Comparative evaluation of Baccharis trimera, Pimpinella anisum and statin on the biochemical profile of Wistar rats
Keywords:
Pimpinella anisum, Baccharis trimera, statin, cholestero, LDL-c, HDL-cAbstract
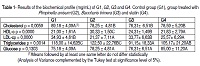
Many are the plants for therapeutic purposes. Baccharis trimera is known to treat rheumatism, diabetes, and liver disorders. Pimpinella asinum is known to control colds, cough, bronchitis, fever, cramps and inflammation. The aim of this study was to evaluate the use of B. trimera and P. anisum and compare with statin effects on plasma lipids of Wistar rats. Sixty Animals were divided in control group (CG) and G2 (treated with anise), G3 (B. trimera) and G4 (simvastatin). Plants and statin were administrated by intra-gastric route twice a day for 30 days. No modifications in glycaemia were observed in the experimental groups. Reductions were observed in cholesterol levels in treated groups. For LDL-c levels, significant differences were observed in G2 and G4. G3 showed significant reduction in the triglycerides levels and no significant differences were observed in the glycaemia in the studied groups. Increased levels of HDL-c were presented by the groups treated with the plants. The group treated with B. trimera showed significant reduction in triglycerides when compared to the control group. The use of the plants also shows Atherogenic Index lower than control group and the one treated with simvastatin. Our results suggest that the plants used in this work have similar or better effects in the lipid profile of Wistar rats when compared to the use of statin.
References
Lee CY, Lee MJ, Kim JM, Choi SM, Kang KK, Kim OJ, Lee BM. Oryza sativa L. extracts inhibit nitric oxide production and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in murine macrophage cells and lungs of antigen-challenged allergic mice. Int Journalof Phytomedicine 2015; 7 (1) 01-07.
- Ghosh S, Ahire M, Patil S, Jabgunde A, Bhat Dusane M, Joshi BN, Pardesi K, Jachak S, Dhavale DD, Chopade BA. Antidiabetic Activity of Gnidia glauca and Dioscorea bulbifera: Potent Amylase and Glucosidase Inhibitors. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012;2012:929051. doi: 10.1155/2012/929051.
- Paiva AF, Bonomo LF Boasquivis PF, Paula ITBR, Guerra JF, Leal WM, Silva ME, Pedrosa ML, Oliveira RP. Carqueja (Baccharis trimera) Protects against Oxidative Stress and β-Amyloid-Induced Toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015; 2015:740162. doi: 10.1155/2015/740162.
- Pádua B C, Rossoni Júnior JV, Magalhães CL, Chaves MM, Silva ME, Pedrosa ML, de Souza GH, Brandão GC, Rodrigues IV, Lima WG, Costa DC. Protective effect of Baccharis trimera extract on acute hepatic injury in a model of inflammation induced by acetaminophen. Mediators Inflamm 2014; 2014:196598. doi: 10.1155/2014/196598.
- Oliveira CB, Comunello LN, Lunardelli A, Amaral RH, Pires MG, da Silva GL, Manfredini V, Vargas CR, Gnoatto SC, de Oliveira JR, Gosmann G. Phenolic enriched extract of Baccharis trimera presents anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. Molecules 2012; 17(1):1113-23.
- Trojan-Rodrigues M, Alves TL, Soares GL, Ritter MR. Plants used as antidiabetics in popular medicine in Rio Grande do Sul, southern Brazil. J Ethnopharmacol 2012;139 (1):155-63. Review.
- Mendes FR, Tabach R, Carlini EA. Evaluation of Baccharis trimera and Davilla rugosa in tests for adaptogen activity. Phytother Res 2007, 21 (6): 517-522.
- Borella JC, Duarte DP, Novaretti AAG, Menezes Jr A, França SC, Camila B. Rufato CB, Santos PAS, Rodrigo C.S. Veneziani RCS, Lopes NP. Seasonal variability in the content of saponins from Baccharis trimera (Less.) DC (Carqueja) and isolation of flavone. Rev Bras Farmacogn 2006; 16(4): 557-561.
- Oliveira CB, Comunello LN, Maciel ES, Giubel SR, Bruno AN, Chiela EC, Lenz G, Gnoatto SC, Buffon A, Gosmann G. The inhibitory effects of phenolic and terpenoid compounds from Baccharis trimera in Siha cells: differences in their activity and mechanism of action. Molecules 2013;18(9):11022-32.
- Silva, F G, Oliveira CBA, Pinto J E B P; Vivian E. Nascimento V E, Santos S C, Seraphin J C, Pedro H. Ferri P H 2007. Seasonal variability in the essential oils of wild and cultivated Baccharis trimera. J Braz Chem 18 (5): 990-997.
- Koeduka T, Baiga TJ, Noel JP, Pichersky E. Biosynthesis of t-anethole in anise: characterization of t-anol/isoeugenol synthase and an O-methyltransferase specific for a C7-C8 propenyl side chain. Plant Physiol 2009; 149(1): 384-94.
- Janahmadi M, Farajnia S, Vatanparast J, Abbasipour H, Kamalinejad M. The fruit essential oil of Pimpinella anisum L. (Umblliferae) induces neuronal hyperexcitability in snail partly through attenuation of after-hyperpolarization. J Ethnopharmacol 2008; 20(3):360-5.
- Tirapelli CR, de Andrade CR, Cassano AO, De Souza FA, Ambrosio SR, da Costa FB, de Oliveira AM. Antispasmodic and relaxant effects of the hidroalcoholic extract of Pimpinella anisum (Apiaceae) on rat anococcygeus smooth muscle. J Ethnopharmacol 2007;110(1):23-9.
- Al Mofleh I A, Alhaider AA, Mossa JS, Al-Soohaibani MO, Rafatullah S. Aqueous suspension of anise [quot ]Pimpinella anisum [quot] protects rats against chemically induced gastric ulcers. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(7):1112-8.
- Lee SJ1, Choi HN1, Kang MJ1, Choe E2, Auh JH3, Kim JI1. Chamnamul [Pimpinella brachycarpa (Kom.) Nakai] ameliorates hyperglycemia and improves antioxidant status in mice fed a high-fat, high-sucrose diet. Nutr Res Pract 2013;7(6):446-52.
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes--2014. Diabetes Care 2014;37 Suppl 1:S14-80. doi: 10.2337/dc14-S014.
- Schulpis K, Karikas GA. Serum cholesterol and triglyceride distribution in 7767 school-aged Greek children. Pediatrics. 1998 May;101(5):861-4.
- Munshi RP, Joshi SG1, Rane BN. Development of an experimental diet model in rats to study hyperlipidemia andinsulin resistance, markers for coronary heart disease. Indian J Pharmacol. 2014 May-Jun;46(3):270-6. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.132156.
- Dickel ML1, Rates SM, Ritter MR. Plants popularly used for loosing weight purposes in Porto Alegre, South Brazil. J Ethnopharmacol 2007;109(1):60-71.
- Kreydiyyeh SI, Usta J, Knio K, Markossian S, Dagher S. Aniseed oil increases glucose absorption and reduces urine output in the rat. Life Sci 2003;74(5):663-73.
- Saddala RR, Thopireddy L, Ganapathi N, Kesireddy SR. Regulation of cardiac oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats treated with aqueous extract of Pimpinella tirupatiensis tuberous root. Exp Toxicol Pathol 2013 Jan;65(1-2):15-9. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2011.05.003.
- Jamshidzadeh A, Heidari R, Razmjou M, Karimi F, Moein MR, Farshad O, Akbarizadeh AR, Shayesteh MR. An in vivo and in vitro investigation on hepatoprotective effects of Pimpinella anisumseed essential oil and extracts against carbon tetrachloride-induced toxicity. Iran J Basic Med Sci 2015; 18(2):205-11.
- Shojaii A, Abdollahi Fard M. Review of Pharmacological Properties and Chemical Constituents of Pimpinella anisum. ISRN Pharm 2012; 2012:510795. doi: 10.5402/2012/510795.
- Simões-Pires CA, Queiroz EF, Henriques AT, Hostettmann K. Isolation and on-line identification of antioxidant compounds from three Baccharis species by HPLC-UV-MS/MS with post-column derivatisation. Phytochem Anal 2005; 16(5): 307-14.
- Padua B C, Rossoni Júnior JV, Magalhães CL, Chaves MM, Silva ME, Pedrosa ML, de Souza GH, Brandão GC, Rodrigues IV, Lima WG, Costa DC. Protective effect of Baccharis trimera extract on acute hepatic injury in a model of inflammation induced by acetaminophen. Mediators Inflamm 2014; 2014:196598. doi: 10.1155/2014/196598.
- Soicke H, Leng-Peschlow E. Characterization of flavonoids from Baccharis trimera and their antihepatotoxic properties. Planta Med 1987; 53(1):37-9.
- Muneera KE, Majeed A, Naveed AK. Comparative evaluation of Nigella sativa (Kalonji) and simvastatin for the treatment of hyperlipidemia and in the induction of hepatotoxicity. Pak J Pharm Sci 2015;28(2):493-8.
- Kapourchali FR, Surendiran G, Goulet A, Moghadasian MH. The Role of Dietary Cholesterol in Lipoprotein Metabolism and Related Metabolic Abnormalities: A Mini-review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2015 Jun 9:0. [Epub ahead of print].
- Baibata D, Ionescu G, Petcov B, Mancas S. Non-High-Density Lipoproteins Cholesterol and Cardio-Metabolic Risk. Maedica (Buchar) 2015; 10(1):33-8.
- Sirtori CR. The pharmacology of statins. Pharmacol Res 2014; 88:3-11. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2014.03.002.
- Macedo AF, Taylor FC, Casas JP, Adler A, Prieto-Merino D, Ebrahim S. Unintended effects of statins from observational studies in the general population: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med 2014;12:51. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-12-51.
- Covelli D, Vannucchi G, Campi I, Currò N, D'Ambrosio R, Maggioni M, Gianelli U, Beck-Peccoz P, Salvi M. Statins may increase the risk of liver dysfunction in patients treated with steroids for active graves' orbitopathy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015; 100(5):1731-7.
- Ovbiagele B, Buck BH, Liebeskind DS, Starkman S, Bang OY, Ali LK, Villablanca JP, Salamon N, Yun SW, Pineda S, Saver JL 2008. Prior antiplatelet use and infarct volume in ischemic stroke. J Neurol Sci 15; 264(1-2): 140-4.
- Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med 2002; 346(16): 1221-31.
- Padua BC, Rossoni Junior JV, de Brito Magalhaes CL, Seiberf JB, Araujo CM, Bianco de Souza GH, Chaves MM, Silva ME, Pedrosa ML, Costa DC. Baccharis trimera improves the antioxidant defense system and inhibits iNOS and NADPH oxidase expression in a rat model of inflammation. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 2014; 14(11):975-84.