Treatment with Green Tea Prevents Intracerebroventricular Streptozotocin Induced Cognitive Impairment and Oxidative Stress in Mice
Keywords:
Hippocampus, degenerative disease, green teaAbstract
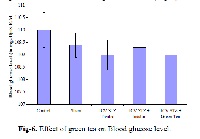
Green tea polyphenols have demonstrated significant antioxidant, anticarcinogenic, anti-mutagenic and antidiabetic in numerous human, animal and in vitro studies. Hence present study was design to evaluate the influence of green tea in streptozotocin induced oxidative stress in mice. Morris water maze, Elevated plus maze and passive avoidance apparatus was used for the evaluation of learning and memory. Brain thiobarbituric acid reactive substance was also estimated. Intracerebroventricular administration of streptozotocin reduces the learning and memory and increase the concentration of thiobarbituric acid reactive substance in mice. Green tea significantly improves the learning and memory and reverses the increase thiobarbituric acid reactive substance concentration in mice. The result of present study indicates that green tea improve the learning and memory. It also reduces the streptozotocin induced oxidative stress.
References
Bliss TVP, Collingridge GL. A synaptic
model of memory: long-term memory
potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature
, 361: 31-39.
Zhao WQ, Chen H, Quon MJ’ Alkon DL.
Insulin and insulin receptor in experim
-ental models of learning and memory. Eur.
J. Pharmacology 2004, 490: 71-81.
Park CR. Cognitive effects of insulin in the
central nerous system. Neuroscience
Biobehavior Reviews 2001, 25: 311-323.
Agrwal R, Tyagi E, Shukla R, Nath C. A
study of brain insulin receptors AChE
activity and oxidative stress in rat model of
intracerebroventricular STZ induced
dementia. Neuropharmacolgy 2009, 56:
-787.
Lannert H, Hoyer S. Intracerebroventricular
administration of streptozotocin causes
long-term diminutions in leaning and
memory abilities and cerebral energy
metabolism in adult rats. Behavior
Neuroscience 1998, 112: 1199-1208.
Prickaerts J, Fahring T, Blokland. Cognitive
performance and biochemical markers in
septum, hippocampus and striatum of rats
after an ICV injection of STZ: a correlation
analysis. Behavior Brain Research 1999,
: 73-88.
Sharma M, Gupta YK. Chronic treatment
with trans resveratrol prevents
intracerebroventricular streptozotocin
induced cognitive impairement and
oxidative stress in rats. Life Science 2002,
: 2489-2498.
Canuti CI, Shukitt HB, Joseph JN.
Neurobehavioral aspects of antioxidants in
aging. International Journal of
Developmental Neuroscience 2000, 18(4-
: 367- 81.
Li Q, Zhao HF, Zhang ZF, Liu ZG, Pei R.
Long –term administration of green tea the
catechins prevents age-related spatial
learning and memory decline in
C57bl/6 J mice by regulating hippocampal
cyclic amp-response binding protein
lgnaling cascade. Neuroscience, 2009; 159:
-1215.
Sharangi AB. Medicinal and therapeutic
potentialities of tea (Camellia sinensis
L.)-A review. Foood Researh International
, 42: 529-535.
Levites Y, Amit T, Mandel S, Youdim
MB. Neuroprotection and neurorescue
against Abeta toxicity and PKC-dependent
release of nonamyloidogenic soluble
precursor protein by green tea polyphenol (-
)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. FASEB 2003,
: 952–954.
Khan N, Mukhtar H. Multitargeted therapy
of cancer by green tea polyphenols.
Cancer Lett. 2008: 269-280.
Kaur T, Pathak CM, Pandhi P, Khandiya
KL. Effect of green tea extract on
learning, memory, behavior and
acetylcholinestrase activity in young and
old male rats. Brain and cognition 2008, 67:
-30.
Akanmu MA, Nwobudike NL, Ilesanmi
OR. Analgic, learning and memory and
anxiolytic effects of insulin in mice.
Behevioral brain Research 2009, 190: 237-
Morris RGM. Development of a water maze
procedure for studing spatial learning in
rats. J of Neurosci. Meth. 1984, 47-60.
Parle M, Dhingra D. Ascorbic acid: a
promising memory-enhancer in mice. J
Pharmacol. Sci. 2003: 129-135.
Sonkusare S, Srinivasan K, Kaul C,
Ramarao P. Effect of donepezil and
lercanidipin on memory impairment
induced by intracerebroventricular
streptozotocin in rats. Life Sciences 2005,
(1): 1-14.
Yagi K. Assay for serum lipid peroxide
level and its clinical significance. In: K
Yagi Editor. Lipid Peroxide in Biology and
Medicine. Academic Press Inc, New
York, 1982. pp. 232-242.
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Far AL,
Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the
folin-phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951,
-275.
Murali B, Upadhyaya UM, Goyal RK.
Effect of chronic treatment with
enicostemma littorale in non-insulindependent diabetic (NIDDM) rats. J.
Ethanopharmacol 2002. 81:199-204.
Lannert H, Wirtz P, Schuhmann V,
Galmbacher R. Effects of Estradiol [-
(beta)] on learning, memory and cerebral
energy metabolism in male rats after
intracerebroventricular administration of
streptozotocin. Journal of Neura
Transmission 1998, 105: 1045-63.
Sharma M, Gupta YK.
Intracerebroventricular injection of
streptozotocin in rats produces both
oxidative stress in the brain and cognitive
impairment. Life Sciences 2000,
/9:1021–9.
Matsuoka Y, Hasegawa H, Okuda S,
Muraki T, Uruno T, Kubota K.
Ameliorative effects of tea catechins on
active oxygen-related nerve cell
injuries. The Journal of Pharmacology and
Experimental Therapeutics 1995, 274: 602–
Hong JT, Ryu SR, Kim HJ, Lee JK, Lee
SH, Kim DB, et al.. Neuroprotective
effect of green tea extract in experimental
ischemia-reperfusion brain injury.
Brain Research Bulletin 2000, 53: 743–749.
Forster MJ, Dubey A, Dawson KM, Stutts
W A, Lal H, Sohal R S. Age - related
losses of cognitive function and motor skills
in mice are associated with oxidative
protein damage in the brain. Proceedings of
the National Academy of Sciences of the
United States of America 1996, 93: 4765–
Skrzydlewska E, Ostrowska J, Farbiszewski
R, Michalak K. Protective effect of
green tea against lipid peroxidation in the
rat liver blood serum and the brain.
Phytomedicine 2002, 9: 232–238.
Morris KA, Chang Q, Mohler, EG, Gold
PE. Age related memory impairments
due to reduced blood glucose responses to
epinephrine. Neurobilogy of Aging
, 1-10.