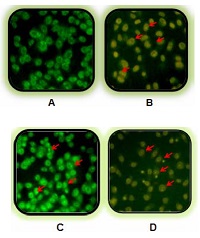
Nobiletin Increased Cytotoxic Activity Of Doxorubicin On Mcf-7 Cells But Not On T47d Cells
Keywords:
Nobiletin, doxorubicin, breast cancer, cell cycle, apoptosisAbstract
Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid, shows strong cytotoxic effect in several cancer cell lines. The aim of this research was to investigate cytotoxic activities of nobiletin alone and in combination with doxorubicin. Cell viability assay of nobiletin, doxorubicin, and combination treatments were carried out by using MTT assay. Apoptosis assay was done using double staining method using Ethidium Bromide-Acridine Orange. Cell cycle distribution was determined by flowcytometry FACS-Calibur and data was analyzed by using ModFit LT 3.0 program. Nobiletin (5, 10 and 15 µM) increased cytotoxic effect of doxorubicin compared with doxorubicin alone in MCF-7 cells but not in T47D cells. The strongest cytotoxic activity was showed by the combination of 200 nM doxorubicin and 15 µM nobiletin in MCF-7 cells. Single treatment of doxorubicin 200 nM, nobiletin 15 µM and their combination induced G2/M accumulation in MCF-7 cells. Combination of 15 µM and nobiletin 200 nM doxorubicin showed strong synergism on apoptosis induction of MCF-7 cells. Single treatment of nobiletin 15 µM and doxorubicin 7.5 nM induced T47D cell accumulation in G1 phase and G2/M phase respectively, while their combination induced accumulation of T47D cells in G2/M phase. Nobiletin is potentially to be developed as co-chemotherapeutic agent for breast cancer, while molecular mechanism need to be explored.
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E. Cancer
Statistics, 2010, CA Cancer J Clin, doi:
;10:3322/caac.20073.
Fimognari C, Nusse MN, Lenzi M, Sciuscio
D, Cantelli-Forti G and Hrelia P.
Sulforaphane Increases The Efficacy of
Doxorubicin in Mouse Fibroblasts
Characterized by p53 Mutations, Mutation
Research, 2006;601:92–101.
Murakami A, Nakamura Y, Torikai K,
Tanaka T, Koshiba T, Koshimizu KKuwahara
S, Takahashi Y, Ogawa K, Yano M, Tokuda
H, Nishino H, Mimaki Y, Sashida Y,
Kitanaka S and Ohigashi H. Inhibitory Effect
of Citrus Nobiletin on Phorbol Ester-Induced
Skin Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and
Tumor Promotion in Mice, Cancer Res.,
;60:5059–5066
Ohnishi H, Asamoto M, Tujimura K,
Hokaiwado N, Takahashi S, Ogawa K,
Kuribayashi M, Ogiso T, Okuyama H and
Shirai T. Inhibition of Cell Proliferation by
Nobiletin, A Dietary Phytochemical,
Associated With Apoptosis and Characteristic
Gene Expression, But Lack Of Effect on
Early Rat Hepatocarcinogenesis In Vivo,
Cancer Sci., 2004;95(12):936-942.
Yoshimizu N, Otani Y, Saikawa Y, Kubota T,
Yoshida M, Furukawa T, Kumai K,
Kameyama K, Fujii M, Yano M, Sato T, Ito
A and Kitajima M. Anti-tumour Effects of
Nobiletin, A Citrus Flavonoid, on Gastric
Cancer Include: Antiproliferative Effects,
Induction of Apoptosis and Cell Cycle
Deregulation, Aliment Pharmacol Ther,
;1:95-101.
Morley KL, Ferguson PJ and Koropatnick J.
Tangeretin and Nobiletin Induce G1 Cell
Cycle Arrest But Not Apoptosis In Human
Breast and Colon Cancer Cells, Cancer Lett,
;251(1):168-78.
Miyamoto S, Yasui Y, Tanaka T, Ohigashi H
and Murakami A. Suppressive Effects of
Nobiletin on Hyperleptinemia and ColitisRelated Colon Carcinogenesis In Male ICR
Mice, Carcinogenesis, 2008;29(5):1057-1063.
Davis JM, Navolanic PM, WeinsteinOppenheimer CR, Steelman LS, Wei H,
Konopleva M, Blagosklonny MV and
McCubrey JA. Raf-1 and Bcl-2 Induce
Distinct and Common Pathways That
Contribute to Breast Cancer Drug Resistance.
Clin. Canc. Res. 2003;9:1161-1170.
Zampieri L, Bianchi P, Ruff P and Arbuthnot
P. Differential Modulation by Estradiol of Pglycoprotein Drug Resistance Protein
Expression in Cultured MCF7 and T47D
Breast Cancer Cells, Anticancer Res.,
;22:2253-2259.
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA. The Hallmarks
of Cancer. Cell, 2000;100:57-70.
Emami A, Zeinali S, Motahari Z and Azizi E.
Resistance to Adriamycin Alters the
MDR1/P-gp, Topoisomerase II-alpha Gene
and Protein Expression Levels in T47D
Human Breast Cancer Cells, Conference
Module of 2005 AAPS Annual Meeting and
Exposition, downloaded from:
www.aapsj.orgabstractsAM_2005AAPS2005
-001197.pdf, on accessed in September 2009.
. Li X, Lu Y, Liang K, Liu B and Fan Z.
Differential Responses to Doxorubicininduced Phosphorylation and Activation of
Akt in Human Breast Cancer Cells, Breast
Cancer Research, 2005;7:589-597.
Minotti G, Menna P, Salvatorelli E, Cairo G
and Gianni L. Anthracyclins: Molecular
Advances and Pharmacologic Developments
in Antitumor Activity and Cardiotoxicity.
Pharmacol Rev., 2004;56:185-228.
Luo G, Guan X and Zhou L. Apoptotic Effect
of Citrus Fruit Extract Nobiletin on Lung
Cancer Cell Line A549 in vitro and in vivo,
Cancer Biol Ther, 2008;(6):966-973.