Antifibrotic effect of Pluchea sagitallis (Lam.) cabrera aqueous extract in grx cell lineage
Keywords:
hepatic fibrosis, hepatic stellate cell, Pluchea sagitallisAbstract
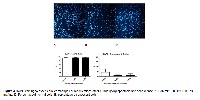
Liver fibrosis is a complex disease that is caused by inappropriate tissue repair due to the deposition of connective tissue. When a chronic lesion affects the liver, regenerative response fails and hepatocytes are replaced with abundant extracellular matrix (ECM). The imbalance between production and degradation of ECM will result in the accumulation of proteins that change normal liver architecture, and thus its functionality. The main source of ECM is the activated hepatic stellate cell (HSC). In order, to clarify possible therapeutic approaches to the disease, this work aimed to evaluate the possible antifibrotic action of Pluchea sagitallis (Lam.) Cabrera on an activated HSC immortalized lineage (GRX). Our results demonstrated that the P. sagittalis aqueous extract at 0.039 and 0.078 mg/mL concentrations was able to reduce cell growth and proliferation. Regarding to oxidative stress evaluation, there was no statistically significant difference between the treated group and the control. Staining with OilRed-O (ORO) showed a statistically significant increase in intracellular lipid content after 5 days of treatment, exerting in vitro effect on the GRX phenotypic change of activated towards the quiescent state. These results were confirmed by colorimetric quantification of lipid content. Regarding the TGF-β1 and collagen production, there were no statistically significant differences observed between the groups. In conclusion, the P. sagittalis aqueous extract reduces the growth and proliferation of GRX cells and induces the reversal of activated towards a quiescent phenotype. There was no decrease in cell proliferation either by necrosis or by apoptosis via activation of the senescence. Thus, our data suggest that the extract showed an antifibrotic effect, possibly by activating phenotype reversal.
References
Bissell DM, Roulot D, George J. Transforming growth
factor beta and the liver. Hepatology;2001(34):859–67.
Bitencourt S, de Mesquita FC, Caberlon E, da Silva GV,
Basso BS, Ferreira GA, de Oliveira JR. Capsaicin induces de-differentiation of activated hepatic stellate cell.
Biochem Cell Biol 2012;.
Borojevic R, Monteiro AN. Vinhas SA, Domont GB,
Moura˜o PA, Emonard H, Grimaldi G, Grimaud JA. Establishment of a continuous cell line from fibrotic schistosomal granulomas in mice livers. vol. 1985;.
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for
the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal
Biochem;1976(72):248–54.
Co´rdova WHP, Mesa. LG, Hill ALP. Metabo´litos secundarios y actividad antimicrobiana de Pluchea carolinensis.
Revista Cubana de Farma´cia;2006(40).
Co´rdova WHP, Tabart J. Quesada AG, Sipel A, Hill ALP,
Kevers C, Dommes J. Antioxidant capacity of three Cuban
species of the genus Pluchea. Cass( Asteraceae) Journal of
Food Biochemistry;2010(34):249–261.
Duval F. Moreno-Cuevas JE, Gonza´lez-Garza MT,
Rodr´ıguez-Montalvo C, Cruz-Vega DE. Liver fibrosis and
protection mechanisms action of medicinal plants targeting
apoptosis of hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells;.
Duval F. Moreno-Cuevas JE, Gonza´lez-Garza MT,
Rodr´ıguez-Montalvo C, Cruz-Vega DE. Protective mechanisms of medicinal plants targeting hepatic stellate cell
activation and extracellular matrix deposition in liver fibrosis. Chin Med;2014(9):27–10.
Ferris H, Zheng L. Plant Sources of Chinese Herbal Remedies: Effects on Pratylenchus vulnus and Meloidogyne javanica. J Nematol;1999(31):241–63.
Filippi-Chiela EC, Oliveira MM, Jurkovski B, CallegariJacques SM, da Silva VD, Lenz G. Nuclear morphometric
analysis (NMA): screening of senescence, apoptosis and
nuclear irregularities. PLoS One;2012(7):10–1371.
Friedman SL. Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis,
an integrated cellular response to tissue injury. J Biol
Chem;2000(275):2247–50.
Friedman SL. Hepatic fibrosis-overview.
Toxicology;2008(254):120–9.
Friedman SL. Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol
Rev;2008(88):125–72.
Guimara˜es EL. Franceschi MF, Grivicich I, Dal-Pizzol
F, Moreira JC, Guaragna RM, Borojevic R, Margis R,
Guma FC. Relationship between oxidative stress levels
and activation state on a hepatic stellate cell line. Liver
Int;2006(26):477–85.
Halliwell B, Whiteman M. Measuring reactive species
and oxidative damage in vivo and in cell culture: how
should you do it and what do the results mean? Br J
Pharmacol;142(231-55):10–1038.
Kissmann KG, Groth D. Plantas Infestantes e Nocivas.
BASF Brasileira S/A 2ª. 1992;2.
Lotersztajn S, Julien B. Clere FT, Grenard P, Mallat AH.
Hepatic fibrosis: Molecular mechanisms and drug targets.
Annu harmacol Toxicol;2005(45):605–28.
McCuskey RS. Functional morphology of the liver with
emphasis on microvasculature. In: Tavaloni N, Berk PD
eds. Hepatic transport and bile secretion: physiology and
pathophysiology. New York: Raven Press Ltd.1993;1-10;.
Neuman MG. Apoptosis in diseases of the liver. vol. 2001;.
Pe´rez-Garc´ıa F, Mar´ın E. Adzet T, Can˜igueral S. Activity of plant extracts on the respiratory burst and the stress
protein synthesis. Phytomedicine;2001(8):31–8.
Pe´rez-Garc´ıa F, Mar´ın E. Can˜igueral S, Adzet T. Antiinflammatory action of Pluchea sagittalis: involvement of
an antioxidant mechanism. Life Sci;1996(59):2033–40.
Ram´ırez-Zacar´ıas JL, Castro-Mun˜ozledo F, Kuri-Harcuch
W. Quantitation of adipose conversion and triglycerides
by staining intracytoplasmic lipids with Oil red O. Histochemistry; 1992.
Reyes-Trejo B, Joseph-Nathan P. Modhephene derivates
from Pluchea sericea. Phytochemistry;1999(51):75–78.
Rockey D. The cellular pathogenesis of portal hypertension: stellate cell contractility, endothelin, and nitric oxide.
Hepatology;1997(25):2–5.
Souza IC, Martins LA. Coelho BP, Grivicich I, Guaragna
RM, Gottfried C, Borojevic R, Guma FC. Resveratrol inhibits cell growth by inducing cell cycle arrest in activated
hepatic stellate cells. Mol Cell Biochem;.
Spiller F. Anti-inflammatory effects of red pepper (Capsicum baccatum) on carrageenan- and antigen-induced inflammation. J Pharm Pharmacol;2007(60).
Vicente CP, Fortuna VA, Margis R. Trugo L, Borojevic R.
Retinol uptake and metabolism, and cellular retinol binding protein expression in an in vitro model of hepatic stellate cells. Mol Cell Biochem;1998(187):11–21.
Winau F. Quack C, Darmoise A, Kaufmann SH. Starring stellate cells in liver immunology. Curr Opin
Immunol;2008(20):68–74.
Ye Y, Dan Z. All-trans retinoic acid diminishes collagen
production in a hepatic stellate cell line via suppression
of active protein-1 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase signal. J
Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci;2010(30):726–33