Evaluation of anti-microbial potential of some medicinal plants
Keywords:
Medicinal plants, zone of inhibition, minimum inhibitory concentration, Ampicillin, GriseofulvinAbstract
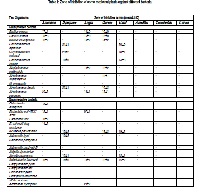
The ethanolic extracts of the eight medicinal plants were tested to determine antibacterial activities against fourteen gram positive and twenty two gram negative bacteria. Five out of eight extracts revealed prominent antibacterial activity. Ampicillin was used as a standard for anti-bacterial activity. The significant zone of inhibition was exhibited by Digitalis purpurae (23±2) against Corynebacterium hofmanii. Sambucus nigra and Urtica urens exhibited minimum inhibitory concentration (12 mg/ml) against Staphylococcus epidermidis and Streptococcus fecalis. Saprophytes, dermatophytes and yeasts were used to screen antifungal activities of these selected medicinal plants. Griseofulvin was used as a standard anti-fungal drug. Four out of eight of the tested plant extracts had significant antifungal activity. Urtica uren produced the most significant zone of inhibition (32±1) against Rhizopus specie. Whereas the lowest minimum inhibitory concentration was exhibited by Urtica urens (20mg/ml) against Aspergillus flavus. The above results justify the use of medicinal plants and its extracts in the formulation of anti-microbial medicaments.
References
. Noor jahan, Ahmad. M, Mehjabeen,
Sherwani SK, Naqvi GR. Anti-microbial
potency against microbes found in
clinical sample and toxicity studies on
selected medicinal plants. International
Journal of Pharmacy. 2013;4(4): 109-
. Harbottle H, Thakur S, Zhao S, White
DG. Genetics of Antimicrobial
Resistance. Anim. Biotechnol., 2006;17,
-124.
. Dahanukar SA, Kulkarni RA, Rege NN.
Pharmacology of Medicinal Plants and
Natural Products. Indian J
Pharmacology. 2000;32: S81-S118.
. Cowan MM. Plant products as antimicrobial agents. Clinical microbiology
reviews. 1999;12:564-82.
. Ahmad, M., Mehjabeen, Zia-Ul-Haq Mand
Noor Jahan. Determination of LD50 and
ED50 by dose response relationship and
assessment of toxicological and nontoxicological behaviour of Ipomoea
hederacea. J. Pharmacy Res.,
;4(4),1176-1178.
. Rajendran NK, Ramakrishnan J. In vitro
evaluation of anti-microbial activity of
crude extracts of medicinal plants
against multi drug resistant pathogens.
Bibad. 2009;2(2): 97-101.
. Perez C, Paul M and Bazerque P. An
antibiotic assay by the agar well
diffusion method. Acta Biol Med Exp.
;15: 113-5.
. Yogeshkumar V, Rathish N, Sumitra C.
Anti-bacterial evaluation of Sapindus
emarginatus Vahl leaf in in-vitro
conditions. Int. J. Green Pharmacy.
;3(2): 165-166.
. Sherwani SK. Phytochemical and Antibacterial screening of crude extract of
Sargassum terrimum J. Agardh against
potential human pathogens. FUUAST J.
Biol. 2012;2(2): 65-68.
. Baqir SNS, Dilnawaz S, Rah S.
Screening of Pakistani plants for
antibacterialactivity. Pak J. Sci. Ind Res.
;28(4): 269-275.
. Pinner R, Teutsch S, Simonsen L, Klug
L, Graber J, Clarke M, Berkelman R.
Trends in infectious diseases mortality in
the United States. J. Am. Med. Assoc.
;275:189ă193.
. Murray M. The healing power of herbs.
Prima Publishing. Rocklin, CA. 1995;pp.
ă171.
. Leung A, Foster S. Encyclopedia of
Common Natural Ingredients. 2nd ed.
New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons;
;40-41.
. Duke JA. Handbook of Medicinal Herbs.
Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press;
;p.423.
. Bhowmik D Chiranjib, Kumar KPS.
Traditional herbal drugs: digitalis and its
health benefits. Int J Pharm Biomed Sci.
;1(1), 16-19.
. Stambergova A, Supcikova M,
Leifertova I. Evaluation of phenolic
substances in Arctostaphylos uva-ursi.
Part 4. Determination of arbutin,
methylarbutin and hydroquinone in the
leaves by HPLC. Cesk Farm.
;34:179ă182.
. Gulcin I, et al. Antioxidant, antimicrobial,
antiulcer and analgesic activities of
nettle (Urtica dioica L.).J.
Ethnopharmacol. 2004;90(2-3): 205-15.
. Zhongguo Z, Yao ZZ. Study on chemical
constituents from Cicuta virosa var.
latisecta. 2009;34(6):705-7.