In Vitro studies on antibacterial activity and phytochemical analysis of whole plant extracts of Stelleria media
Keywords:
Stelleria media, Chickweed phytochemical analysis, antimicrobial activity, activity index, therapeutic purposeAbstract
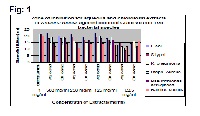
The whole plant extracts of Stelleria media were examined for the presence of alkaloids and phenolics with simultaneous study on the antimicrobial properties of these extracts. Investigation was carried out using four different concentration (62.5, 125, 250 and 500 mg/ml) of extract to determine the quantitative effectiveness. Preliminary evaluation of both the aqueous and the chloroform fractions showed a broad spectrum of activity ((p<0.05)) since the extracts inhibit the growth of both gram positive and gram negative bacterial isolates. Clinical isolates used in present investigation were E.coli, S.typhi, K. pneumonia, Staph. Aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacillus subtilis. The phytochemical analysis revealed the presence of alkaloids, saponins, tannins, flavonoids, cardiac glycosides, anthraquinones and cyanogenetic glycosides in varying concentration. Both the chloroform and aqueous extracts inhibited the growth of the test organisms with Salmonella typhi and E.coli showing the highest susceptibility but the pathogens were found to be less sensitive for chloroform extract in comparison to the aqueous extract which could be due to the domination of antimicrobial activity of water soluble polar compounds. This research supports the local use of the plant, Stelleria media for prophylactic and therapeutic purposes against bacterial infection.
References
Adel M, Mahasneh, Ahmad A, El-Oqlah,
Antimicrobial activity of extracts of herbal
plants used in the traditional medicine of
Jordan. Journal of Ethno pharmacology 64
271–276
Anonymous,1999. Natural peptides offer safe
alternative to agricultural fungicides.
Biotechnology Lab. International. 2 (5), 1.
Brantner, A., Grein, E., 1994. Antibacterial
activity of plant extracts used externally in
traditional medicine. Jouranl of
Ethnopharmacology 44, 35–40.
Brooks GF, Butel JS, Morse SA, 2004. In
Medical Microbiology. 23rd Edition, Mc
Graw-Hill Publishers. Pp 161-175.
Cheesbrough M, 1982. Medical laboratory
Manual for tropical countries. Microbiology.
English language book service (ELBS)
Vol.11. pp. 283-378.
Culer I, 1982. Methodology for the analysis
of vegetable drugs.Practical Manual on the
industrial Utilisation of Medicinal and
Aromatic Plants Center Building, Romania,
pp. 67-81
Duke JA, Wain KK, 1981. Medicinal plants
of the world. Computer enteries. 3 vols.
F. Lyumugabe,G. Kamaliza, E. Bajyana and
P. H. Thonart,2010. Microbiological and
physico-chemical characteristic of Rwandese
traditional beer “Ikigage”. African Journal of
Biotechnology Vol. 9(27), pp. 4241-4246.
Ghazal, S.A., Abuzarqa, M., Mahasneh, A.M.
Antimicrobial activity of Polygonum
equisetiforme extracts and flavonoids.
Phytotherapy Research 6, 265–269.
Hart CA, Kariuki S,1998. Antimicrobial
resistance in developing countries. Br. Med.
J. 317: 647-650.
Hewitt W, Vincent S, 1989. In: Theory and
application of microbiological assay.
Academic Press, San Diego, p. 39.
Joy R. Borchardt et al, 2009. Antioxidant and
antimicrobial activity of seed from plants of
the Mississippi river basin. Journal of
Medicinal Plants Research Vol. 3(10), pp.
-718.
Mahasneh, A.M., 1986. Antimicrobial
activity of plant extract and pure judicin from
Aretmisia judiaca. Jordan Medical Journal 20,
–24.
Mahasneh, A.M., Abbas, J.M., El-Oqlah,
A.A., 1996. Antimicrobial activity of extracts
of herbal plants used in the traditional
medicine of Bahrain. Phytotherapy Research
, 251–253.
Nishino, C., Enoki, N., Tawata, S., Morik, A.,
Kobayashi, K., Fukushima, M., 1987.
Antibacterial activity of flavonoids against
Staphylococcus epidermidis a skin bacterium.
Agric Biological Chemistry 51, 139–143.
Nostro A, Germano MP, D'Angelo V, Marino
A, Cannatelli MA,2000. Extraction methods
and bioautography for evaluation of
medicinal plant antimicrobial activity. Lett.
Appl. Microbiol. 30(5): 379.
Singh B, Sahu PM, Sharma MK,2002. Antiinflammatory and Antimicrobial activities of
triterpenoids from Strobilanthes callosus
Nees. Phytomed. 9:355-359.
Trease GE, Evans WC (2002).
Pharmacognosy. 15th Edn. Saunders, pp.
-393.
Voss A,1996. Staphylococcus aureus. PanEuropean Antibiotic Resistance and Infection
Control. Chemother. J. 5: 5-6.
Wiedemann B, 1996. Epidemiology, Control
and Treatment of Multiresistant GramnegativeRods. Drugs 52(Suppl. 2): 95-100.
Wurochekke AU, Nok AJ, 2004. In Vitro
antitrypanosomal activity of some medicinal
plants used in the treatment of
trypanosomiasis in Western Nigeria. Afr. J.
Biotech. 3 (9): 481-483.2006;29 (3): 460-6.