Protective Effect of aqueous bark extract of Terminalia Arjuna against Alcohol-Induced Hepato and Nephrotoxicity in Rats
Keywords:
Alcohol, Hepatotoxicity, Nephrotoxicity, Oxidative stress, Terminalia ArjunaAbstract
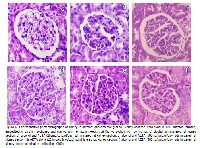
Present study is an attempt to forward a locally available aqueous bark powder extract of Terminalia arjuna (AETA) as potential therapeutic agent against alcohol-induced oxidative/nitrosative stress mediated hepato and nephrotoxicity in rats. Alcohol administration significantly raised the plasma concentrations of nitrogenous compounds and increased activities of alcoholic marker enzymes, gamma glutamyl transferase (γGT), plasma transaminases (AST and ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). Besides, we found abnormalities in the levels of plasma lipids, lipoproteins in alcohol administered rats along with increased lipid peroxidation and nitric oxide (NOx) levels. Moreover, significantly decreased hepatic and kidney antioxidant enzymes, superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and the content of reduced glutathione (GSH) in alcohol administered rats were noticed. Administration of AETA to alcoholic rats significantly brought these alterations in plasma to normal and also significantly reduced the levels of lipid peroxidation and restored the enzymic and nonenzymatic antioxidants in liver. These findings were further confirmed by hepatic and kidney histopathological studies. Co-administration of alcohol along with AETA offers protective effect against alcohol-induced stress and these protective effects are due to its multiple actions of its bioactive compounds.
References
Singal K, Ashwani, and Sarat C Jampana. Current Management of Alcoholic Liver Disease. Current drug abuse reviews 2014; 7(1): 18-28.
Kumar SD and Vasudevan DM. Alcohol induced effects on kidney. Indian J Clin Biochem 2008; 23: 4-9.
Ponnappa BC, Rubin E. Modeling alcohol's effects on organs in animal models. Alcohol Res Health 2000; 24: 93-104.
Zelickson, B. R., Benavides, G. A., Johnson, M. S., Chacko, B. K., Venkatraman, A., Landar, A., and Darley-Usmar, V. M.. Nitric oxide and hypoxia exacerbate alcohol-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in hepatocytes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics 2011; 1807(12): 1573-1582.
Reddy, VD, Padmavathi, P., Kavitha, G., Saradamma, B and Varadacharyulu, N. Alcohol-induced oxidative/nitrosative stress alters brain mitochondrial membrane properties. Molecular and cellular biochemistry 2013; 375(1-2): 39-47.
McCarty MF. Nutraceutical strategies for ameliorating the toxic effects of alcohol. Medical hypotheses 2013; 80: 456-462.
Seeff, Leonard B., Karen L. Lindsay, Bruce R. Bacon, Thomas F. Kresina, and Jay H. Hoofnagle. Complementary and alternative medicine in chronic liver disease. Hepatology 2001; 34(3): 595-603.
Dwivedi S. Terminalia arjuna Wight & Arn. A useful drug for cardiovascular disorders. J Ethnopharmacol 2007; 114: 114-129.
Khare CP Ed. Indian medicinal plants: an illustrated dictionary. Springer, New Delhi. 2007.
Tyagi P, Khan HA. Amelioration of oxidative stress in the joint tissue may be the basis for the antiarthritic activity of Terminalia arjuna bark extract. Int J Rheum Dis 2014- In Press.
Ghosh J, Sil PC. Arjunolic acid: A new multifunctional therapeutic promise of alternative medicine. Biochimie 2013; 95: 1098-1109.
Sultana B, Anwar F, Przybylski R. Antioxidant activity of phenolic components present in barks of Azadirachta indica, Terminalia arjuna, Acacia nilotica, and Eugenia jambolana Lam. trees. Food Chem 2007; 104:1106-1114.
Subramaniam, S., Ramachandran, S., Uthrapathi, S., Gnamanickam, V. R., and Dubey, G. P. Anti-hyperlipidemic and antioxidant potential of different fractions of Terminalia arjuna Roxb. bark against PX-407 induced hyperlipidemia. Indian journal of experimental biology 2011; 49(4), 282-288.
Kumar S, Singh AK, Verma S.K. Antibacterial and phyto-chemical analysis of some medicinal plants and their efficacy on multidrug resistant bacteria. J Pure Applied Microbiol 2013; 7: 2191-2204.
Ahmad, M. S, Ahmad, S, Gautam, B, Arshad, M and Afzal, M. Terminalia arjuna, a herbal remedy against environmental carcinogenicity: An in vitro and in vivo study. Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics 2014; 15(1): 61-67.
Sivalokanathan S, Ilayaraja M, Balasubramanian MP. Antioxidant activity of Terminalia arjuna bark extract on N-nitrosodiethylamine induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats. Mol Cell Biochem 2006; 281: 87-93.
Shukla SK, Sharma SB, Singh UR. Pre-treatment with α-tocopherol and Terminalia arjuna ameliorates, markers of inflammation, cardiac and apoptotic markers in experimental myocardial ischemic rats. Redox Report 2014- In Press
Halder, S., Bharal, N., Mediratta, P. K., Kaur, I., & Sharma, K. K.. Anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory and antinociceptive activity of Terminalia arjuna Roxb bark powder in mice and rats. Indian journal of experimental biology 2009; 47(7): 577.
Kapoor D, Vijayvergiya R, Dhawan V. Terminalia arjuna in coronary artery disease: Ethnopharmacology, pre-clinical, clinical & safety evaluation. J Ethnopharmacol 2014; 155: 1029-1045.
Gupta, Amit K., Manoj K. Rai, Mahendra Phulwaria, Tanvi Agarwal, and N. S. Shekhawat. "In vitro propagation, encapsulation, and genetic fidelity analysis of Terminalia arjuna: a cardioprotective medicinal tree. Applied biochemistry and biotechnology 2014; 173(6): 1481-1494.
Sinha M, Manna P, Sil PC. Aqueous extract of the bark of Terminalia arjuna plays a protective role against sodium-fluoride-induced hepatic and renal oxidative stress. J Nat Med 2007; 61: 251-260.
Manna, P., Sinha, M., and Sil, P. C. Aqueous extract of Terminalia arjuna prevents carbon tetrachloride induced hepatic and renal disorders. BMC complementary and alternative medicine 2006; 6(1): 33.
Vasanthi P, Parameswari CS. Aqueous extract of Terminalia arjuna prevents cyclosporine-induced renal disorders. Comp Clin Pathol 2014; 23: 583-588.
Devi, R. S, Narayan, S, Vani, G and Shyamala Devi, C. S. Gastroprotective effect of Terminalia arjuna bark on diclofenac sodium induced gastric ulcer. Chemico-biological interactions 2007; 167(1): 71-83.
Kumar, B., Vijayakumar, M., Govindarajan, R., & Pushpangadan, P. Ethnopharmacological approaches to wound healing—exploring medicinal plants of India. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2007; 114(2): 103-113.
Chaudhari M, Mengi S. Evaluation of phytoconstituents of Terminalia arjuna for wound healing activity in rats. Phytother Res 2006; 20: 799-805.
Reddy VD, Padmavathi P, Paramahamsa M and Varadacharyulu, N. Modulatory role of Emblica officinalis against alcohol induced biochemical and biophysical changes in rat erythrocyte membranes. Food Chem Toxicol 2009; 47: 1958-1963.
Raghavan B, Krishna Kumari S. Effect of Terminalia arjuna stem bark on antioxidant status in liver and kidney of alloxan diabetic rats. Ind J Physiol Pharmacol 2006; 50: 133-142.
Das, K., Chakraborty, P. P., Ghosh, D., and Nandi, D. K. Protective effect of aqueous extract of Terminalia arjuna against dehydrating induced oxidative stress and uremia in male rat. Iranian journal of pharmaceutical research 2010; 9(2): 153.
Fawcett JK, Scott J. A rapid and precise method for the determination of urea. J Clin Pathol 1960; 13: 156-159.
Caraway WT. Uric acid. Standard methods of clinical chemistry. 1963; 4: 239-247.
Laurence KM, Abbott AL. A micromethod for the estimation of serum bilirubin. J Clin Pathol 1956; 9: 270-273.
Owen, J. A., Betty Iggo, F. J. Scandrett, and C. P. Stewart. The determination of creatinine in plasma or serum, and in urine; a critical examination. Biochemical Journal 1954; 58(3): 426.
Reitman S, Frankel S. A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol 1957; 28: 56-63.
Tietz NW. Fundamentals of clinical chemistry, WB Saunders, Philadelphia 1976; 518-19.
Rosalki SB, Tarlow D. Optimized determination of γ-glutamyltransferase by reaction-rate analysis. Clin Chem 1974; 20: 1121-1124.
Allian CC, Poon LS, Chan CSG, Richmand W and Fu P. Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin Chem 1974; 20: 470-475.
Zlatkis A, Zak B, Boyle AJ. A new method for the direct determination of serum cholesterol. J Lab Clin Med 1953; 41: 486.
Fossati P, Prencipe L. Serum triglycerides determined colorimetrically with an enzyme that produces hydrogen peroxide. Clin Chem 1982; 28: 2077-2080.
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 1972; 18: 499-502.
Kumari K, Mathew BC, Augusti KT. Antidiabetic and hypolipidemic effects of S-methyl cysteine sulfoxide isolated from Allium cepa Linn. Ind J Biochem Biophys 1995.32: 49-54.
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 1979; 95: 351-358.
Sastry KVH, Modgal RP, Mohan J, Tyagi JS and Rao GS. Spectrophotometric determination of serum nitrite and nitrate by Copper - Cadmium alloy. Anal Biochem 2002; 306: 79-82.
Aebi H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymology 1984; 105: 121-126.
Kakkar P, Das B, Viswanathan PN. A modified spectrophotometric assay of superoxide dismutase. Ind J Biochem Biophys 1984; 21: 130-132.
Ellman GL. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 1959; 82: 70-77.
Lowry OH, Roseberough NJ, Farr AL and Ramdall R. Protein measurement with the Folin-phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 1951; 193: 263-275.
Wang Z, Yao T, Song Z. Chronic Alcohol Consumption Disrupted Cholesterol Homeostasis in Rats: Down‐Regulation of Low‐Density Lipoprotein Receptor and Enhancement of Cholesterol Biosynthesis Pathway in the Liver. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2010; 34: 471-478.
Das, S. K, Dhanya, L, Varadhan, S, Mukherjee, S and Vasudevan, D. M. Effects of chronic ethanol consumption in blood: a time dependent study on rat. Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry 2009; 24(3): 301-306.
Amanvermez, R, Ankarali, S, Tuncel, O. K, Tomak, L and Alvur, M. Effect of chronic high dose-alcohol consumption on the general biochemical parameters. Turkish Journal of Biochemistry 2009; 34(3): 113-120.
Rodrigo, Ramón, Cleofina Bosco, Patricia Herrera, and Gonzalo Rivera. Amelioration of myoglobinuric renal damage in rats by chronic exposure to flavonol-rich red wine. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2004; 19(9): 2237-2244.
Kwiterovich Jr PO. The metabolic pathways of high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein, and triglycerides: a current review. Am J Cardiol 2000; 86: 5-10.
Kim, E., Yang, J., Lee, H., Park, J. R., Hong, S. H., Woo, H. M. and Yang, S. R. γ-Glutamyl Transferase as an Early and Sensitive Marker in Ethanol-Induced Liver Injury of Rats. In Transplantation proceedings 2014; 46(4): 1180-1185.
Yuan, G., Al-Shali, K. Z., & Hegele, R. A. Hypertriglyceridemia: its etiology, effects and treatment. Canadian Medical Association Journal 2007; 176(8): 1113-1120.
Grauvogel, J., Daemmrich, T. D., Ryschich, E., Gebhard, M. M., & Werner, J. Chronic alcohol intake increases the severity of pancreatitis induced by acute alcohol administration, hyperlipidemia and pancreatic duct obstruction in rats. Pancreatology 2010; 10(5): 603-612.
Brinton, E. A., & Nanjee, M. N. Effects of ethanol intake on high density lipoprotein metabolism in humans. In High Density Lipoproteins, Dyslipidemia, and Coronary Heart Disease 2010: (129-138). Springer New York.
Shaila, H. P., Udupa, S. L., & Udupa, A. L. Hypolipidemic activity of three indigenous drugs in experimentally induced atherosclerosis. International journal of cardiology 1998; 67(2): 119-124.
Del Rio D, Stewart AJ and Pellegrini N. A review of recent studies on malondialdehyde as toxic molecule and biological marker of oxidative stress. Nutr Metabol Cardiovascu Dis 2005; 15: 316-328.
Niemela O. Distribution of ethanol-induced protein adducts in vivo: relationship to tissue injury. Free Radic Biol Med 2001; 31: 1533-1538.
Tuma, J and Casey, CA. Dangerous byproducts of alcohol breakdown-focus on adducts. Alcohol Research and Health 2003; 27: 285-290.
Zhang, A., Sun, H., & Wang, X. Recent advances in natural products from plants for treatment of liver diseases. European journal of medicinal chemistry 2013; 63: 570-577.
Masella, Roberta, Roberta Di Benedetto, Rosaria Varì, Carmela Filesi, and Claudio Giovannini. Novel mechanisms of natural antioxidant compounds in biological systems: involvement of glutathione and glutathione-related enzymes. The Journal of nutritional biochemistry 2005; 16(10): 577-586.