyruvate Transaminase (SGPT), Serum Glutamate Oxalate Transaminase (SGOT), Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) and Bilirubin levels compared with control. Oral administration of 400mg extracts of P. cornucopiae (/kg) for 30 days to Sodium Arsenite treated rats showed significant ameleoration in these levels. Thus, the entire study reveals that ethanolic extract of P. cornucopiae at the dose of 400 mg/kg-1 body weight shows hepatoprotective effect against arsenic induced toxicity.
References
. Singh A, Handa SS. Hepatoprotective
activity of Apiumgraveolensand
Hygrophila. J. Ethnopharmacol.,
,15;49(3):119-26.
. National Research Council: Arsenic in
Drinking Water. National Academy
Press, Washington, D.C. (1999).
. National Research Council: Arsenic in
Drinking Water: Update. National
Academy Press, Washington, D.C.
(2001).
. Abernathy CO, Liu YP,LongfellowD,
Aposhian HV, BeckB, FowlerB, Goyer
R, Menzer R, Rossman T, Thompson
C, and Michael W. Arsenic: Health
effects, mechanisms of actions, and
research issues. Environ. Hlth.
Perspect., 1999,107, 593-597.
. Tchounwou PB, Wilson B, and Ishaque
A. Important considerations in the
development of public health advisories
for arsenic and arseniccontaining
compounds in drinking water. Rev.
Environ. Hlth., 1999.14, 211-229.
. Sordo M, Herrera LA. OstroskyWegmanPand RojasE. Cytotoxic and
genotoxiceffects of As, MMA, and DMA
on leukocytes and stimulated human
lymphocytes.
Teratog.Carcinog.Mutagen., 2001, 21,
-260.
. Rossman TG, Uddin A, Nand Burns.J.
Evidence that arsenite acts as a
cocarcinogen in skin cancer. Toxicol.
Appl. Pharmacol., 2004.198, 394-404.
. Kitchin KT. Recent advances in
carcinogenesis: modes of action,
animal model systems and methylated
arsenic metabolites. Toxicol. Appl.
Pharmacol., 2001,.172, 249-261
. Marafante E, Vahter M, and Envall J.
The role of methylation in the
detoxication of arsenate in the rabbit.
Chem. Biol. Interact., (1985). 56, 225-
. Delnomdedieu M, Basti MM, Styblo M,
Otvos JD, and Thomas DJ.
Complexation of arsenic species in
rabbit erythrocytes.Chem Res
Toxicol.1994. 7(5):621-7.
. Styblo M, Yamauchi H, and Thomas
DJ. Comparative in vitro methylation of
trivalent and pentavalent arsenicals.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 1995. 135,
-178.
. Geubel AP, Mairlot MC., Buchet JP,
Dive C, and Lauwerys R. Abnormal
methylation capacity in human liver
cirrhosis. Int. J. Clin.
Pharmacol.Res.,1988.8(2), 117-122
. Aposhian HV. Biochemical toxicology
of arsenic. In: Reviews of Biochemistry
and Toxicology (Eds: E. Hodgson, J.R.
Bend and R.M. Philpot). Vol. 10,
Elsevier, New York. 1989, 265-299
. Aposhian HV, &Aposhian MM.
Arsenic toxicology: Five
questions.Chem Res
Toxicol.2006.19(1):1-15.
. Yang C, and Frenkel K, Arsenicmediated cellular signal transduction,
transcription factor activation, and
aberrant gene expression: implications
in carcinogenesis. J. Environ.
Pathol.Toxicol.Oncol., 2002.21, 331-
. Qian Y, Castranova V. and ShiX J.
New perspectives in arsenic-induced
cell signal transduction.
Inorg.Biochem., 2003.96, 271-278.
. Wasser SP, and Weis AL. Medicinal
properties of substances occurring in
higher Basidiomycetes mushrooms:
current perspective (review).
International Journal of Medicinal
Mushroom,1999. 1: 31ă62.
. Jose N, and Janardhanan KK.
Antioxidant and antitumour activity of
Pleurotusflorida. Current Science.
79(7) 10: 941 ă 943.
. Chang ST, Arora DK, Mukerji KG,
Marth EH. (Eds.), Hand Book of
Applied Mycology. Marcel Dekker Inc.,
New York, 1991. 221ă240.
. Ajith TA, and Janardhanan KK. Indian
Medicinal Mushrooms as a Source of
Antioxidant and Antitumor Agents.
Journal of Clinical and Biochemical
Nutrition, 2007. 40: 157ă162.
. Reitmann S, and Frankel S. „A
colorimetric method for determination
of serum glutamate oxalacetic and
glutamic pyruvate transaminases,‰
Amer J Clin Path, 1957.28(1): 56-63.
. Kind PRN, King EJ. Estimation of
Plasma Phosphatase by Determination
of Hydrolysed Phenol with Aminoantipyrine.J Clin Path, 1954. 7(4), 322-
. Jendrassik L, Grof P, ereinfachte.
PhotometrischeMethodenzurBestimmu
ng des Blubilirubins, Biochem.Z., 1938.
, 81-89.
. Mitra SK, Venkataranganna MV,
Sundaram R, and Gopumadhavan S.
Protective effect of HD-03 a herbal
formulation, against various
hepatotoxic agents in rats. Journal of
Ethanopharmacology, 1998.63:181- -
. Chattopadhyay RR. Possible
mechanism of hepatoprotective activity
of Azadirachtaindicaleaf extract: part II.
Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2003.
: 217- 219.
. El-Gazzar UB, El-Far AH, and Abdel
maksoud HA. The Ameliorative effect
of Phoenix dactyliferaextract on carbon
tetrachloride hepatotoxicity in New
Zealand Rabbits. Journal of Applied
Sciences Research, 2009. 5(9): 1082-
. Fowler BA, Woods JS, and Schiller
CM. Ultrastructural and biochemical
effects of prolonged oral arsenic
exposure on liver mitochondria of rats.
Environ. Hlth. Perspect., 1977.19, 197-
. Moss DW, Henderson AR, and
Kachmar JF. In Fundamentals of
Clinical Chemistry. 3rd Edn. (Ed: N.W.
Tietz). W.B. Saurders,
Philadelphia.1987, 346-421.
. Simko V, Alkaline phosphatase in
biology and medicine. Digestive
Diseases and Sciences.,1991. 9: 189-
. Moss DW. The nature and origin of
alkaline phosphatase in hepatotoxicity
disease. Z. Med. Lab. Diagnost.,30:
-363.
. Poole A, and Leslie GB. A practical
approach to toxicological investigation,
Cambridge, 1989.44-86.
. Ringler DH. and Dabich L.
Haematology and clinical biochemistry
in the laboratory Rat, Vol. I, ed. By H.J.
Barker, J.R. Lindsey and S.H.
Weisbroth, Academic Press, London,
, 105-118
. Achliya GS, Wadodkar SG, Dorle AK.
Evaluation of hepatoprotective effect of
AmalkadiGhritaagainst carbon
tetrachloride induced hepatic damage
in rats. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,
90: 229- 232.
. Rajesh MG, and Latha MS. Preliminary
evaluation of the antihepatotoxic
activity of Kamilari, a polyherbal
formulation. Journal of
Ethnopharmacology,2004. 91: 99-104.