IN-VITRO NEPHROPROTECTIVE ROLE OF ETHANOLIC ROOT EXTRACT OF Boerhaavia diffusa AGAINST CISPLATIN-INDUCED NEPHROTOXICITY
Keywords:
Cisplatin, ROS, Oxidative stress, Nephroprotection, B.diffusaroot extractAbstract
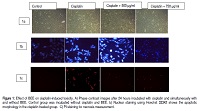
Context and purpose of the study: The present study was carried out to investigate the antioxidant and nephroprotective role of ethanolic root extract of Boerhaavia diffusa (ERE). Results: Antioxidant activity of ERE was studied using DPPH free radical scavenging activity, Nitric oxide scavenging activity and reducing power assay. To study the nephroprotective role of ERE against cisplatin, a porcine renal epithelial cell line (LLC-PK1) was used. Cisplatin increases the apoptotic and necrotic cells and also increases the production of ROS in the treated cells. Co-treatment of ERE decrease the apoptotic and necrotic cells and attenuates the ROS production. This nephroprotective activity could probably be correlated with the phytochemicals like polyphenols (4.5 ±0.02 mg/g), flavonoids (4.2 ±0.08 mg/g) and tannins (6.5 ±0.3 mg/g) present in the extract. Brief summary and potential implications: These findings suggested that toxicity induced by cisplatin could be reduced by the presence of phytoconstituents in the ERE. This study showed that phytoconstituents present in B.diffusa could manage the nephrotoxicity induced by life saving drugs and it can be considered to be given as an adjuvant therapy.
References
Delord JP, Puozzo,C., Lefresne,F., Bugat, R. Combination chemotherapy of vinorelbine and cisplatin:a phase I pharmacokinetic study in patients with metastatic solid tumors. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:553-60.
Kuhlmann MK, Burkhardt, G., Kohler, H. Insights into potential cellular mechanisms of cisplatin nephrotoxicity and their clinical application. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1997;12:2478-80.
Rooseboom M, Schaaf G, Commandeur JN, Vermeulen NP, Fink-Gremmels J. Beta-lyase-dependent attenuation of cisplatin-mediated toxicity by selenocysteine Se-conjugates in renal tubular cell lines. The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics. 2002;301(3):884-92. Epub 2002/05/23.
Jiang M, Wei Q, Pabla N, Dong G, Wang CY, Yang T, et al. Effects of hydroxyl radical scavenging on cisplatin-induced p53 activation, tubular cell apoptosis and nephrotoxicity. Biochemical pharmacology. 2007;73(9):1499-510. Epub 2007/02/13.
Joy J, Nair, C. K. Amelioration of cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in Swiss albino mice by Rubia cordifolia extract J Can Res Ther. 2008;4:111-5.
Shukla SK, Gupta S, Ojha SK, Sharma SB. Cardiovascular friendly natural products: a promising approach in the management of CVD. Natural product research. 2010;24(9):873-98. Epub 2010/05/13.
Jain GK, Khanna, N.M. Punarnavoside: a new anti-fibrinolytic agent from Boerhaavia diffusa Linn. Indian J Chem. 1989;28:163-6.
Akhter F, Hashima, A., Khan, M.S., Ahmada, S., Iqbal, D., Srivastava, A.K., Siddiqui, M.H. Antioxidant, α-amylase inhibitory and oxidative DNA damage protective property of Boerhaavia diffusa (Linn.) root. S Afr J Bot. 2013;88:265-72.
Mandeep K, Rajesh, K.G. Anti-Convulsant Activity of Boerhaavia diffusa: Plausible Role of Calcium Channel Antagonism. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011:7.
Shabbir M, Khan MR, Saeed N. Assessment of phytochemicals, antioxidant, anti-lipid peroxidation and anti-hemolytic activity of extract and various fractions of Maytenus royleanus leaves. BMC complementary and alternative medicine. 2013;13:143. Epub 2013/06/27.
Wolfe K, Wu X, Liu RH. Antioxidant activity of apple peels. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry. 2003;51(3):609-14. Epub 2003/01/23.
Quettier-Deleu C, Gressier B, Vasseur J, Dine T, Brunet C, Luyckx M, et al. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activities of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) hulls and flour. Journal of ethnopharmacology. 2000;72(1-2):35-42. Epub 2000/09/01.
Singleton VL, Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am J Enol Vitic 1965;16:144-58.
Koleva, II, van Beek TA, Linssen JP, de Groot A, Evstatieva LN. Screening of plant extracts for antioxidant activity: a comparative study on three testing methods. Phytochemical analysis : PCA. 2002;13(1):8-17. Epub 2002/03/20
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Analytical biochemistry. 1982;126(1):131-8. Epub 1982/10/01.
Periyar RRS, Toda, S., Kandasamy, M. Phytochemical screening and “in-vitro” anti-oxidant activity of methanolic root extract of Erythrina indica. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2012;2(3):1696-700.
Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. Journal of immunological methods. 1983;65(1-2):55-63. Epub 1983/12/16.
Yoshiko K, Munekazu, G. Cisplatin-induced renal injury in LLC-PK1 cells. AATEX Special Issue. 2007;14:453-6.
Elumalai P, Gunadharini DN, Senthilkumar K, Banudevi S, Arunkumar R, Benson CS, Sharmila G, Arunakaran J. Induction of apoptosis in human breast cancer cells by nimbolide through extrinsic and intrinsic pathway. Toxicol Lett. 2012; 215, 131-42
Jiang M, Pabla N, Murphy RF, Yang T, Yin XM, Degenhardt K, white E, Dong Z. Nutlin-3 protects kidney cells during cisplatin theraphy by suppressing Bax/Bak activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012; 282, 2636-45
Cummings BS, Schnellmann RG. Cisplatin-induced renal cell apoptosis: Caspase 3-dependent and -independent pathways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002; 302, 8-17
Potterat O. Antioxidants and free-radical scavengers of Natural Origin. Curr Org Chem. 1997;1:415-40.
Kannan RRR, Arumugam, R., Anantharaman, P. In vitro antioxidant activities of ethanol extract from Enhalus acoroides (L.F.) Royle. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2010:898-901.
Miller RP, Tadagavadi RK, Ramesh G, Reeves WB. Mechanisms of Cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Toxins. 2010;2(11):2490-518. Epub 2011/11/10.
Mohamed EM. Effect of Camel’s Milk on Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Swiss Albino Mice. Am J Biochem & Biotech. 2010;6(2):141-74.
Atasayar S, Gurer-Orhan H, Orhan H, Gurel B, Girgin G, Ozgunes H. Preventive effect of aminoguanidine compared to vitamin E and C on cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2009; 61, 23-32.
Gaedeke, J., Fels, L.M., Bokemeyer, C., Mengs, U., Stolte, H., Lentzen, H. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity and protection by silibinin. 1996; 11, 55-62.
Song J, Liu D, Feng L, Zhang Z, Jia X, Xiao W. Protective Effect of Standardized Extract of Ginkgo biloba against Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:846126. Epub 2013/12/29.