Azadirachta indica Leaf Extract Ameliorates Hyperglycemia and Hepatic Glycogenosis in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Wistar Rats
Keywords:
Diabetes, Azadirachta indica, hepatic glycogenosis, oxidative stress, liverAbstract
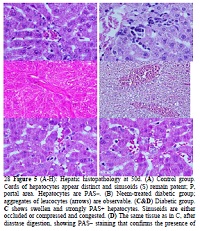
We studied the effects of ethanolic leaf extract of Azadirachta indica (AIE) on hepatic microscopic anatomy and oxidative stress markers in diabetic rats. Seventy-five Wistar rats (8 weeks old) were randomly assigned to five treatment groups: control; diabetic; diabetic+AIE; AIE only; and diabetic+glibenclamide. Hyperglycemia was induced in fasted rats with streptozotocin. AIE was administered orally at 500 mg/kg bw/d and glibenclamide at 600 μg/kg bw/d for 50 days (50 d). Animals were sacrificed on treatment days 7, 21 and 50. The liver was stained with PAS. Hepatic markers of oxidative stress were also estimated. At 50 d, histological study of the liver of diabetic rats showed swollen PAS+ hepatocytes, whose content was confirmed to be glycogen. On the contrary, hepatocytes of AIE-treated diabetic rats lacked glycogen. The major finding in these rats was exacerbated oxidative stress. Our findings in this model showed the beneficial effect of AIE in the amelioration of diabetic hepatic glycogenosis.
References
xpert committee on the
Definition, Diagnosis and Classification of
Diabetes Mellitus and its Complications.
; Part 1: pg 2.
Mohan V, Sandeep S, Deepa R, Shah B,
Varghese C
Indian scenario. Indian J Med Res 2007; 125:
-230.
Dham S, Shah V, Hirsch S, Banerji MA. The
role of complementary
medicine in diabetes. Current Diabetes
Reports 2006; 6: 251-258.
Hsia SH, Bazargan M, Davidson MB. Effect
of pancreas tonic (an ayurved
supplement) in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Metabolism 2004; 53: 1166-1173.
Shekhar KC, Achike FI, Kaur G, Kumar P,
Hashim R. A preliminary evaluation of the
efficacy and safety of Cogent db (an
ayurvedic drug) in the
patients with type 2 diabetes. J Altern Compl
Med 2002; 8: 445-457.
Liu Y
and opportunities. Life Sci 2008; 82: 445-
Ioset JR, Raoelison GE, Hoatettmann K.
Detection of aristolochic acid in Chinese
phytomedicines an
as slimming regimens. Food Chem Toxicol
; 41: 29-36.
Anderson IB, Mullen WH, Meeker JE,
Khojasteh-Bakht SC, Oishii S, Nelson SD,
Blanc PD. Pennyroyal toxicity: measurement
of toxic metabolite levels in two cases and
review of the literature. Annals of Internal
Med 1996; 124: 726-734.
Ben-Yahia M, Mavier P, Metreau JM, Zafrani
ES, Fabre M, Gatineau-Saillant G, Dhumeaux
D, Mallat A. Chronic active hepatitis an
cirrhosis induced by wild germander. 3 cases.
Gastroenterol Clin Biol 1993; 17: 959-962.
Martocchia A, Risicato MG, Mattioli MA,
Ruco L, Falaschi P. Association of diffuse
liver glycogenosis and mild focal
macrovesicular steatosis in a
poorly controlled type 1 diabetes. Intern
Emerg Med 2008; 3: 273-274.
Torbenson M, Chen Y, Brunt E, Cummings
OW, Gottfried M, Jakate S, Liu Y, Yeh MM,
Ferrell L. Glycogenic hepatopathy: an
Baynes JW. Role of oxidative stress in
development of complications in diabetes.
Diabetes 1991; 40: 405-412.
Nishikawa T, Edelstein D, Du XL.
Normalizing mitochondrial superoxide
production blocks three pathways of
hyperglycaemic damage. Nature 2000; 404:
-90.
Wolff SP, Bascal ZA, Hunt JV. Autoxidative
glycosylation: free radicals and glycation
theory. Prog Clin Res 1989; 304: 259-275.
Blakytny R, Harding JJ. Glycation (nonenzymatic glycosylation) inactivates
glutathione reductase. Biochem J 1992;.288:
-307.
Yoshida K, Hirokawa J, Tagami S,
Kawakami Y, Urata Y, Kondo T. Weakened
cellular scavenging activity against oxidative
stress in diabetes mellitus: regulation of
glutathione synthesis and efflux. Diabetologia
; 38: 201-210.
Chattopadhyay RR. Possible mechanism of
antihyperglycaemic effect of Azadirachta
indica leaf extract. Part V. J Ethnopharmacol
; 67: 373-376.
Lal MA, Korner A, Matsuo Y, Zelenin S,
Cheng SXJ, Jaremko G, DiBona GF, Eklof
AC, Aperia A. Combined antioxidant and
COMT inhibitor treatment reverses renal
abnormalities in diabetic rats. Diabetes 2000;
: 1381-1389.
Lenzen S. The mechanism of alloxan- and
streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetologia
; 51: 216-226.
Gupta S, Kataria M, Gupta PK, Murganandan
S, Yashroy RC. Protective role of extract of
neem seeds in diabetes caused by
streptozotocin in rats. J Ethnopharmacol
; 90: 185-189.
Sathishsekar D, Subramanian S. Beneficial
effects of Momordica charantia seeds in the
treatment of STZ-induced diabetes in
experimental rats. Biol Pharm Bull 2005; 28:
-983.
Sumanth M, Rana AC. In vivo antioxidant
activity of hydroalcoholic extract of
Taraxacum officinale roots in rats. Indian J
Pharmacol 2006; 38: 54-55.
Murty SK, Narayana RD, Krishna RD,
Gopalakrishna ML. A preliminary study on
hypoglycaemic and antihyperglycaemic effect
of Azadirachta indica. Indian J Pharmacol
; 10: 247-250.
Khosla P, Bhanwra S, Singh J, Seth S,
Srivastava RK. A study of hypoglycaemic
effects of Azadirachta indica (neem) in
normaland and alloxan diabetic rabbits.
Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2000; 44: 69-74.
Chattopadhyay RR. Possible mechanism of
antihyperglycaemic effect of Azadirachta
indica leaf extract. Part IV. Gen Pharmac
; 27: 431-434.
Szayna M, Doyle ME, Betkey JA, Holloway
HA, Spencer RGS, Greig NH, Egan JM.
Exendin-4 decelerates food intake, weight
gain and fat deposition in Zucker rats.
Endocrinol 2000; 141: 1936-1941.
Siddiqui BS, Afshan F, Gulzar T, Hanif M.
Tetracyclic triterpenoids from the leaves of
Azadirachta indica. Phytochemistry 2004; 65:
-2367
Sanders RA, Rauscher FM, Watkins III JB.
Effect of quercetin on antioxidant defence in
STZ-induced diabetic rats. J Biochem Mol
Toxicol 2001; 15: 143-149.
Dias AS, Porawski M, Alonso M, Marroni N,
Collado PS, Gonzalez-Gallego. Quercetin
decreases oxidative stress, NFkB activation
and iNOS overexpression in liver of STZinduced diabetic rats. J Nutr 2005; 135: 2299-
Stone BE, Van Thiel DH. Diabetes mellitus
and the liver. Semin Liver Dis. 1985; 5: 8-28.
Munns CF, McCrossin RB, Thomsett MJ,
Batch J. Hepatic glycogenosis: reversible
hepatomegaly in type 1 diabetes. J Paediatr
Child Health 2000; 36: 449-452.
Mauriac P. ‘Gros ventre, hepatomegaly,
troubles de la croissance chez les enfants
diabetiques, traits depuis plusieurs anbnees
par l’insuline’. Gas Hebd Sci Med Bordeaux
; 51: 402.
Ozen H. Glycogen storage diseases: new
perspectives. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13:
-2553.
Iancu TC, Shiloh H, Dembo L. Hepatomegaly
following short-term high-dose steroid
therapy. J Paediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1986;
: 41-46.
Khandelwal RL, Zinman SM, Zebrowski EJ.
The effect of STZ-induced diabetes and of
insulin supplementation on glycogen
metabolism in rat liver. Biochem J 1977; 168:
-548.
Bahnak BR, Gold AH. Effects of alloxan
diabetes on the turnover of rat liver glycogen
synthase. J Biol Chem 1982; 257: 8775-8780.
Ferrannini F, Lanfranchia A, RohnerJfanrenaud F, Manfredini G, Vandewerve V.
Influence of long-term diabetes on liver
glycogen metabolism in rat. Metab 1990; 39:
-1088.
Duvnjak M, Virovie L, Tomasic V, Balieevie
D, Smircie-Duvnjak L. Hepatomegaly and
elevated aminotransferases in a patient with
poorly regulated diabetes. Acta Clin Croat
; 43: 143-146.
Fridell JA, Saxena R, Chalasani NP, Goggins
WC, Powelson JA, Cummings OW.
Complete reversal of glycogen hepatomegaly
with pancreas transplantation: two cases.
Transplantation 2007; 83: 84-86.
Vischer UM, Jornot L, Wollheim CB, Theler
JM. Reactive oxygen intermediates induce
regulated secretion of van Willbrand factor
from cultured human endothelial cells. Blood
; 85: 3164-3172.
Ortmann C, Brinkmann B. The expression of
P-selectin in inflammatory and noninflammatory lung tissue. Int J Legal Med
; 110: 155-158.
Fernekorn U, Butcher EC, Behrends J,
Karsten CM, Robke A, Schulze TJ. Selectin,
platelet plays a critical role in granulocyte
access to the pregnant mouse uterus under
physiological and pathological conditions.
Biol Reprod 2007; 76: 645-653.
Chosay JG, Essani NA, Dunn CJ, Jaeschke H.
Neutrophil margination and extravasation in
sinusoids and venules of the liver during
endotoxin-induced injury. Am J Physiol
; 272: G1195-G1200.
Ortiz de Montellano PR. Cytochrome P450:
structure, mechanism and biochemistry. 3rd
Ed, Kluver Academic/Plenum Publishers,
New York NY. 2005.
Dostalek M, Hardy KD, Milne GL, Morrow
JD, Chen C, Gonzalez FJ, Gu J, Ding X,
Delinda AJ, Jeffrey AJ, Martha VM, Peter
GF. Development of oxidative stress by
cytochrome P450 induction in rodents is
selective for barbiturates and related to loss of
pyrimidine-depenedent protective systems. J
Biol Chem 2008; 283: 17147-17157.
Shertzer HG, Nebert DW, Puga A, Ary M,
Sonntag D, Dixon K, Robinson LJ,
Cianciolo E, Dalton TP. Dioxin causes a
sustained oxidative stress response in the
mouse. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun
; 253: 44–48.
Albano E, Tomasi A, Persson J, Terelius Y,
Gloria-Gatti L, Ingelman-Sundberg M,
Dianzani MU. Role of ethanol-induced
cytochrome P450 (P450IIE1) in catalysing
the free radical activation of aliphatic
alcohols. Biochem Pharmacol 1991; 41:
-1902.
Dasgupta T, Banerjee S, Yadavan PK, Rao
AR. Chemopreventive potential of
Azadirachta indica (neem) leaf extract in
murine carcinogenesis model systems. J
Ethnopharmacol 2004; 92: 23-36.
Heyneman R, Burvenich C, Vercauteran R.
Interaction between the respiratory burst
activity of neutrophil leucocytes and
experimentally induced Escherichia coli. J
Dairy Sci 1990; 73: 985-994.
Bonder CS, Ajuebor MN, Zbytnuik LD,
Kubes P, Swain MG. Essential role for
neutrophil recruitment in concanavalin Ainduced hepatitis. J Immunol 2004; 172: 45-
Akpinar E, Ozden I, Savci N, Emre A. The
role of leucocyte-derived free oxygen radicals
in the pathogenesis of experimental acute
pancreatitis. HPB Surgery 1995; 8: 237-239.
Brahmachari G. Neem – An omnipotent
plant: Retrospection. Chem Biochem 2004; 5:
-421.
Tolman KG, Foneska V, Dalpiaz A, Tan MH.
Spectrum of liver disease in type 2 diabetes
and management of patients with diabetes and
liver disease. Diabetes Care 2007; 30: 734-