Antidiabetic activity of leaves of Anthocephalus indicus A. Rich. in alloxan induced diabetic rats
Keywords:
Anthocephalus indicus, antidiabetic, leaf extract, histopathologyAbstract
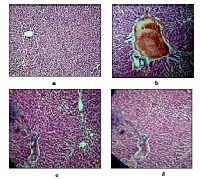
The present study aims to examine the antidiabetic potential of leaves of Anthocephalus indicus A. Rich. The aqueous extract of leaves was screened for serum glucose lowering activity. Diabetes was induced in Sprague Dawley adult male rats by intra peritoneal injection of alloxan monohydrate at 80mg/kg bw. to the rats. Aqueous leaves extract of Anthocephalus indicus A. Rich. at 400mg/kg bw was given orally to control and diabetic rats for 21 days. Blood samples taken from retro orbital plexus of rats were analysed for serum glucose level, total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein (HDL- cholesterol) and low density lipoprotein (LDL- cholesterol) as per standard kit method. The rats feed with aqueous leaves extract showed significant reduction in blood glucose, total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL and LDL as compared to diabetic rats. Aqueous leaf extract results for antidiabetic activity were compared with standard drug glibenclamide at 10mg/kg bw. and the antidiabetic acitivity was found to be significant. Histopathological study of liver and pancreas of rats showed that alloxan caused damage in the liver cells and degeneration of pancreatic islet cells. Administration of aqueous leaves extract caused an improvement in damaged liver cells and degenerated pancreatic islet cells. Thus, Anthocephalus indicus can be considered as a good natural antidiabetic drug.
References
. Ragavan B and Krishna KS.
Antidiabetic effect of T. Arjuna Bark
extract in alloxan induced diabetic
rats. Ind J Clin Biochem 2006; 21:
-128.
. Trivedi NA, Majumder B, Bhatt JD,
Hemavathi KG Effect of Shilajit on
blood glucose and lipid profile in
alloxanăinduced diabetic rats. Indian J
Pharmacol 2004; 36: 373-76.
. Pavana P, Sethupathy S, Manoharan
S. Antihyperglycemic and Anti lipid
peroxidative effect of Tephrosis
purpura seed extract in streptozotocin
induced diabetic rats. Ind J Clin
Biochem 22: 77-83.
. Kecskemeti V, Bagi Z, Pacher P, Posa
I, Kocsis E, Koltai MZ. New trends in
the development of oral antidiabetic
drugs. Current Medicinal Chemistry
; 9: 53-71.
. Schuster DP and Duvuuri V. Diabetes
mellitus. Clinics in Pediatric Medicine
and Surgery. 2002; 19: 79-107.
. Rao BK, Kesavulu MM, Apparao C.
Evaluation of antidiabetic effect of
Momordica cynobalaria fruit in alloxan
diabetic rats. J Fitoterapia 2003; 74:
-13.
. Schweitzer M, Tessir D, Valhos WD,
Leiter L, Collet JP, Moqueen MJ,
Harvey L, Alaupovic FA. Comparison
of pravastatin and gemfibrozil in the
treatment of dyslipoproteinemia in
patients with non-insulin dependent
diabetes mellitus. J Atherosclerosis
; 162: 201-10.
. Berger W. Incidence of severe side
effects during therapy with sulphonyl
ureas and biguanide. Hormones
Metabolic Res 1985; 17: 111‐115.
. Rang HP Dale MM and Rittar JM. The
endocrine system Pharmacology.
Longman Group Ltd. UK, 1991, pp.
‐508.
. Shetti AA, Sanakal RD and Kaliwal
BB. Antidiabetic effect of ethanolic
leaf extract of Phyllanthus amara in
alloxan induced diabetic mice. Asian J
Plant Sci and Res 2012; 2: 11-15.
. Bailey J and Day C. Traditional plant
medicines as treatments for diabetes.
Diabetes Care 1989; 12: 553-564.
. Andrew P. The constituents of
medicinal plants-An introduction to the
chemistry and therapeutics of herbal
medicine. CABI publishing, USA,
. Sircar NN. Pharmacological basis of
Ayurvedic therapy; in Cultivation and
utilization of medicinal plants.
Publication and Information
Directorate, CSIR, Delhi, 1992, pp.
-518.
. Slkar IV, Kakkar KK, Chakre OJ.
Glossary of Indian Medicinal Plants
with Active Principles. CSIR, New
Delhi, 1992.
. Dubey A, Nayak S and Goupale DC.
Anthocephalus cadamba A Review.
Pharmacogn J 2011; 2: 71-76.
. Brown RT and Fraser SB.
Anthocephalus alkaloids, cadambine
and 3đ-dihydrocadambine.
Tetrahedron Lett 1974; 23: 1957-
. Richard T, Brown and Chapple LC.
Anthocephalus alkaloids: cadamine
and isocadamine. Tetrahedron Lett
19: 1629-1630.
. Ling Li L, Ying-tong D, Qiang Z, Xin F,
Feng Z, Dong-Liuc, Xiao-Jiang H and
Hong-Ping H. Aminocadambines A
and B, two novel indole alkaloids from
Neolamarckia cadamba. Tetrahedron
Lett 2010; 51: 5670-5673.
. Kapil A, Kouli B, Suri OP.
Antihepatotoxic effects of chlorogenic
acid from Anthocephalus cadamba.
Phytother. Res. 1995; 9: 189ă193.
. Umachigi SP, Kumar GS, Jayaveera
KN, Kishore Kumar DV, Ashok Kumar
CK and Dhanapal R. Antimicrbial,
wound healing and antioxidant
activites of Anthocephalus indicus. Afr
J Tradition Complem. and Altern
Medicines 2007; 4: 481-487.
. Bacchav RS, Buchake VV, Aher SS,
Rode RR and Saudagar RB.
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory
activities of Anthocephalus cadamba
Roxb leaves in wistar rats. Adv in
pharmacol and toxicology 2009; 10:
-130.
. Ambujakshi HR, Antony ST,
Kanchana Y, Patel R, Thakkar H and
Shyamananda. Analgesic activity of
Anthocephalus cadamba leaf extract.
J Pharmacy Res 2009; 2: 1279-1280.
. Kumar V, Khanna AK, Khan MM,
Singh R, Singh S, Chander R, Mahdi
F, Saxena JK Saxena S, Singh VK
and Singh RK. Hypoglycemic, lipid
lowering and antioxidant activities in
root extract of Anthocephaus indicus
in alloxan induced diabetic rats. Indian
J Clin Biochem 2009; 24: 65-69.
. Kumar SCA, Varadharajan R,
Muthumani P and Meera R.
Pharmacognostic and preliminary
phytochemical investigations on the
stem of Saccharum spontaneum. J
Pharmaceutical Sci and Res 2009; 1:
-136.
. Edeoga HO, Okwu DE and Mbaebie
BO. Phytochemical constituents of
some Nigerian medicinal plants.
African J Biotechnol. 2005; 4: 685-
. Sachan NK, Kumar Y, Pushkar S,
Thakur RN, Gangwar SS and
Kalaichelvan. Antidiabetic potential of
alcoholic and aqueous extracts of
Ficus racemosa Linn. bark in normal
and alloxan induced diabetic rats.
International J Pharma Sci and Drug
Res 2009; 1: 24-27.
. Chaurasia S, Saxena RC, Chaurasia
ID and Shrivastav R. Antidiabetic
activity of Luffa aegyptica (Mill) in
alloxan induced diabetic rats. J Chem
Pharm Res 2011; 3: 522-525.
. Perfumi M and Tacconi R.
Antihyperglycemic effect of fresh of
Optuniadillenii fruit from Tenerife
(Canary islands). Indian J Pharmacol
34: 41.
. Jarald EE, Joshi SB and Jian DC.
Antidiabetic activity of aqueous extract
of and non-polysaccharide fraction of
Cynodon dactylon Pers.Indian J
Experimental Biology 2008; 46: 660-
. Lillie RD. Histopathological Technic
and Practical Histochemistry.
McGraw-Hill Company Toronto, 1954,
pp. 114.
. Noor A, Gunashekaran S, Manickam
AS and Vijayalakshmi MA.
Antidiabetic activity of Aloe vera and
histology of organs in streptozotocin
induced diabetic rats. Current Sci
; 94: 1070-1075.
. Zafar M, Naeem-Ul-Hassan Naqvi S,
Ahmed M and Kaimkhani Z A. Altered
liver morphology and enzymes in
streptozotocin induced diabetic rats.
Int J Morphol 2009; 27: 719-725.
. Lanzen S and Panten U. Alloxan
history and mechanism of action.
Diabetologia 1988; 31: 337-342.
. Elsner M, Tiedge M, Guldabakke B,
Munday R and Lenzen S. Importance
of the GLUT2 glucose transporter for
pancreatic β cell toxicity of alloxan.
Diabetologia 2002; 45: 1542-1549
. Shamaony LA, Khazraji SM, Twaij
HA. Effect of a valuable extract on
some blood parameters in diabetic
animals. J Ethnopharmacol 1994; 43:
-171.
. Anderson JR. MuirÊs Textbook of
Pathology. ELBS, 1994, pp. 20-63.
. Ikechukwu CF and Obri AI.
Histological changes in the pancreas
following administration of the
ethanolic extract of Alchornea
cordifolia leaf in alloxan induced
diabetic rats. Nigerian J Physiol Sci
; 24: 153-155
. Buko VO, Bukivskaya V, Nikitin Y,
Tarasov L, Zavodnik A, Borodinsky B,
Corenshtein. Hepatic and pancreatic
effect of polyenoylphosphatidylcholine
in rats with alloxan induced diabetes.
Cell . Biochem Funet J 1996; 14: 131-
. Mahera N and Shaikh A. Histological
and Histochemical changes in diabetic
male rat liver and intestine and
protective effect of cinnamon oil. J
Fac Med Baghdad 2010; 52: 366-371.
. Bussa SK and Pinnapareddy J.
Antidiabetic activity of stem bark of
Neolamarckia cadamba in alloxan
induced diabetic rats. Int J Pharmacy
and Technology 2010; 2: 314-324.
. Gurjar H, Jain SK, Irchhaiya R,
Nandanwar R, Sahu VK and Saraf H.
Hypoglycemic effects of methanolic
extract of Anthocephalus cadamba
bark in alloxan induced diabetic rats.
Int J pharmaceutical Sci and Res
; 1: 79-83.