Anthelmintic activity of Ethanolic extract of whole plant of Eupatorium Odoratum. L
Keywords:
Anthelmintic activity, Eupatorium Odoratum, Pheretima posithuma, Piperazine citratAbstract
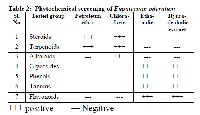
Successive extracts from the Whole plant of Eupatorium Odoratum. L (Asteraceae) were investigated for their anthelmintic activity against Pheretima posthuma and three concentrations (10, 50 and 100 mg/ml) of each extracts were studied in activity, which involved the determination of time of paralysis and time of death of the worm. Ethanolic extract exhibited significant anthelmintic activity at highest concentration of 100 mg/ml. Piperazine citrate in 10 mg/ml concentration as that of extract was included as standard reference and 1% Gum acacia in normal saline as control. The anthelmintic activity of ethanloic extract was significant followed by hydroalcoholic extract of Eupatorium Odoratum.
References
Bundy DA: Immunoepidemiology of
intestinal helmintihc infection, The global
burden of intestinal nematode disease.
Trans. Royal. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg.
,8:259-61.
Coles GC:. Anthelmintic resistance and the
control of worms. J Med. Microb
,48:323-325.
Geerts S, Gryseels B: Drug resistance in
human helminths: current situation and
lessons from the livestock. Clin. Microbiol.
Rev.(2000),13(2):207-222.
Sangster NC: Anthelmintic resistance: past,
present and future. Intl. J.
Parasitology.1999,29:115-124.
Padilha T: Resíduos de Anti-helmínticos na
Carne e Leite. In: Controle dos
Nematóides Gastrintestinais em
Ruminantes. Padilha, T., Ed., General
Pacheco, Embrapa-CNPGL.1996,258.
Turnipseed SB, Roybal JE, Rupp HS,
Gonzalez SA, Pfenning AP, Hurlbut JA:
Confirmation of avermectin residues in
food matrices with negative-ion
atmospheric pressure chemical ionization
liquid chromatography / mass spectrometry.
Rapid. Comm. Mass. Spec.1999,13:493-
Hamond JA, Fielding D, Bishop SC:
Prospects for plant anthelmintics in tropical
veterinary medicine. Vet. Res.
Comm.1997,21:213-228.
Schmidt GJ, Schilling EE: Phylogeny and
Biogeography of Eupatorium (Asteraceae:
Eupatorieae) Based on Nuclear ITS
Sequence. Amer. J. Bot.2000, 87(5):716-
Sasaki Yohei, Matsumoto Atsushi, Takido
Michio, Yoshimura Mamoru, Nagumo
Seiji: "Study on Eupatorium Plants Called
"Fujibakama". Jap. J.
Pharmacog.2006,60(1):15-20.
Rejitha Gopinath:
Diuretic activity of Eupatorium odoratum L
inn. J. Pharm. Res, 2009;2(5): 844-846.
Victor B Owoyele, Joseph O Adedij,
Ayodele O Soladoy: Anti-inflammatory
activity of aqueous leaf extract
of Chromolaena odorata.
Inflammopharmacology. 2005,13(5-
:479-484.
Biswal PR, Sardar KK, Parija SC, Mishra
PR, Mishra SN: Wound healing effect of
eupatorium odoratum linn, and himax in
rabbits. Indi. J. of Indige. Medi..
,19(1):71-4
Lakshman Lal: Studies on natural
repellents against potato tuber moth
(Phthorimaea operculella Zeller) in country
stores. Potato Research. 1987,30( 2): 329-
Apichart Suksamrarn, Apinya Chotipong,
Tananit Suavansri, Somnuk Boongird,
Puntip Timsuksai, aovaluk Vimuttipong and
Aporn Chuaynugul: Antimycobacterial
activity and cytotoxicity of flavonoids from
the flowers of Chromolaena odorata. Arch.
of Pharmaco. Res.2004,27(5):507-511.
Prasad S, Narayana K, Jayakumar K:
Phytochemical analysis of toxic plant
Chromolaena odorata (Eupatorium
odoratum). J. of Indi. Soci. of Toxic.
,1(1):
Kumar GS, Jayaveera KN, Kumar CK
Ashok, Umachigi P Sanjay,Vrushabendra
Swamy BM, Kumar DV Kishore:
Antimicrobial effects of Indian medicinal
plants against acne-inducing bacteria. Tropi.
J. of Ph. Res. June .2007,6 (2):717-723.
Vidyarthi RD: A Textbook of Zoology.
th ed. New Delhi: Chand and Co.
Press.1977,329-31.
Thorn GW, Adams RD, Brunwald E,
Isselbacher KJ, Petersdorf RG: Harrison’s
Principles of Internal Medicine. New York;
Mc Grew Hill.1977,1088-90.
Vigar Z: Atlas of Medical Parasitology. 2nd
ed. Singapore:Publishing House;
,216-18.
Ghosh T, Maity Tk, Bose A and Dash GK:
Anthelmintic activity of Bacopa monierri,
Indi. J.Nat Pro.2005,21:16-19.
Mathew AS, Patel KN, Shah BK: Indi. J.
Nat.Prod.1995,14 (1):11.
Vagdevi HM, Latha KP, Vaidya VP,
Vijayakumar M, Pai KS: Synthesis and
Pharmacological screening of some novel
naphtha (2, 1-b) Furo-pyrazolines,
isoxazoles and isoxazolines, Indi. J. harma.
Sci.2001, 63: 286-291.
Bolton S: In Pharmaceutical StatisticsPractical and Clinical Applications. New
York: Marcel Dekker. 1997,69-78.
Bate-Smith EC: The phenolic constituents
of plants and their taxonomic
significance 1. Dicotyledons. J. Linn. Soc.
Bot. 1962,58:95-173.
Martin RJ: Mode of action of Anthelmintic
drugs. Vet. J.1997, 154:11-34.
Gamenara DE, Pandolfi, Saldana J,
Dominguez L, Martinez MM, Seoane G:
Nematocidal activity of natural polyphenols
from bryophytes and their derivatives.
Arzneimittelforschung.2001,51:506-510.
Athnasiadou S, Kyriazakis I, Jackson F,
Coop RL: Direct anthelmintic effects of
condensed tannins towards different
gastrointestinal nematodes of sheep: In vitro
and in vivo studies. Vet.
Parasitol.2001,99:205-219.
Thompson DP, Geary TG: The structure
and function of helminth surfaces. In:
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of
Parasites (J. J. Marr, Ed.), 1st ed. Academic
Press, New York.1995,203-232.
Coop RL, Holmes PH: Nutrition and
parasite interaction. Int. J. Parasitol.
,26:951-962.
Van houtert MFJ, Sykes AR: Implications
of nutrition for the ability of ruminants to
withstand gastrointestinal nematode
infections. Int. J. Parasitol. 1996,26:1151-
Donaldson J, Van houtert MFJ, Sykes AR:
The effect of protein supply on the
peripaturient parasite status of the mature
ewe. Proc. New Zealand Soc. An.
Prod.1997,186-189.
Waller PJ, Bernes G, Thomsborg SM,
Sukur A, Richter SH, Ingebrigtsen K,
Hoglund J: Plants as de-worming agents of
livestock in Nordic countries: historical
perspective,popular beliefs and prospects
for the future. Acta Vet.Scand.2001,42:31-
Wang Y, Waghorn GC, Douglas GB, Barry
TN, Wilson GF: The effect of condensed
tannins in Lotus corniculatus upon nutrient
metabolism and upon body and wool
growth in grazing sheep. Proc. New
Zealand Soc. of An. Prod. 1994,54:219-
Received.
Pessoa LM, Morais SM, Bevilaqua CM,
Luciano JH: Anthelmintic activity of
Essential oil of Ocimum gratissimum Linn.
and eugenol against Haemonchus
contortus. Vet. Parasitol.2002,109:59-63.
Lahlou M: Potential of Origanum
compactum as a cercaricide in Morocco.
Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol.2002,96:587-