In vitro and in vivo anti-snake venom (Daboia russelli) studies on various leaf extracts of Acalypha indica Linn.
Keywords:
Acalypha indica, Daboia russelli, anti-snake venom, miceAbstract
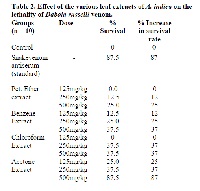
The study aims to examine the Daboia russelli venom neutralization potential of the various leaf extracts of Acalypha indica (Euphorbiaceae) by in vitro and in vivo antisnake venom studies. In vitro HRBC membrane stabilization properties of these extracts at concentrations ranging from 2-400 μg/ml revealed inhibition of haemolysis induced by Russell’s viper venom, in a concentration dependent manner. The neutralizing potency of different leaf extracts viz., petroleum ether, benzene, chloroform and acetone extracts of Acalypha indica prepared by successive solvent extraction at intraperitoneal dose levels of 250, 500 and 750 mg/kg revealed that the acetone extract possessed the most significant activity on venom-induced lethality.
References
Chopra RN, Nayar SL, Chopra IC. Glossary
of Indian medicinal plants, CSIR Publication,
New Delhi; 1956. p. 40.
Peter J Houghton, Ibironke M, Osibogun.
Flowering plants used against snakebite. J
Ethnopharmacol 1993; 39: 1-29.
Siddiqui MB, Husain W, Traditional
antidotes of snake poison in Northern India.
Fitoterapia 1990; 61: 41 - 44.
Suryanarayana Raju M. Native plats used in
snakebite and other poisonous animals among
the tribals of East Godavari District of
Andhra Pradesh. Aryavaidyan 1996; 9: 251-
Annie Shirwaikar, Rajendran K, Ramgopal
Bodla, Dinesh Kumar C. Neutralization
potential of Viper russelli russelli (Russell's
viper) venom by ethanol leaf extract of
Acalypha indica. J Ethnopharmacol 2004;
(2-3): 267-273.
Harborne JB, Phytochemical Methods, 2nd
Edition Chapman and Hill, London; 1984. p.
- 175.
Balu S, Alagesaboopathy. Antisnake venom
activities of some species of Andrographis.
Ancient Sciences of Life 1995; 14 (3): 187-
Murugesh N, Vembar S, Damodaran C,
Studies on erythrocyte membrane IV: in vitro
haemolytic activity of oleander extract.
Toxicology Letter 1981; 8: 33-36.
Theakston, RDG, Reid HA. Development of
simple standard assay procedures for the
characterization of snake venoms. Bull World
Health Organ 1983; 61 (6): 949-956.
Maeno H, Mitishashi S, Konosi I, Hoshi S,
Honuna M. Phosphoprotein phosphatases
from rat cerebral cortex. Japanese J Exp Med
; 32: 55-64.
Abi D. Effects of calcium antagonists on the
erythrocyte membrane. J Pharm
Pharmacol1991; 43: 22-25. Ethanopharm
, 43:167–71.