Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Tamarindus indica L.
Keywords:
Tamarindus indica, antioxidant, Nitric oxide, Hydroxyl radical, Escherichia coliAbstract
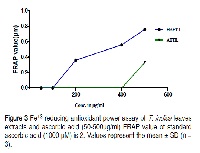
In this study, in vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of aqueous and Hydroalcoholic extracts of leaves Tamarindus indica were investigated. In-vitro antioxidant assay was performed by DPPH (1, 1 –diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl) assay, Hydroxyl radicals scavenging assay, Ferric reducing assay, Nitric oxide radical scavenging assay. Percentage of free radical scavenging potential was determined using ascorbic acid as a standard in each method. In Ferric reducing antioxidant power assay, antioxidant power was determined by measuring ferric reducing values. It was observed that hydroalcoholic extracts were having more potential antioxidants. Hydroalcoholic extract at 500 µg/ml shown maximum FRAP value 0.76±0.08. IC50 values were determined for each extracts. Lowest IC 50 value was exhibited by HAETIS in DPPH, Hydroxyl radical scavenging, Ferric reducing and NO scavenging methods are: 195.30µg/ml,182.02µg/ml,196.23µg/ml respectively. These results indicated that the anti oxidant capacities depends on concentration and nature of extracts. Antimicrobial activities were evaluated by determining inhibition zone diameter and calculated MIC values. Aqueous extracts of Tamarindus indica leaves shown maximum inhibition zone diameter against gram positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus 17.33±1.5 mm and was exhibited by Ciprofloxacin used as standard 36.0±2.0mm. In gram negative bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa hydroalcoholic extracts of Tamarindus indica leaves shown 24.66±.51mm and Gentamicin used as standard 37.0±1.73. Aqueous extracts of leaves shown good antimicrobial activity against gram positive bacteria and hydroalcoholic extracts of leaves in gram negative bacteria. Minimum inhibitory concentration shown by different extracts were in the range of 8-20mg/ml. Hydroalcoholic extracts of leaves shown lowest minimum Inhibitory concentration 8mg/ml against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
References
. Basu K, Singh B, Singh MP, Indian
Medicinal Plants. 2nd Ed, Lalit Mohan
Basu Deherdun,India. 2006; 2: 887 -
. Havinga RM, Hart A, Putscher J.
Tamarindus indica L (Fabaceae) :
Pattern of use in Traditional African
medicine. J Ethnopharmacology
; 127:573-588.
. Maiti R, Jana D, Das UK, Ghosh D.
Antidiabetic effect of aqueous extract
of seed of Tamarindus indica in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
J Ethnopharmacology. 2004; 92: 85ă
. Bhutkar MA, Bhise SB. Anti-Oxidative
Effect of Tamarindus Indica in Alloxan
Induce Diabetic Rats. International
Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical
and Biomedical Sciences. 2011; 2
(3):1006-1009.
. Ramchander T, Rajkumar D,
Sravanprasad M, Venkateshwarlu G,
Dhanalakshmi CH. Antidiabetic Activity
of Aqueous Methanolic Extracts of Leaf
of Tamarindus indica International
Journal of Pharmacognosy and
Phytochemical Research. 2012; 4(1):5-
. Siddhuraju P. Antioxidant activity of
polyphenolic compounds extracted
from defatted raw and dry heated
Tamarindus indica seed coat, LWTFood Sci. Technol. 2007; 40 : 982ă990.
. Jindal V, Dingra D, Sharma S, Parel
M , Harna RK . Hypolipidemic and
weight reducing activity of the ethanolic
extract of Tamarindus indica fruit pulp
extract in cafeteria diet and sulpirideinduced obese rats, Journal of
Pharmacology and
Pharmacotherapeutics. 2011; 2 (2) 80-
. Martinello F, Soares SM, Franco JJ,
Santos AC, Sugohara A, Garcia SB,
Curti C, Uyemura SA. Hypolipemic and
antioxidant activities from Tamarindus
indica L. pulp fruit extract in
hypercholesterolemic hamsters, Food
and Chem. Tox . 2006; 44:810ă818.
. Doughari JH. Antimicrobial Activity of
Tamarindus indica Linn. Trop J of
Pharma. Res. 2006; 5 (2): 597-603.
. Gumgumjee NM, Khedr A, Hajar AS.
Antimicrobial activities and chemical
properties of Tamarindus indica L.
Leaves extract, African J Microb.
Res.2012; 6(32):6172-6181.
. Abdollahi M, Ranjbar A, Shadnia S,
Nikfar S, Rezaiee A. Pesticides and
oxidative stress: A review, Med Sci
Monit, 2004; 10(6):144ă 147.
. Rahimi R, Nikfar S , Larijani B,
Abdollahi M, A review on the role of
antioxidants in the management
of diabetes and its complications,
Biomed & Pharmacoth , 2005;
:365ă373.
. Karaman Y, Sahin F, Gulluce M,
Ogutcu H, Sengul M, & Adþguzel A.
Antimicrobial activity of aqueous and
methanol extracts of Juniperus
oxycedrus L. J Ethnopharmacol., 2003;
: 213ă235.
. Chopra RN, Nair SL and Chopra JC .
Glossary of Indian medicinal Plants,
(New Delhi CSIR), 1992.
. Vani T, Rajani M, Sarkar S, and
Shishoo CJ. Antioxidant properties of
the Ayurvedic Formulation Triphala and
its constituents. Int J Pharmacogn,
; 35: 313-17.
. Devi PU, Ganasoundari A, Vrinda B.
Radiation protection by the Ocimum
sanctum flavonoids orientin and
vicenin: Mechanisms of Action, Radiat.
Res. 2002; 154(4): 455-460.
. Benzie FF, Strain JJ. Ferric
Reducing/ Antioxidant Power
Assay: Direct Measure of Total
antioxidant Activity of Biological Fluids
and Modified Version
for Simultaneous Measurement
of Total Antioxidant Power
and Ascorbic Acid Concentration.
Methods in Enzymology. 1999;
:15-23.
. Ebrahimzadeh MA, Nabavi SF, Nabavi
SM. Essential oil composition and
antioxidant activity of Pterocarya
fraxinifolia. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2009;
(13): 957-963.
. Ebrahimzadeh MA, Nabavi SM, Nabavi
SF, Eslami B, Ehsanifar S. Antioxidant
activity of Hyoscyamus squarrosus
fruits, Pharmacol. online. 2009; 2: 644-
. Nabavi SM, Ebrahimzadeh MA, Nabavi
SF, Bahramian F. In vitro antioxidant
activity of Phytolacca americana
berries. Pharmacol. online 2009;1: 81-
. Marcocci L, Maguire JJ, Droy-Lefaix
MT, Packer L. The nitric oxidescavenging Properties of Ginkgo biloba
extract. Biochem. Biophys. Res.
Commun. 1994; 201, 748-755.
. Collins GH, Lynes PM, Grange JM .
Microbiological Methods, 7th Ed.
Butterwort-Heinemann Ltd, Britain.
; 175-190.
. National Committee for Clinical
Laboratory Standards. Standard
methods for dilution antimicrobial
susceptibility tests for bacteria that
grow aerobically, 2nd Ed. Approved
standard M7-A2. National Committee
for Clinical Laboratory Standards,
Villanova, Pa. 1990.
. Juan. Xu, Shubing. Chen and Qiuhui.
Hu, „Antioxidant activity of brown
pigment and extracts from black
sesame seed (Sesamum indicum L.),‰
Food Chemistry. 2005; 91(1):79-83.
. Auroma OI. Methodological
consideration for characterizing
potential antioxidant actions of
bioactive components in plant foods ,
Mutat Res 2003; 544:203-15.
. Dorman HJD Peltoketo A, Hiltunen R
,Tikkanen MJ 2003 . Characterization
of antioxidant properties of deodourised aqueous extract from
selected lamiaceae herbs. Food.
Chem. 2003; 86: 255-262.
. Shimada K,Fujikawa K, Yahara K,
Nakamura T. Antioxidant properties of
xanthan on Autoxidation of soyabean
oil in cyclodextrin emulsion, J Agric
Food Chem 1992;40:945-948.
. Yokozawa T, Chen CP, Dong E,
Tanaka T, Nonaka GI, Nishioko I.
Study on the inhibitory effect of tannins
and flavonoids against the 1, 1-
diphenyl- 2 picrylhydrazyl radical,
Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998; 56: 213-
. Ghosh T, Maity TK, Das M, Bose A and
Dash DK in vitro Antioxidant and
Hepatoprotective Activity of Ethanolic
Extract of Bacopa monnieri Linn.
Aerial Parts I J of Pharmaco. & Therap.
; 6:77-85.
. Nakken KF, Pihl A. Hydroxyl radical
scavenging properties of some plant
extracts, Radiat. Res. 1965; 26: 519-
. Repine JE, Fox RB, Berger EM.
FentonÊs reaction in the living systems,
J. Biol. Chem. 1981; 256:7094-8005.
. Meir S, Kanner J, Akiri B, Hadas SP.
Determination and involvement of
aqueous reducing compounds in
oxidative defense system of various
senescing leaves, J. Agri. Food
chem.: 1995; 43:1813-1819.
. Marletta MA. Nitric oxide: Biosynthesis
and biological significance, Trends Biol
Sci 1989; 14: 488-492.
. Marcocci I, Poacker L, Droy-Lefaix M,
Sakak GAM, Meth. Enzymol. 1994
:234: 462.
. Valero M, Salmeroj MC.Antibacterial
activity of 11 essential oil against
Bacillus cereus in tyndallized carrot
broth , Int.J.Food. Microbiol. 2003;
:73-81.
. Falzari LM, Menary RC. Chamomile for
oil and Dried flowers. RIRDC Publication No. 02/156 RIRDC Project No.
UT-28 A, Australia. 2003.
. Daniyan SY and Muhammad HB.
Evaluation of the antimicrobial activities
and phytochemical properties of
extracts of Tamarindus indica against
some diseases causing bacteria,
African Journal of Biotechnology 2008;
(14):2451-2453.
. Marjorie MC. Plant products as
antimicrobial agents, Clin Microbiol Rev
, 12(4):564 582.
. Humeera N, Kamili AN, Amin S,
Bandh SA, Lone BA, Gousia N
.Antimicrobial and antioxidant
activities of alcoholic extracts of Rumex
dentatus L, Microbial Pathogenesis
xxx; 2013; 1- 4 .
. Lee SH, Chang KS, Su MS. Effect of
some Chinese medicinal plant extracts
on five different fungi, Food Control
.2007; 1: 1-8.