Studies on antimicrobial effect of natural dyes and pigments obtained from the leaf of Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. and Tectona grandis L.f.
Keywords:
Antimicrobial activity, Artocarpus hetphyllus Lam, Tectona grandis L.f., Silk fabric, Mordants, Disc diffusionAbstract
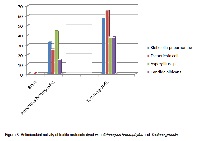
At present there is a renewed interest for value addition of textiles by using natural products. Many of the plant materials, from which natural dyes are obtained, also found to have some medicinal values. However, it is a matter of concern that the indigenous knowledge of extraction, processing and practice of using natural dyes has diminished to a great extent among the new generation of ethnic people due to easy availability of cheap synthetic dyes. In view of this, the present study was undertaken so as to revive and popularise the age-old art of dyeing with natural dyes. During the investigation dyeing materials were prepared from leaves of Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. (Jack fruit) and Tectona grandis L.f. (Teak). Silk fabrics were dyed with the extracted colouring materials and were estimated for their wash fastness to ensure the durability of the colour on the fabrics. Finally, the antimicrobial effect of the two different natural dyed fabrics was studied against Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, Candida albicans and Aspergillus sp. The dye prepared from leaves of Tectona grandis L.f. was found to be most effective by showing maximum zone of inhibition as compared to Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. The textile material impregnated with two natural dyes resulted in the maximum zone of inhibition rate (65%) against Escherichia coli as recorded in the silk samples dyed with Tectona grandis. It can be concluded that the natural dyes obtained from these two plants under study could provide special aesthetic values, which is not only environmentally friendly but gives added qualities to the textile production because of the antimicrobial potential of the dyes.
References
Padhy RN, Rathi D. Effect of mordants on dyeing of cotton with vegetable dyes. Text Dyer Printer. 1990; 23(25): 27-28.
Anitha K, Prasad SN. Developing multiple natural dyes from flower parts of Gulmohur. Current Science. 2007; 92(12): 1681-1682.
Allen RLM. Colour chemistry, Nelson, London. ISBN 1971; 978-0-177-61717-1.
Goodarzian H, Ekrami E. Evaluation of vat dye solubility using derivative spectrophotometry.World Applied Sciences Journal. 2010; 9(4): 434-436.
Kulkarni SS, Gokhale AV, Bodake UM et al. Cotton dyeing with Natural Dye Extracted from Pomegranate Peel. Universal Journal of Environmental Research and Technology. 2011; 1(2): 135-139.
Adeel S, Ali S, Bhatti I A et al. Dyeing of Cotton Fabric Using Pomegranate (Punica Granatum) Aqueous Extract. Asian J.Chem. 2009; 21(5): 3493-3499.
Vankar PS, Shankar R, Wijayapala S. Dyeing Cotton, Silk and Wool Yarn with Extract of Garnicia mangostana Pericarp. JTATM. 2009; 6(1).
Purwar R, Joshi M. Recent developments in antimicrobial finishing of textiles - a review. AATCC Review. 2004; 4(3): 22-25.
Gao Y, R. Cranston. Recent Advances in Antimicrobial Treatments of Textiles. Text. Res. J. 2008; 78(1): 60-72.
Pavlidou V. New Multifunctional Textiles: Antimicrobial Treatments, In "Proceedings of the Intelligent Textile Structures-Application, Production and Testing International Workshop" 2005; Thessaloniki, Qinguo F,X Hongxia, K Yong."Effect of UV Curable Pretreatments on the Color Quality of Inkjet Printed Polyester Fabrics". Research Journal of Textile and Apparel. 2008; 1:12.
Sahbha S Nodig, Rao S Gurumadhava. Effect of-an indigenous formulation of wound healing rat. Indian drug. 1993; 36(12): 731-734.
Fernando MR, Thabrie MI. Studies on the possible toxicity of Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. Cyllon journal of medical science. 1989; 32(1): 1-7.
S Krishna Mahesh, Nair A Jayakumaran. Anthraquinones from leaves of Tectona grandis: A detailed study on its antibacterial activity and other biological properties. International Journal of Phytomedicine. 2011; 3(1): 50-58.
Das Pijush Kanti, Mondal Amal Kumar. Biodiversity and Conservation of Some Dye Yielding Plants for Justification of its Economic status in the Local areas of Lateritic Zone of West Bengal, India. Advances in Bioresearch. 2012; 3(1): 43-53.