Anti-diabetic and acute toxicity studies of Annona squamosa L. ethanolic leaves extract.
Keywords:
Alloxan, Glibenclaimide, custard apple, hypoglycaemic, toxic effectsAbstract
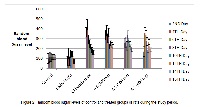
Aim of this research work was to explore the anti-diabetic activity and acute toxicity of Annona squamosa L. leaves ethanolic extract in albino rats and mice respectively. Diabetes was induced by Alloxan (120 mg/kg). Seven rats were taken in each group. Glibenclaimide (0.25 mg/kg) was taken as the standard drug. A. squamosa was administered orally in 100mg, 200mg and 400mg doses in three different groups of diabetes- induced rats. A. squamosa leaves extracts were found to have significant anti-diabetic activity. Acute toxicity study was carried out on administration of 800mg/kg, 1600mg/kg and 5000 mg/kg body weight. No acute toxicity was observed at 800mg/kg and 1600mg/kg doses. At 5000mg/kg body weight dose 100% fatality was recorded within 24 hours. Our research work revealed the safe and effective anti-diabetic activity of Annona squamosa ethanolic leaves extract.
References
Holman RR and Turner RC. Oral Agents and Insulin in the Treatment of Diabetes.Blackwell, Oxford,1991.
Khare CP. India Medicinal Plants, 1st ed. Ny: Springer International Publication. 2007.
Al-Awadi FM, Khattar MA and Gumma KA. On the mechanism of the hypoglycemic effect of a plant extract. Diabetologia.1985;28: 432–434.
Kalidindi N, Thimmaiah NV, Jagadeesh NV. Nandeep R, Swetha S, Kalidindi B. Anti-fungal and antioxidant activities of organic and aqueous extracts of Annonasquamosa Linn. Leaves. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis. 2015;23(4):795-802.
National Research Council. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 7th ed. Washington, DC, National Academy Press.1996.
Shirwaikar A, Rajendran K, Kumar C. Pharmaceutical Biology, - Taylor & Francis.2004.
Ankur Rohilla and Shahjad Ali. Alloxan Induced Diabetes: Mechanisms and Effects. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences. 2012;3(2):819-823.
Snedecor GW, Cochrane WG. Statistical Methods. Sixth edition. Ames, Iowa: The Iowa State University press.1967.
Kameshwara Rao Giri R, Kesavulu MM and Apparao C. Herbal medicine: In the management of diabetes mellitus. ManpharVaidhyaPatrica.1997.
Valiathan MS, Healing plants. Curr. Sci. 1998;75:1122–1126.
Morton J. Sugar Apple. In: Fruits of warm climates. Julia F. Morton, Miami, FL. 1987:69-72.
Vohora SB, Kumar I and Naqvi SAH. Phytochemical, pharmacological, antibacterial and anti-ovulatory studies on Annonasquamosa. Planta Med. 1975;28:97–100.
Brosky G and Logothelopoulos J. Streptozotocin diabetes in the mouse and guinea pig. Diabetes.1969;18:606–609.
Xia M and Laychok SC. Insulin secretion myoinositol transport and Na+-K ATPase in glucose desensitised rat islets. Diabetes.1993;42:1392–1400.
Panda S, Kar A. Anti-diabetic and anti-oxidative effects of Annonasquamosa leaves are possibly mediated through quercetin-3-O-glucoside. Biofactors. 2007;31(3-4):201-10.
Gupta RK, Kesari AN, Watal G, Murthy PS, Chandra R, Maithal K, Tandon V. Hypoglycaemic and antidiabetic effect of aqueous extract of leaves of Annonasquamosa (L.) in experimental animal. Current Science. 2005;88(8):1244-1254.
El Banna H, Ramadan A, Elzorba H, Sayed F. Some pharmacological and toxicological activities of Annonasquamosa Linn.ethanolic extract. World Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2016;5(12):188-202.
Onwusonye JC, Uwakwe AA, Patrick-Iwuanyanwu KC. Acute and sub-acute toxicity studies of methanol leaf extracts of Annonasquamosa Linn. in mice sky journal of biochemistry Research. 2014;3(7):035-053.
Sharma Abhishek L and Vd. Goray Namrata P. Pharmacognostical studies on the leaf of Annonasquamosa Linn. Phcog J; 2009;1(2):88-93.
Madhu CH, Jonathan Brainard P, Prithvi Raj G, Swapn J, Samba Siva Rao A. Anti-ulcer activity of aqueous extract of Annonasquamosa leaves on rats. Int J Pharm Sci& Res. 2012;3(11): 4429-4433.
Richa Mishra, DewasyaPratap Singh and Brijeshkunvar Mishra Anti-nociceptive and Anti-inflammatory Activity of Annonasquamosa L. Leaf Extract in Mice and Rats Research J. Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry. 2012;4(3):182-185.
Kumar SA, Venkatarathanamma V, Naga Saibabu V, Seetha Ram K. Anti-pyretic activity of Annona plants leaves on brewer’s yeast induced febrile rats. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2015;8(3):210-212.
Masimba EI, Baraka S. Oral acute toxicity study of Annonasquamosa L. leaves extract and fractions in albino mice Journal of Advanced Scientific Research. J Adv Sci Res. 2016;7(1):38-42.