Phytochemical Screening and Biological Studies of Shilajit (Asphaltum)
Keywords:
Shilajit, phytochemical screening, anti-microbial activityAbstract
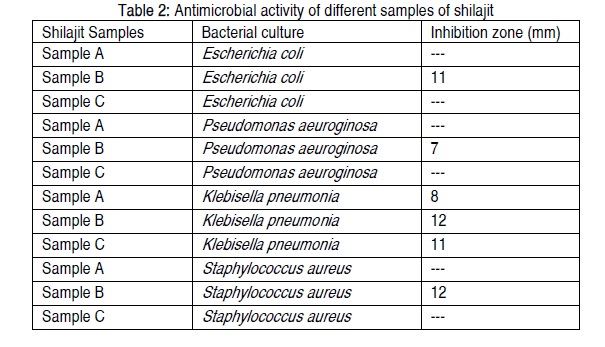
Shilajit (asphaltum) is produced by the long term humification of dead plant material and organic vegetable matter by different micro-organisms and has great potential for the treatment of a variety of human conditions. This treatise reviews its origin, sources, chemical composition, biological and commercial importance. Phytochemical analysis was done by standard methods to evaluate different Shilajit (asphaltum) classes of compounds in different samples of shilajit which are responsible for their biological activity. Shilajit`s anti-microbial activity has been evaluated against four different bacterial strains viz., Escherichia coli, Psuedomonas aeuroginosa, Klebisella pneumonia and Staphylococcus aureus. Phytochemical analysis illustrated that shilajit contains terpenoids, cardiac glycosides, saponins and reducing sugars. Surprisingly, some classes of compounds are absent in shilajit viz., alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins and anthraquinones. . Shilajit showed no response towards halophytic bacteria and negligible activity was shown towards other strains of bacteria. Since anti-microbial activity is based on environmental factors its activity varied between locations.
References
Parkesh J, and Chandern S. In vitro antimicrobial activity of extracts of Launaea procumbeans (Labiateae). Afr J Biomed Res 2006;9:89-93.
Wilson E, Rajmanickam GV, Dubey GP, Klose P, Musial F, Saha FJ, and Rampp T. Review on Shilajit used in Traditional Indian Mediciene. J Ethnopharmacol.2011;136: 1-9.
Cornejo JM, Jim L, Caballero F, and Maccioni M. “Fulvic acid inhibits aggregation and promotes disassembly of tau fibrils associated with alzheimer’s disease.” Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2011;27:143-153.
Ghosal S, Singh K, Kumar S, and Srivatsava R. Anti ulcerogenic activity of fulvic acids and 4-metoxy-6-carbomethyl biphenyl isolated from shilajit, Phytother Res 1988;2:187-191.
Ghosal S.“Chemistry of shilajit, an immunomodulatory Ayurvedic rasayan,” Pure and Applied Chemistry 1990;62:1285–1288.
Ghosal S. Shilajit in perspective, First ed. Alpha Science International Limited,
Agarwal SP, Khanna R, Karmarkar R, Anwer MK, and Khar RK. Shilajit; a review. Phytother Res. 2004; 2:401-405.
Trivedi NA, Mazumdar B, Bhatt JD, and Hemavanti KG. Effect of Shilajit on blood glucose and lipid profile in alloxon induced diabetic rats. Indian J Pharmacol 2004;36: 373-376.
Rege AA, Ramkrishna Y, Ambaye RY, and Deshmukh Y. Evaluation of in vitro inhibitory effect of selected plants and shilajit on HIV –Reverse Transcriptase, Indian J of Natural Products and Resources 2012;3:145-151.
Rege AA, Ambaye RY, and Deshmukh RA. In vitro testing of Shilajit for anti-HIV activity. Int J Pharmacol Biol Sci 2009;3:57-64.
Rege, AA, and Chowdhary A.S. Evaluation of Shilajit as Putative HIV-Protease Inhibitor. International J of Advanced Res 2014;2:154-157.
Eisenberg DM, Davis RB, and Ettner, SL. Trends in alternative medicine use in the United States, results of a follow-up national survey. JAMA 1998;280:1569-1575.
Joshi A, Bhobe M, and Saatarkar A. Phytochemical investigation of the roots of Grewia microcos Linn. J Chem Pharma Res 2013;5:80-87.
Abdullahi MN, Ilyas N, and Ibrahim H. Evaluation of phytochemical screening and analgesic activity of aqueous extract of the leaves of Microtrichia perotitii dc (Asteraceae) in mice using hotplate method. Med Plant Res 2013;3:37-43.
Ayoola GA, Coker, HB, Adesegun SA, Adepoju-Bello AA, Obaweya K, Ezennia EC, and Atangbayila TO. Phytochemical screening and antioxidant activities of some selected medicinal plants used for malaria therapy in southwestern Nigeria. Trop J Pharm Res 2008;7:1019-1024.
Zaidan MRS, Rain, NA, Badrul AR, Adlin A, Norazah A, and Zakiah I. In vitro screening of five local medicinal plants for antibacterial activity using disc diffusion method. Trop Biomed 2005;22:165-170.
Borokini TI, and Ayodele AE. Phytochemical screening of Tacca leontopetaloides L.) Kuntze collected from four geographical locations in Nigeria. Int J Modern Bot 2012; 2:97–102.
Vladimir K, and Ludmila M. Glycosides in Medicine: "The role of glycosidic residue in biological activity". Curr Med Chem 2001;8:1303-1328.
Feng N, Ye W, Wu P, Huang Y, Xie H, Wei X. Two new antifungal alkaloids produced by Streptoverticillium morookaense. J Antibiot 2007;60:179–183.
Niv P, and Yechiel S. A molecular mechanism for lipopolysac- charide protection of gram negative bacteria from antimicrobial peptides. J Biol Chem 2005;280:10378-10387.
Zhao WH, Hu ZO, Okubo S, Hara Y, and Shimamura T, Mechanism of synergy between epigallocatechin gallate and b- lactams against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2001;45: 1737–1774.