Protective effect of Pisonia aculeata on Rifampicin and Isoniazid induced hepatotoxicity in rats
Keywords:
Pisonia aculeata, Rifampicin, Isoniazid, Biochemical parameters, Antioxidants, Lipid peroxidation, HistopathologyAbstract
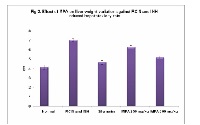
Pisonia aculeata is traditionally used in treatment of liver disorder and thought to have a protective effect which may be beneficial to reduce symptoms of hepatotoxicity. The current study aimed to evaluate the scientific merit of these anecdotal claims in an in vivo model. Methanolic extract of leaves of Pisonia aculeata (250 and 500 mg/kg, p.o.) showed a remarkable hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity against Rifampicin and Isoniazid induced hepatotoxicity as judged from the serum marker enzymes and antioxidant levels in liver tissues. Acetaminophen induced a significant rise in aspartate amino transferase (AST), alanine amino transferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), total bilirubin, gamma glutamate transpeptidase (GGTP), lipid peroxidase (LPO) with a reduction of total protein, superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, glutathione peroxidase (GPx), reduced glutathione (GSH), Glutathione reductase (GR), Vitamin C and E. Treatment of rats with different doses of plant extract (200 and 300 mg/kg) significantly (P<0.001) altered serum marker enzymes and antioxidant levels to near normal against acetaminophen treated rats. Also the extract was effectively altered the drug metabolizing enzymes such as Cytochrome P450, NADPH Cytochrome C reductase and glutathione S transferase. The activity of the extract at dose of 500 mg/kg was comparable to the standard drug, silymarin (50 mg/kg, p.o.). Histopathological changes of liver sample were compared with respective control. Results indicate the hepatoprotective and antioxidant properties of Pisonia aculeata against rifampicin and isoniazid -induced hepatotoxicity in rats.
References
Pushpangadan P, Kumar B,
Vijayakumar M and Govindarajan R
Ethnopharmacological approaches to
wound healing exploring medicinal
approaches to wound healing exploring
medicinal plants. J Ethnopharmacol.
;114:103-113.
Subramaniam A, Evans DA,
Rajasekharan S and Pushpangadam
P,Effect of Trichopus zeylanicus Gaertn
(active fraction) on phagocytosis by
peritoneal macrophages and humoral
immune in response in mice.Indian J
Pharmacol. 2000;32:221-225.
Howard RA. Flora of the Lesser
Antilles, Leeward and Windward
Islands. Dicotyledoneae, Part 1,
;673.
Liogier HA. Discriptive flora of Puerto
Rico and adjacent islands. 1985;1:352.
Bhupinder Singh K, Sarita A, Nita K,
Usha G. Effect of cimetidine on
hepatotoxicity induced by isoniazidrifampicin combination in rabbits.
Indian Journal of Gastroenterology.
;26,18-21.
Reitman S and Frankel A. Colorimetric
method for determination of serum
glutamate oxaloaectate and glutamic
pyruvate transaminase. American J Clin
Pathol. 1957;28:56-58.
Kind PR, and King EJ. Estimation of
plasma phosphates by determination of
hydrolyzed phenol with antipyrin. J Clin
Pathol. 1954;7:322-326.
Szaszi G. A kinetic photometric method
for serum gamma glutamyl
transpeptidase. Clin Chem. 1969;15:124
-126.
Mallay HT, and Evelyn KA. Estimation
of serum bilirubin level with the
photoelectric colorimeter. J Biol Chem.
;119:481–484.
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL,
and Randall RJ. Protein measurement
with Folin–Phenol reagent. J Biol
Chem. 1951;193:265-275.
Devasagayam TPA and Tarachand U.
Decreased lipid peroxidation in the rat
kidney during gestation. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 1987;56:836–
Marklund S and Marklund G.
Involvement of superoxide anion radical
in the auto oxidation of pyrogallol and a
convenient assay for superoxide
dismutase. Eur J Biochem. 1974;47:469-
Sinha AK. Colorimetric assay of
catalase. Analytical Biochem.
;47:389-394.
Rotruck JT, Pope AL, Ganther HL and
Swanson AB. Selenium: Biochemical
role as a component of glutathione
peroxidase. Science. 1973;179:588-590.
Omura T, Sato R. The carbon monoxidebinding pigment of liver microsomes. I.
Evidence for its hemoprotein nature. J.
Biol. Chem. 1964;239:2370–8.
Williams Jr CH, Kamin H. Microsomal
triphosphopyridine nucleotide-
cytochrome c reductase of liver. J. Biol.
Chem. 1962;237:587–95.
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, and Jakoby WB.
Glutathione S-transferase, the first
enzymatic step in mercapturic acid
formation. J. Biol. Chem.
;249:7130-7139.
Galigher AE and Kozloff EN. Essential
Practical Micro technique, 2nd edn, Lea
and Febiger, Philadelphia. 1971;p.77.
Hussain Z, Kar P, Husain SA. Indian J
Experimental Biol. 2003;41:226.
Mitra SK, Venkataranganna MV,
Sundaram R, Gopumadhavan S.
Protective effect of HD-03, a herbal
formulation,against various hepatotoxic
agents in rats. J Ethnopharmacol.
;63:18-186.
Sodhi CP, Rana SF, Attri S, Mehta S,
Yaiphei K, Mehta SK. Oxidative-hepatic
injury of isoniazid-rifampicin in young
rats subjected to protein and energy
malnutrition. Drug Chem Toxicol.
;21:305-317.
Nemesanszky E, Enzyme test in
hepatobiliary disease. In Enzyme Test in
Diagnosis (eds Moss DW and Rosalki
SB), Arnold, London. 23–59.
Amacher DE, Serum transaminase
elevations as indicators of hepatic injury
following the administration of drugs
Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 1998;27:119-
Isselbacher KJ, Braunwald E, Wilson
JD, Martin JB, Fauci AS, Kasper DL.
Harrison’s principles of internal
medicine, 13th edn. McGraw-Hill, New
York. 1994;1444.
Georgieva N, Gadjeva V, Tolekova A.
New isonicotinoylhydrazones with ssa
protect against oxidativehepatic injury of
isoniazid. TJS 2004;2:37–43.
Ramaiah SK, Apte U, Mehendale HIM.
Cytochrome P4502E1 induction
increases thioacetamide liver injury in
diet-restricted rats. Drug Metab Dispos.
;29:1088-95.
Shakun NP, Shmanko VV. Synergistic
effect of rifampicin on hepatotoxicity of
isoniazid. Antibiot Med Biotekhnol.
;30:185-9.
Steele MA, Burk RF and Des PRM.
Toxic hepatitis with isoniazid and
rifampicin: a meta-analysis. Chest.
;99:465-471.
Wu JW, Leev SD, Yeh PF. IsoniazidRifampicin induced hepatitis in hepatitis
B carriers. Gastroentrology.
;98:502-4.
Dwivedi Y, Rastogi R, Garg NK, and
Dhawan BN. Prevention of paracetamolinduced hepatic damage in rats by
picroliv, the standardized active fraction
from Picrorhiza kurroa. Phytotherapy
Research. 1991;5:115-119.
Mandal PK, Bishayee A and Chatterjee
M. Stimulation of tissue repair by
Mikania cordata root extract in carbon
tetrachloride-induced liver injury in
mice. Phytotherapy Research.
;7:103-105.
Boyer TD, Vessey DA., Holcomb C,
Saley N. Studies of the relationship
between the catalytic activity and
binding of non-substrate ligands by the
glutathione S-transferase. Biochem J.
;217:179–185.
Masukawa T, Iwata H. Possible
regulation mechanism of microsomal
glutathione S-transferase activity in rat
liver. Biochem Pharmacol.
;35:435–438.