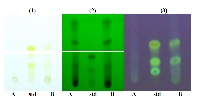
Constituents of the rhizome of Curcuma aeruginosa and its DNA fingerprint
Keywords:
Curcuma aeruginosa, Zingiberaceae, TLC, GC-MS, DNA fingerprintsAbstract
Identity of the rhizhome of Curcuma aeruginosa Roxb. was established by three techniques: (1) the DNA fingerprint, (2) the chemical constituents of its volatile oils by using gas chromatographmass spectrometer, and (3) thin-layer chromatography (TLC) of the methanol extract. These three techniques were used to differentiate C. aeruginosa from its similar species. Result from the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, different polymorphic bands between the two specimens were found. The relative amounts of camphor, curzerenone and epicurzerenone in the C. aeruginosa rhizome were 16.85, 16.81 and 3.5% of total peak areas, whereas 6.04, 0 and 62.84% of total peak areas were found in the Curcuma sp. The thin-layer chromatogram revealed that Curcuma sp. contained curcumine, whereas only traces were detected in C. aeruginosa.
References
Jarikasem S, Thubthimthed S,
Chawanannoraseeth K, Suntrontarasat T:
Essential Oil from Three Curcuma species
Collected in Thailand. In Proceedings of
WOCMAP III: 3-7 February 2003;
Chiangmai. Edited by E. Brovelli et al.
International Society for Horticultural
Science (ISHS); 2005;37-41.
Wangsomnuk PP, Wangsomnuk P, Maza
B: Biodiversity and molecular aspects of
Curcuma species from North-Eastern
Thailand. In Proceedings of the 3rd
Symposium on the Family Zingiberaceae:
-12 July 2002; Khon Kaen. Edited by
Chantaranothai P, Larsen K, Sirirugsa P,
Simpson D: Applied Taxonomic Research
Center; 2002;109-19.
The National Center for Biotechnology
Information. Available at
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/. Accessed
April 20, 2011.
British Phamacopoeia 2010: Essential oils
in herbal drugs. London, England: The
Stationary Office at the University Press.
;vol.4:p A289.
Davies NW. Gas chromatographic
retention indices of monoterpenes and
sesquiterpenes on methyl silicone and
Carbowax 20M phase. J. of
Chromatography. 1990:503(1):1-24.
Welsh J, McClelland M. Fingerprinting
genomes using PCR with arbitrary
primers. Nucl Acids Res. 1990;18:7213-8.
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ,
Rafalski JA, Tingey SV. DNA
polymorphism amplified by arbitrary
primers are useful as genetic markers.
Nucl Acids Res.1990;18:6531-5.