Antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic effects of alcoholic and aqueous stem bark extracts of Limonia acidissima, linn in alloxan induced diabetic rats
Keywords:
Limonia acidissima Linn, Antidiabetic activity, Antihyperlipidemic activity, Alloxan, HistopathologyAbstract
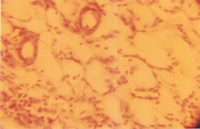
The present study was designed to investigate the antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic effects of the alcoholic and aqueous extract obtained from the stem bark of Limonia acidissimaLinn (Rutaceae) using alloxan induced diabetic model in rats for 14 days. The alcoholic extract (200mg/kg) showed significant activity (P<0.01) in lowering blood glucose level than the aqueous extract (200mg/kg) which was comparable to glibenclamide (5mg/kg), a standard antidiabetic drug. Different biochemical parameters i.e. TGL(triglycerides), HDL, LDL, VLDL and total cholesterol level were also carried out which show that both alcoholic and aqueous extracts has significantly (p<0.001) reversed the diabetes-included hyperlipidemia compared to standard drug. Concurrent histological studies of the pancreas of these animals showed comparable regeneration by alcoholic and aqueous extracts which were earlier, necrosed by alloxan. The data suggests that the alcoholic extracts (200 mg/kg) may be effectively utilized as antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic agents and supports its traditional usage in the control of diabetes. However, further pharmacological evaluations are required to isolate and identify the active antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic principles in the plant as well as elucidating their mechanisms of action.
References
. The wealth of India, Institute of
science communication; Council of
Scientific & Industrial Research, New
Delhi, India, Ist edition, 1956;Reprint
:Vol-IV:18-20.
. Vaidaya ratnam P.S. Varier, Arya
Vaidya sala, Kottakkal, Indian
medicinal plants, Orient Longman
Ltd., Madras, Vol-III, 1995:327-332.
. Chopra RN, Nayar SL, Chopra IC.,
Glossary of Indian medicinal plants,
PID, New Delhi, 1956:117.
. Gupta VC, Hussain SJ, Imam S,
Important folk-medicinal plants and
traditional knowledge of tribals of
Aurangabad and Nasik forest divisions
of Maharashtra, India. Hamdard
Medicus, 1997;40:59-61.
. Morton J, Wood-Apple. In: Fruits of
warm climates. Julia F. Morton, Miami,
FL, 1987;190-191.
. FRLHT’s Amruth, jan.-fab. Vol.-8,
Issue-1,2004;14.
. Smith Albert C, Flora Vitiensis nova: a
new flora of Fiji, National Tropical
Botanical Garden, Lawai, Kauai,
Hawaii, 1985;3:526,527,758.
. Kirtikar KR, Basu BD, Indian medicinal
plants, Vol.-I, Published by
International book distributors,
Dehradun, 2005;496-499.
. Dr. Duke’s phytochemical and
ethanobotenical Databases.
. Macleod JK, Moeller DR, Bandara
BMR, Gunatilaka AAL, Wijeratne
EMK, Acidissimin: a new limonoid
from Limonia acidissima, Journal of
natural products, 1989;52(4):882-885.
. Kumawat BK, Rajkumar M, singh Y,
Antidiarrhoeal activity of alcoholic and
aqueous extracts of Limonia
acidissima, Linn. stem bark, Indian J.
Nat. Prod, 2010;26(4):23-27.
. Harborne JB. Phytochemical methods,
A guide to modern techniques of plant
analysis, III edition, 2005;4-8,72-
,134-135.
. Furis BS, Hannaford AJ, Rajesh V,
Suilap NG and Taichan AR. Vogels
Text Book of Practical Organic
Chemistry, Longman group
publication, 1978;400-402.
. Donald J. Ecobiscon, The basis of
toxicity testing, 2nd Edition. CRC
Press, 1997;43-49.
. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development,
Guidance document on Acute Oral
Toxocity Testing, Environment
Directorate, OECD, Peris, 2001;1-24.
. Ragava NB. and krishnakumari S,
antidiabetic effect of t. arjuna bark
extract in alloxan induced diabetic
rats, Indian Journal of Clinical
Biochemistry, 2006;21(2):123-128.
. Deore SL, Khadabadi SS., Daulatkar
VD, Deokate UA, Farooqui IU.
Evaluation of hypoglycemic and
antidiabetic activity of bark of Butea
monosperma, Phcog Mag.,
;4(Suppl 13):16,18
. Staley P, Kammakakannan N,
Venugopal P. Menon. Anti diabetic
and hyper lipedemic effect of alcoholic
Syzigium cumini seeds in alloxan
induced diabetic albino rats, Journal of
Ethano pharmacology, 2004;91:209-
. Triender P, Determination of glucose
using glucose oxidase with an
alternative oxygen acceptor, Annual
Clinical Biochemistry,1969;6:24–27.
. Vogel H. Gerhard, Drug discovery and
Evaluation pharmacological Assays,
Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg,
New York, 2002;947-1051.
. Snedeeor GW, Cochran WG, in:
Statistical Methods, Oxford and IBII
Publishing Co., New Delhi, 1967;33.
. Lillie RD. Histopathologic Technic and
Practical Histochemistry, McGraw-Hill
Company, Toronto, 1954;114.
. Nagappa AN, Thakurdesai PA, Venkat
Rao N, Singh J. Antidiabetic activity of
Terminalia catappa Linn fruits, J.
Ethnopharmacol, 2003;88:45-50.