Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity of leaf and callus extracts of Coleus forskohlii
Keywords:
Coleus forskohlii, callus, inflammation, analgesic, edemaAbstract
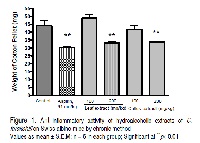
Though all sixteen combinations of NAA + BAP, and NAA + KN induced callus from leaf explants of Coleus forskohlii with a variable response, 0.5 mg/l NAA + 1.5 mg/l BAP was the most efficient (100%) followed by 1.0 mg/l NAA + 2.5 mg/l KN (86%). Investigations were made for anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity of hydroalcoholic extracts of leaf and callus on Swiss albino mice. Anti-inflammatory studies were performed by Carrageenan induced paw edema (acute) and Cotton pellet induced granuloma (chronic) models, while the analgesic activity was tested by: glacial acetic acid induced writhing and tail immersion models. Maximum anti-inflammatory activity was exhibited by 200 mg/kg callus extract (43% in acute and 22.3% in chronic) followed by 200 mg/kg leaf extract (37% in acute and 21.8% in chronic) compared to standard drug, the aspirin (27.4% in acute and 29.9% in chronic). In writhing model, 200 mg/kg callus extract exhibited highly significant (p < 0.01) reduction in writhing count compared to 200 mg/kg (p < 0.01) leaf extract. In tail immersion model also the reaction time was significantly reduced (p < 0.01) by both callus and leaf extracts throughout observation period of 3 hrs. The results obtained supported the use of this plant in traditional medicine.
References
. Sosa S, Balicet MJ, Arvigo R,
Esposito RG, Pizza C, Altinier GA.
Screening of the topical
antiinflammatory activity of some
Central American plants. J
Ethanopharmacol 2002; 8: 211ă215
. Devalapally H, Sripal Reddy M,
Rajnarayan K, Krishna DR, Prabhakar
MC, Inflammation: novel therapeutic
approaches and its management. Ind
J Pharm Sci 2003; 65: 565-575
. Michel YB, Dubois CG, Allen HL,
Chronic pain management. In: Healy
TEJ (ed). Hodder Arnold: London
; 1213ă1220
. Pilotto A, Franceschi M, Leandro G.
The risk of upper gastrointestinal
bleeding in elderly users of aspirin
and other non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs: the role of
gastroprotective drugs. Aging Clin Exp
Res. 2003; 15: 494ă499
. David JJ, Douglas. Acute post
operative pain. In A practice of
Anaesthesia, Healy TEJ (ed). Hodder
Arnold: London 2003; 1213ă1220
. Selima K, Ugur C, Narayan C C.
Phytochemical constituents
histochemical localization of forskolin
in a medicinal plant Coleus forskohlii.
J Med Plants Res 2011, 4: 711-718
. Shetty K, Biosyntesis and medical
applications of rosmarinic acid. J
Herbs Spices Med Plants 2011; 8:
-182
. Szabo, E, Thelen A, Petersen M.
Fungal elicitor preparations and
methyl jasmonate enhance rosmarinic
acid accumulation in suspension
cultures of Coleus blumei. Plant Cell
Rep 1999; 18: 485-489
. Pabsch K, Peterson M, Rao MN,
Altermann AW, Wandrey C. Chemo
enzymatic synthesis of rosmarinic
acid. Recl Trav Chim Pays-Bas 1991;
: 199-205
. Sunitha K, Bhaskar CK, Chethan CN,
Dinesh Kumar B, Manohar Rao D.
Identification, quantification and
antioxidant activity of secondary
metabolites in leaf and callus extracts
of Coleus forskohlii Ind J Pharmacol
(in press)
. Winter CA, Risley EA, Nuss GW.
Carrageenan induced edema in hind
paw of the rat as an assay for antiinflammatory drugs. Proc Soc Exp
Biol Med 1962; 111: 544-547
. Jennifer P, Ishwa B, Ronald F,
Subramanyam EVS, Antiinflammatory activity of leaves of
Sapindus Trifoliatus Linn. Ind Drugs
; 44: 864-866
. Murashige T, Skoog F. A revised
medium for rapid growth and bio
assay with tobacco tissue culture.
Physiology of plant 1962; 15: 473-497
. Surendra HB, Alpana R, Kiran SB.
Anti-inflammatory activity of Morina
longifolia extract. Adv Pharmacol
Toxicol 2009; 10: 71-79
. Swingle KF, Shideman FE. Phases of
the inflammatory response to
subcutaneous implantation of cotton
pellet and their modification by certain
anti-inflammatory agent. J Pharmacol
Exp Ther 1972; 183: 226-234
. Devalapally, H, Appa Rao AVN,
Prabhakar MC, Pharmacological
investigation of pruning-6‰-O-pcoumarate: A flavonoid glycoside. Ind
J Pharmacol 2004; 36: 244-245
. Kulkarni SK, Handbook of Experiental
pharmacology 2nd ed. Vallabh
Prakasham: New Delhi 1993; 19-51
. Ghosh, MN, Evaluation of Analgesic
activity, In: Fundamentals of
experimental pharmacology 2nd ed.
Scientific book agency: Calcutta 2005;
-71
. Ibrahim RK, Constable F, Vasil IK,
Cell culture and somatic cell genetics
of plants, A.C. Press. Inc., Vol.
Chap.3, 1987; 77-96
. Vinegar R, Schreiber W, Hugo R.
Biphasic development of carrageenan
edema in rats. J Pharmacol Exp
Therap 1969; 166: 96-10
. Panthong A, Kanjanapothi D,
Taesotikul T, Wongcome T,
Reutrakul V. Anti-inflammatory and
antipyretic properties of Clerodendrum
petasites J Ethnopharmacol. 2003;
: 151-156
. Crunkhorn PSC, Meacock. Mediators
of the inflammation induced in the rat
paw by carrageenan. Br J Pharmacol.
; 42: 392-402
. Seibert K, Zhang Y, Leahy K,
Hauser S, Massferrer J, Perkins W,
Lee L, Isakson P, Pharmacological
and biochemical demonstration of the
role of cyclooxygenase 2 in
inflammation and pain. Proc Natl Acad
Sci 1994; 91: 12013ă 12017
. Parmer NS, Ghosh MN, Antiinflammatory activity of gossypin a
bioflavonoid isolated from Hibiscus
vitifolicus Linn. Ind J Pharmacol
; 10: 277-293
. Englberger WU, Hadding E,
Etshenberg E, Graf S, Leyck J,
Winklemann, Parnham MJ.
Rosmarinic acid, a new inhibitor of
complement C3 Convertase with antiă
inflammatory activity. Int J
Immunopharmacol 1988, 10: 729-737
. Kavimani S, Vetrichelvan T, Ilango
R, Jaykar B. Anti inflammatory
activity of the volatile oil of Toddalia
asiatica. Ind J Pharm Sci 1996; 58:
-70
. Amico-Roxas MA, Caruso S,
Trombadore R, Scifo U, Scapagnime.
Gangliosides: antinociceptive effects
in rodents. Arch Int Pharmacody and
Ther. 1984; 272: 103-117
. Ronaldo AR, Mariana LV, Sara MT,
Adriana BPP, Steve P, Ferreira SH,
Fernando QC. Involvement of resident
macrophages and mast cells in the
writhing nociceptive response induced
by zymosan and acetic acid in mice.
Eur J Pharmacol 2000; 387: 111-118
. Rajpal, V. Standardization of
botanicals testing and extraction
methods of medicinal herbs, Easton
publishers: New Delhi 2005; Vol-1-2,
-112