COMPARATIVE IN VIVO STUDY OF TWO DIFFERENT ROUTES: ORAL AND TRANSCRANIAL FOR THE EFFECT OF POLYPHYTO NOOTROPIC FORMULATION FOR ITS MEMORY ENHANCING PROPERTIES
Keywords:
Medhya or Intelligence, Improving Learning and memory, Transcranial application, Pole climbing test for memory, Elevated Plus maze test of memoryAbstract
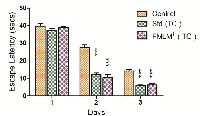
The present study objective is to comparing the effectiveness of the medhya (polyphyto) formulations for its learning and memory activity in two different routes oral and transcranial;could be delivered and targeted to the brain by transcranial delivery route. The unique anatomical arrangement of blood vessels and sinuses in the human skull and the brain, the prevalence of a high density of skin appendages in the scalp, extra cranial vessels of the scalp communicating with the brain via emissary veins and most importantly, the way that the scalp is used in the Ayurvedic medical system in treating diseases associated with the brain show that a drug could be transcranially delivered and targeted to the brain through the scalp. The medhya formulation FMLM; compose of Bacopa monnieri (51.8%), Oscimum sanctum (26.7 %), and Withania somnifera (21.5%) on memory acquisition and retention was studied using Elevated plus maze, Morris water maze (MWM) and Pole Climbing apparatus (PCA) in rat using two different routes, one is per oral (FMLMO) and other one is transcranial (FMLMT). As per the result, on administration of polyherbal formulations FMLMO and FMLMT showed significant (p<0.01) reduction in transfer latency in EPM, MWM and escape latency in PCA test as compared with the control per oral as well as transcranial delivery; whereas trancranially applied FMLMT is equally effective in comparison to standard drug but it is shown an extremely significant (p<0.001) effect compared to control group
References
Mesulam M-M. (2000) In: Principles of behavioral and cognitive neurology, II Edn, Oxford University Press: New York.
Budson AE, Price BH. The New Eng. J. Med. 2005; 352: 692-699.
Ayurvedic Herbs Information. 2014. http://www.holistic-herbalist.com/ayurvedic-herbsinformation. html Accessed on July 24, 2014.
Dhawan, B.N., Singh, H.K., Pharmacology of Ayurvedic nootropic Bacopa monniera. International Convention of Biology and Psychiatry, Bombay, India 1996; Abstract no. 59.
Warrier, P.K., Nambiar, V.P.K., Ramankutty, C. Indian Medicinal Plants. Orient Longman, Chennai, India. 1996; 235-239.
Bone, K., Clinical Applications of Ayurvedic and Chinese herbs: Monographs for the Western Herbal Practitioner. Phytotherapy Press, Warwick, Queensland, Australia, 1996; 137-141.
Singh, H.K., Dhawan, B.N., Neuropsychopharmacological effects of the Ayurvedic nootropic Bacopa monniera Linn. (Brahmi). Indian J. Pharmacol. 1997; 29, 359-365.
Das, A., Shanker, G., Nath, C., Pal, R., Singh, S., Singh, H., A comparative study in rodents of standardized extracts of Bacopa monniera and Ginkgo biloba. Anticholinesterase and cognitive enhancing activities. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002; 73, 893-900.
Roodenrys, S., Booth, D., Bulzoni, S., Phipps, A., Micallef, C., Smoker, J., Chronic effects of Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri) on human memory. Neuropsychopharmacology 2002; 27, 279-281.
Holcomb LA, Dhanasekaran M, Hill AR, Young KA, Rigs M, Manyam BV. Alzheimer’s Disease. 2006; 9: 243-241.
Hanumanthachar Joshi & Milind Parle, Evaluation of nootropic potential of Ocimum sanctum Linn. in mice, Indian Journal of Experimental Biology 2006 Feb; 44:133-136
Godhwani S, Godhwani J L & Vyas D S, Oscimum sanctum: An experimental study evaluating its anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activity in animals, J Ethnopharmacol, 1987; 21: 153.
Kelm M A, Nair M G, Stasburg G M & Dewitt D L, Antioxidant and cyclooxygenase inhibitory phenolic compounds from Oscimum sanctum Linn., Phytomedicine, 2000; 7 : 7.
Bhattacharya S K, Bhattacharya A, Das K, Muruganandam A V & Sairam K, Further investigation on the antioxidant activity of Ocimum sanctum using different paradigms of oxidative stress in rats, J Nat Rem, 2001;1: 5.
Maity T K, Mandal S C, Saha B P & Pal M, Effect of Ocimum sanctum roots extract on swimming performance in mice, Phytother Res, 2000; 14 : 120.
G. Singh*, P. K. Sharma, R. Dudhe and S. Singh, Biological activities of Withania somnifera, Annals of Biological Research, 2010, 1 (3): 56-63.
Schliebs R, Liebmann A, Bhattacharya SK, et al. Systemic administration of defined extracts from Withania somnifera (Indian Ginseng) and Shilajit differentially affects cholinergic but not glutamatergic and GABAergic markers in rat brain. Neurochem Int 1997; 30:181-190.
Vayaskara, N.S.M., Eds., In; Ayurvedic treatment of Kerala, 3rd edn., Vaidyasarathy Press (P) Ltd., Kottayam 1983, 29.
Dash VB. Massage therapy in Ayurveda, Pancakarma therapy of Ayurveda. New Delhi: Concept Publishing Company, 1992; Series no.1.
Gabella G. Cardiovascular System. In: Williams PL, editor. Grays Anatomy. 38th Ed. The Anatomical Basis of Medicine and Surgery. New York: Churchill Livingstone 1995; 1589.
Lorke D. A new approach to practical acute toxicity testing. Arch Toxicol. 1983; 54 (4): 275-287.
Itoh J, Nabeshima T, Kameyama T. Utility of an elevated plus-maze for the evaluation of memory in mice: effects of nootropics, scopolamine and electroconvulsive shock. Psychopharmacology. 1990;101(1):27–33.
Itoh J, Nabeshima T, Kameyama T. Utility of elevated plus-maze for dissociation of amnesic and behavioral effects of drug in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 ;194:71–76
Shib N. Kamila, N. V. Satheesh Madhav, C. N. Sarkar, Evaluation of effective formulation on transcranial treatment on rat. IJBR 2014; 05 (06): 427-431
Morris, R.G.M. "Spatial localization does not require the presence of local cues". Learning and Motivation 1981 May; 2 (2): 239–260.
Cook L, Weidley E. Behavioral effects of some psychopharmacological agents. Ann N Y AcadSci 1957 Mar 14;66 (3): 740-52.
Soman I, Mengi SA, Kasture SB. Effect of leaves of Buteafrondosa on stress, anxiety, and cognition in rats. Pharmacol BiochemBehav 2004 Sep; 79 (1): 11-6.
Gabella G. Cardiovascular System. In: Williams PL, editor. Grays Anatomy. The Anatomical Basis of Medicine and Surgery. 38th Ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone 1995; 1589.
Reddy DS. Assesment of nootropic and amnestic activity of centrally acting agents. Ind. J. Pharmacol. 1997; 29:208-221.