Protective role of Broccoli powder against continuous ingestion of Escitalopram antidepressant drug induced hepatotoxicity in Swiss albino male mice
Keywords:
Escitalopram antidepressant drug, Broccoli powder, CCl4, HepatotoxicityAbstract
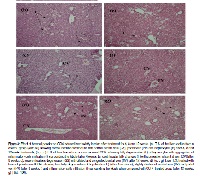
To investigate the protective role of broccoli powder “Brassica Oleracea Italica” against continuous ingestion of escitalopram antidepressant drug induced hepatotoxicity in Swiss albino male mice. Mice were divided into different groups. Group1: Normal control (0.9% NaCl), Group 2: Escitalopram drug treated only (20 mg/kg), Group 3: Broccoli powder with Escitalopram drug treated (200 mg/kg + 20 mg/kg), Group 4: Olive oil vehicle control, Group 5: Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) referenced as positive control (33 mg/kg), Group 6: Broccoli powder with CCl4 treated (200 mg/kg + 33 mg/kg). The effect of these groups on liver tissue was studied after three different time periods for 4, 8 and 12 weeks. The results showed that the treatment with escitalopram drug displayed significantly increased serum SGOT, SGPT, ALP level and alter liver antioxidant enzymes level (LPO, SOD and GSH) that are comparable with CCl4intoxicated group considered as positive control. Comparing escitalopram drug treated group with group that received both broccoli powder and escitalopram drug displayed a significant decrease in serum SGOT, SGPT, ALP levels and restored the level of antioxidant enzymes. The protective effect of broccoli powder on escitalopram drug induced hepatotoxicity was also supported by histopathological studies.
References
. Draz EI, Emara AM, Saad KM,
Badaway A, SE HEN, Abd-Elgelil H.
Genotoxicity of some commonly used
antidepressants (fluoxetine, sertraline
and clomipramine). Mansoura J.
Forensic Med. Clin. Toxicol. 2009; 17:
-78.
. Grover S, Avasth A, Kalita K, Dalal PK,
Rao GP, Chadda RK., et al. IPS
multicentric study: Antidepressant
prescription patterns. Indian J.
Psychiatry. 2013; 55: 41-45.
. Wang HY, Chen YC. Escitalopram
intoxication induced acute psychosis.
J. Clin. Toxicol. 2015; 5: 3.
. Khawam EA, Laurencic G, Malone
Jr DA. Side effects of
antidepressants: an overview.
Cleveland Clinic. J. Med. 2006; 73:
-361.
. Ferguson JM. SSRI antidepressant
medications: adverse effects and
tolerability. Prim. Care. Companion J.
Clin. Psychiatry. 2001; 3: 22-27.
. Voican CS, Corruble E, Naveau S,
Perlemuter G. Antidepressant-induced
liver injury: a review for clinicians. AM.
J. Psychiatry. 2014; 171: 404-415.
. Friedrich ME, Akimova E, Huf W,
Konstantinidis A, Papageorgiou K,
Winkler D., et al. Drug-induced liver
injury during antidepressant
treatment: results of AMSP, a drug
surveillance program. Int J
Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016; 19: 1-9.
. Subramanian V. Hepatoprotective
activity of Brassica oleracea italica
against carbon tetrachloride induced in
albino rats. J. Pharm. Res. 2011; 4:
-1144.
. Owis AI. Broccoli; the Green Beauty: A
Review. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2015; 7: 696-
. Cimen B, Gumus CB, Cetin I, Ozsoy
S, Aydin M, Cimen L. The effects of
escitalopram treatment on
oxidative/antioxidative parameters in
patients with depression. Bull. Clin.
Psychopharmacol. 2015; 25: 272-279.
. Hickox WH. Public health goal for
carbon tetrachloride in drinking
water. 2000. OEHHA CalEPA.
Available from: https://oehha.ca.gov/
. El-Baz FK, Salama ZA, Gaafar AA.
Evaluation of hepatoprotective effect of
broccoli Extract against CCL4 in rats.
Int. J. Med. Biol. Front. 2012; 18: 521-
. Food and Drug Administration,
Guidance for industry: estimating the
maximum safe starting dose in initial
clinical trials for therapeutics in adult
healthy volunteers. Center for Drug
Evaluation and Research (CDER)
. Shin JW, Seol IC, Son CG.
Interpretation of animal dose and
human equivalent dose for drug
development. J. Korean Orient. Med.
; 31: 1-7.
. Powell TR, Fernandes C, Schalkwyk
LC. Depression‐Related Behavioral
Tests. Curr. Protoc. Mouse Biol. 2012;
: 119-127.
. Chahardehi AM, Ibrahim D,
Abolhassani F, Sulaiman SF.
Antidepressant-like effects of selected
crude extracts of Pilea microphylla in
mice model of depression. American J.
Agri. Biol. Sci. 2013; 8: 75-81.
. Kumar V, Tomar A, Singh BK,
Nagarajan K, Machawal L, Bajaj U.
Attenuating depression behavior by
Centella asiatica extract & venlafaxine
in mice induced through Forced swim
and Tail suspension test. Int. J.
Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013; 1: 29-35.
. Chenu F, Guiard BP, Bourin M, Gardier
AM. Antidepressant-like activity of
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
combined with a NK1 receptor
antagonist in the mouse forced
swimming test. Behavioural Brain Res.
; 172: 256-263.
. Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K. Assay
for lipid peroxides in animal tissues
by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal.
Biochem. 1979; 95: 351-358.
. Marklund S, Marklund G.
Involvement of the superoxide anion
radical in the autoxidation of
pyrogallol and a convenient assay for
superoxide dismutase. Eur. J.
Biochem.1974; 47: 469-474.
. Moron MS, Depierre JW, Mannervik B.
Levels of glutathione, glutathione
reductase and glutathione Stransferase activities in rat lung and
liver. Biochimica. ET Biophysica.
Acta.1979; 582: 67-78.
. Abdelmajeed NA. Oxidative tissue
damage induced by citalopram in rat
different organs. Res. J. Medicine Med.
Sci. 2009; 4: 580-586.
. Zlatković J, Todorović N, Tomanović N,
Bošković M, Djordjević S, Lazarević-
Pašti T, et al. Chronic administration of
fluoxetine or clozapine induces
oxidative stress in rat liver: a
histopathological study. Eur. J. Pharm.
Sci. 2014; 59: 20-30.
. Yılmaz A, Elbey B, Yazgan ÜC, Dönder
A, Arslan N, Arslan S, Alabalık U,
Aslanhan H. Protective Effects of
Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester on
Fluoxetine-Induced Hepatotoxicity: An
Experimental Study. BioMed research
international. 2016; 1247191.
. Hashem F, Motawea H, ElShabrawy A, El-Sherbini S, Shaker
K, Farrag A.Hepatoprotective activity
of Brassica oleraceae L. var. italica.
Planta Medica. 2013; 12: 177-185.
. Al-Howiriny T. Evaluation of
hepatoprotective activity of broccoli
‘Brassica oleracea’ in rats. Hungarian
Med. J. 2008; 2: 145-156.
. Al-Ghamdi MS. Protective effect of
Nigella sativa seeds against carbon
tetrachlorideinduced liver damage. Am.
J. Chin. Med. 2003; 31: 721-728.
. Eidi A, Mortazavi P, Bazargan M,
Zaringhalam J. Hepatoprotective
activity of cinnamon ethanolic extract
against CCL4-induced liver injury in
rats. EXCLI J. 2012; 11: 495-507.
. Soujanya S, Lakshman M, Kumar AA,
Reddy AG. Evaluation of the protective
role of vitamin C in imidaclopridinduced hepatotoxicity in male Albino
rats. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med.2013; 4: 63-
. Cordeiro LC, Kaliwal BB. Protective
role of bark extract of Bridelia retusa
Spreng on CCl4 induced histological
toxicity in mice. J. Pharmacognosy.
Phytochem. 2013; 2: 142-148.
. Althnaian T, Albokhadaim I, El-Bahr
SM. Biochemical and histopathological
study in rats intoxicated with carbon
tetrachloride and treated with camel
milk. Springer plus. 2013; 2:57.
. Abdel SO, Sleem AA, Shafee N. Effect
of trazodone and nefazodone on
hepatic injury induced by carbon
tetrachloride. Drug Discov. Ther. 2010;
: 285-297.