Study of Daucuscarota ssp. Sativus and Butea monospermato analyse their Applicability in Pharmaceutical Industry as Antimicrobial Agents
Keywords:
Phytochemical screening, Antimicrobial activity, Black Carrot, KamarkasAbstract
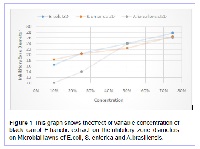
Human Beings have been using plant products to heal the Wounds and Diseases from the inception of humankind. Even when it was not known that microorganisms exist, People have been using antimicrobial agents prepared from plants. These antimicrobial products were prepared by extracting the plant in a suitable solvent. Antimicrobial property is conferred to plants by the presence of various phytochemicals which are the products of several Secondary metabolic pathways. The aim of this project was to decipher the potential use of Daucus carota ssp. Sativus and Butea monosperma in the pharmaceutical industry. In this research, Qualitative phytochemical screening and antimicrobial potential of Black carrot and Kamarkas has been studied. Black carrot showed good antimicrobial activity against A. brasiliensis, E. coli and S. enterica, arranged in descending order of the Slope obtained in each antimicrobial assay. Phytochemical screening showed the presence of Flavonoids, Soluble Phenolic Compounds, Naphthoquinone and traces of Saponins and Alkaloids. The Kamarkas showed antimicrobial activity against S. aureus and to some extent against A. brasiliensis. Phytochemical analysis of Kamarkas showed positive for all phytochemicals.
References
Cowan MM. Plant products as Antimicrobial Agents.
Clinical Microbiology Reviews;1999(12):564–582.
Joshi VK. Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth
in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials.
The internet journal of microbiology;2008(7).
Vinoth B, Manivasagaperumal R, Rajaravindran M. Phytochemical Analysis and antibacterial activity of Azadirachtaindica A JUSS. International Journal of Research in Plant
Science;2012(2):50–55.
Genetics. Jeremy Clorault, EmannuelGeoffriau, Eric Lionneton, Mathilde Briard, Didier Peltier. Carotenoid Biosynthesis genes provide evidence of Geographical subdivision
and extensive linkage disequilibrium in the carrot. Theoretical and Applied. 2010;p. 659–672.
Vishwanath Khandare, Shweta Walia, Meenakshi Singh,
Charanjit Kaur. Black carrot (Daucuscarota ssp. sativus)
juice: Processing effects on antioxidant composition and
color. Food and bioproduct processing;.
Esselen M, Friitz J, Hutter M, N T, S B, U B,
et al. Anthocyannin-rich extracts suppress the DNA
Damaging effects of topoisomerase Poisons in Human
Colon Cancer Cells. Molecular Nutrition & Food
Research;2011(55):143–153.
Shih PH, Wu CH, CT Y, GC Y. Protective effects of
anthocyanins against amyloid β-peptide-induced damage
in neuro-2A Cells. Journal of Agricultural and Food
Chemistry;2011(59):1683–1689.
Rana F, MazumdarAvijit. Review on Butea monosperma.
vol. 2012;.
Tiwari P, Kumar B, Kaur M, Kaur G, HarleenKaurPlants.
Phytochemical screening and Extraction. A Review Internationale Pharmaceuticasciencia;2011(1):98–106.
Joshi VK. Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth
in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials.
The Internet Journal of Microbiology;2008(7).
Hashemi SR, Zulfikar I, Zunita Z, N M. Somchit. The
Effect of Selected Sterilization Methods on Antimicrobial
Activity of Aqueous extract of herbal plants. Journal of
Biological Sciences;2008(8):1072–1076.