Effect of ethanol extracts from Shorea robusta (Dipterocapaceae) bark in paracetamol induced liver damage in rats
Keywords:
Shorea robosta, Hepatoprotective, Paracetamol, SilymarinAbstract
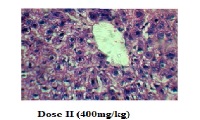
The Hepato protective Activity of the ethanol extract of Shorea robusta was investigated against paracetamol induced hepatic damage. Paracetamol at the dose of 3gm/ kg produced liver damages in rats manifested by the significant (p<0.0005) rise in the level of SGOT, SGPT, ALP, (159.3 ± 3.637; 143.1 ± 1.215; 347.6 ±15.42) compare to with respective control values (51.85 ± 1.527; 26.65 ± 1.095; 84 ± 9.824) respectively. Pre-treatment of rats with the plant extracts 200mg /kg, 400mg/kg and standard (Silymarin 50 mg/ kg) lowered significantly (p<0005) respective serum (SGOT to 92.06±2.473 & 73.97 ±; SGPT to 64.12 ± 2.27 & 45.22 ± 0; ALP to 7814; 195.8 ±13.22 & 168.00±10.16) respectively. It also shows in the reduction of cholesterol and total bilirubin respect to the paracetamol toxicity. In case of total protein paracetamol treated group decrease the total protein content, pre treatment with the plant extracts and silymarine there is an elevation of total protein contents. Histopathology of the liver cell shows less damages in the hepatic cell compare to the paracetamol treated group. On the basis of the investigation we may partially conclude that S.robusta can use to damage hepatic cell injury.
References
Mao A A, Hynniwta TM, Sanjappa M. Plant wealth of north east India with reference to ethnobotany. Indian journal of traditional knowledge. 2009; 8 (1): 96-103.
Kirtikar K R and Basu B D, Indian Medicinal Plant, Vol I, International Book Distributors, Book Seller and Publisher, 2005; 288-290.
Chatterjee A, Prakashi S C, The Treatise on Indian Medicinal Plant, vol II, Publication & Information Directorate, New Delhi, 199: 139.
Wani T A, Analgesic activity of the ethanolic extract of Shorea robusta resin in experimental animal, Indian journal of pharmacology. Indian journal of pharmacology. 2013; 44 (4): 493-498.
G. Jyothi et.al, Anti nociceptive and anti-inflammatory activity of methanolic extract of leaves of Shorea robusta, Pharmacology online, 2008; 1: 9-19.
Karthick C, Chitra M, Radhika K, Protective activity of Shorea robusta leaf against oxidative stress in rats. International journal of pharmaceutical science & research, 2013; 4(12): 4754-4757.
Wani T A , Wound healing activity of ethanolic extract of Shorea robusta gartan .f resin, Journal of experimental biology, 2012; 50: 277-281
Santosh kumar M, Anti ulcerogenic effects of resin from Shorea robusta gaertn.f on experimentally induced ulcer models, International journal pharmacy and pharmaceutical sciences, 2013; 5(1): 2013
Ibrahim M, Khaja M N and Aara A, Hepatoprtective activity of Sapindus mukorossi and Rhem emodi extract in vitro and in-vivo studies. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 2008; 14 (16): 2566-2571.
Arhoghro E M, Ekpo K E, Anosike E O and Ibeh G O, Effect of aqueous extract of bitter leaf (vernoniaamygdalina) on carbon tetra chloride induced liver damage in albino wistar rats, European Journal of. Scientific Research. 2009; 26 (1): 122-130.
Subramoniam et.al. Hepatoprotective Activity of Trichopuszeylanicus extract against Paracetamol Induced Damge in Rats. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology. 1998; 36: 385-389.
Harbone J B. Phyto chemical Methods: A guide to modern technique of plant analysis. 3rd ed. Springer (India) Private limited; 2005.
Rajasekaran A, Periyasamy M, Hepatoprotective effect of ethanolic extract of Trichosanthes lobata on paracetamol induced liver toxicity in rats, Chinese medicine, 2012; 7: 12.
Kokate C K, Practical Pharmacognosy, 4th ed. Vllabh Prakashan, Delhi, 1994.
Khandelwal K R, Practical pharmacognosy: techniques and experiments, 18th ed. Pune, Nirali Prakashan, 2007
Shenoy s et.al, Hepato protective activity of Plectranthus amboinicus against Paracetamol induced hepatotoxicity in rats. International journal of pharmacology and clinical science, 2012; 1(2): 32-38.
Basu S et.al, hepato protective activity of lichi chinensis leaves aganist paracetamol induced liver damage in rats, Ameriacan Eurasian journal of scientific research, 2012; 7 (2): 77- 81.
Porchezhian E et.al .Hepatoprotective activity of Abutilon indicum on experimental liver damage in rats. Phytomedicine, 2005; 12: 62- 64.
Bhakta T et.al. Hepatoprotective activity of Cassia fistula leaf extract. Phytomedicine 2001; 8 (3): 220- 224.
Ramchandrasetty S et.al, Hepatoprotective activity of Calotro pisprocera flower against paracetamol induced hepatic injury in rats. Fitoterapia 2007; 78: 451-454
Blamuruganvelu S et.al, Hepatoprotective activity of Polyalthi longifolia leaves against paracetamol induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Scholars journal of applied medical sciences, 2014; 2 (3A): 908-910.
Arun K. Biswas K and Ramchandrasetty S. Evaluation of the antioxidant and hepato protective acitivity of Madhuka longafolia (koening) leaves. International journal of research in pharmacy and biotechnology, 2013; 1(2): 191-196.
Roy S P et.al. Hepato protective activity of the methanolic extract of the Fagonia indica Burm in Carbon tetra chloride induced hepatotoxicity in albino rats. Asian Paefic journal of tropical bio medicine, 2012; 1457-1460.
Hegde K and Joshi A B, Hepato protective effect Carandus root extract against CCl4 and Paracetamol induced hepatic oxidative stress. Indian journal of experimental biology. 2009; 47: 660-667.
Feng Y et.al. Hepatoprotective effect of Berberine on carbon tetrachloride induced acute hepatotoxicity in rats. Chinese medicine. 2010; 5 (33): 1- 6.
Jafri M A et.al. Hepatoprotective activity of leaves of Cassia occidentalis against paracetamol and ethyl alcohol intoxication in rats, Journal of ethno pharmacology, 1999; 66: 355-361.
Vermeulen, N P E, Bessems JG M and Vandestreat, R. Drug Metabolism. Rev. 1992; 24: 367-407.
Handa S S and Sharma A, Hepatoprotective activity of andrographolide from Andrographis paniculata against CCl4. Indian Journal of Medicinal Research (B) 1990; 92: 276‐83.
Dixon M F, Nimmo J and Prescott L F, Experimental paracetamol induced hepatic necrosis: A histopathological study. J Pathol 1971; 03: 225-227.
Drotman R B, Lawhorn G T, Serum enzymes are indicators of chemical induced liver damage, Drug Chem Toxicol 1978; 1: 163- 171.
Molander D W, Wroblewsk F, La Due J S. Transaminase compared with cholinesterase and alkaline phosphatase an index of hepatocellular integrity, Clin Res Pro, 1955; 3: 20.