In vitro and In vivo study on the effect of Scoparia Dulcis in inhibiting the growth of urinary crystals.
Keywords:
Urolithiasis, Scoparia Dulcis, Natural crystal growth, Western Ghats, tribal medicineAbstract
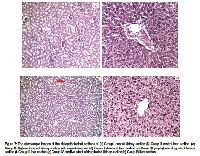
Urolithiasis is a very common and highly recurring painful disease both in developing and developed nations due to the change in lifestyle and food habits. Scoparia Dulcis is herbal plant which has been used as a traditional medicine for dissolving urinary stones by the tribal group of people in Western Ghats, India. This experimental study gives a scientific awareness about the effect of Scoparia Dulcis in dissolving the urinary crystals and will confirm the drug’s effect on the organs like kidney and liver. The invitro testing was done by developing urinary crystals using single diffusion gel growth technique and the water extract of the drug is incorporated to monitor the growth of the crystal. The statistical analysis was done for the in vitro study and has proved 2ml dosage shows the highest significance in variation. In invivo testing, the urinary crystals were induced in Wistar Rats and the drug was fed to monitor its effect on the growth of crystals as well as on nearby organs. The urine and serum samples were tested for all the group of rats and parameters analysis proved the significance of the drug. The histopathology analysis gives the sectional view and report of diseased and treated groups. In both the invitro as well as invivo testing, the drug showed a significant effect in inhibiting the growth of urinary crystals.
References
. Menon M.D, Parulkar B.G, Drach G.W. Campbell’s Urology, seventh ed.W.B. Saunders Company. New York; 1988.
. Pak C.Y.C. Kidney stones. Lancet 1998; 351: 1797-1801.
. Kok D. J. Modulation of calcium oxalate monohydrate crystallization kinetics in vitro. Endocrin Metab Clin 2002; 31:855-867.
. Chow S.Y, Chen S.M, Yang C.M, Hsu H. Pharmacological studies on china herbs [I] Hypotensive effect of 30 chinese herbs. J Formosan Med Assoc 1974; 73: 729-739.
. Manjula K, Rajendran K, Eevera T, Kumaran S. Effect of Costus igneus stem extract on calcium oxalate urolithiasis in albino rats. Urol Res 2012; 40: 499–510.
. Viel T.A, Domingos C.D, Monteiro A.P.S, Lima-Landman M.T.R, Lapa A.J, Souccar C. Evaluation of the antiurolithiatic activity of the extract of Costus Spiralis Roscoe in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 1999; 66: 193–198.
. Grases F, Ramis M, Costa-Bauz A, March J. G. Effect of Herniaria hirsuta and Agropyron repens on calcium oxalate urolithiasis risk in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 1995; 45: 211-214.
. Bayir Y, Halici Y, Kelesc M. S, Colakd S, Cakire A, Kayad Y, Akcay F. Helichrysum plicatum DC. subsp. plicatum extract as a preventive agent in experimentally induced urolithiasis model. J Ethnopharmacol 2011;138: 408– 414.
. Aggarwal A, Tandon S, Singla S. K, Tandon C. Diminution of Oxalate Induced Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Injury and Inhibition of Calcium Oxalate Crystallization in vitro by Aqueous Extract of Tribulus terrestris. Int Brazil J Urol 2010; 36: 480-489.
. Lin W.C, Lai M.T, Chen H.T, Ho C.Y, Man K.M, Shen J.L, Lee Y.J, Tsai F.J, Chen Y.H, Chen W.C. Protective effect of Flos carthami extract against ethylene glycol-induced urolithiasis in rats. Urol Res 2012; 40: 665- 661.
. Freire S.M.F, Emim A.J.S, Lapa A.J, Souccar C, Torres L.M.B. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties of Scoparia dulcis L. extract and glutinol in rodents. Phytother Res 1993; 7: 408-414.
. Hayashi T, Kawaski M, Miwa Y, Taga T, Morita N. Antiviral agents of plant origin III. Scopadulin, a novel tetracyclic diterpene from Scoparia dulcis L. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 1990; 38: 945-947.
. Hayashi T, Asano S, Mizutani M, Takeguchi N, Okamura K, Morita N. Scopadulciol, an inhibitor of gastric H+, K+ – ATPase from Scoparia dulcis and its structure activity relationships. J Nat Prod 1991; 54: 802-809.
. Hayashi T, Okamura K, Tamada Y, Iida A., Fujita T, Morita N. A new chemotype of Scoparia dulcis. Phytochemistry 1993; 33: 349-352.
. Chauhan C.K, Joshi M.J, Vaidya A.D.B. Growth inhibition of struvite crystals by the aqueous root extract of Rotula aquatic. Indian J Biochem Bio 2011; 48: 201-207.
. Griffith D.P. Struvite. Kidney Int 1978; 13: 372-382.
. Coe F.L, Parks J.H, Asplin J.R. Medical process: The pathogenesis and the treatment of kidney stones.The New Eng J Med 1992; 327: 1141-1152.
. Hesse A and Heimbach D. Causes of phosphate stone formation and the importance of metaphylaxis by urinary acidification: a review. World J Urol 1999; 17: 308-315.
. Takasake E. The neurotoxicity of drugs. Urology Int 1975; 30: 585- 587.
. Lyon E.S, Borden T.A, Vermeulen C.W. Experimental oxalate lithiosis produced with ethylene glycol. Invest Urol 1966; 4: 143-151.
. Ahmed M, Shikha H.A, Sadhu S.K, Rahman M.T, Datta B.K. Analgesic, diuretic and anti-inflammatory principle from Scoparia Dulcis. Die Pharmazie 2001; 56: 57-60.
. Rushton H.G and Spector M. Effects of magnesium deficiency on intratubular calcium oalate formation and crystalluria in Hyperoxaluric rats. J Urology. 1982; 127: 598-602.
. Selvam G.S and Varalakshmi P. Effect of different isomers of tartarate on oxalate metabolism in Hyperoxaluric rats. Med Sci Res. 1989; 17: 685-689.