Ethnobotanical studies on some wild plants of head Qadirabad and adjoining areas, Pakistan
Keywords:
Ethnobotany, Qadirabad, Pteridophyte, Papilionaceae, Piles, constipationAbstract
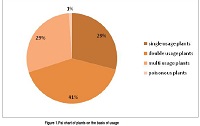
An Ethno botanical survey was carried out during 2011-2012 in order to document the importance of the plants in Qadirabad, Tehsile Phalia and District Mandi Bahauddin, Punjab, Pakistan. A total of 54 plants were collected belonging to 29 families, from which 50 were dicots and 4 were monocots, 28 families were angiosperms and only 1 was Pteridophyte. Papilionaceae was the dominant family. The plant species collected from the studied area and were identified with flora of Pakistan. Plants were categorized in single usage plants, two usage plants, and multi usage plants. It was observed that mostly plants were used for treatment of different kinds of diseases like stomachic diseases, Piles, constipation; bleeding wounds, snake bite etc. Cutting of trees for earning livelihood were common. It was also observed during this study, that harvesting of the plants is very common for local uses
References
. Pei S. Ethno botany and sustainable use
of plant resources in the HKH mountain
region, Punjab workshop on ethno botany
and its application to conservation and
community Development in the Hindu
kush Himalayan HKH region, Nepal,
Punjab, Pakistan. Biol Conser 1995; 63:
-210.
. Schultes RE. Ethnobotany and
technology in the Northwest Amazon: A
partnership. In Sustainableharvest and
marketing of rain forest products, Eds.
Plotkin and Famolare, Island Press, CA,
pp: 45-76
. Shanmugam SG, Muthuraja M, Annadurai
M, Dhanasekaran GS and Gobinathan S:
Ethnobotanical studies on the plants used
for the preparation of baskets and ropes
by Paliyar tribes of pachalur in Dindigul
District of Tamil Nadu, India. Life sciences
leaflets 2012; 4:27-30
. Singh A and Dubey NK : An
ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants in
Sonebhadra District of Uttar, Pradesh,
India with reference to their infection by
foliar fungi.Journal of Medicinal Plants
Research 2012; 6: 2727-2746
. Taj S, Wazir SW, Subhan M, Hassan H,
Khan SU and Kamal M: Some of the
ethnobotanically important plants of Godi
Khel and its outskirts hilly areas, District
Karak, Pakistan Pak J Pl Sci 2012; 15: 39-
. Ekka RN and Dixit VK:
Ethnopharmacognostical studies of
medicinal plants of Jashpur District,
Chattisgarh Int. J. Green Phar 2007; 1: 2-
. Majeed AK, Shaukat M, Javed S and R.
Ilyas: Middle-East Journal of Scientific
Research 2011; 7: 397-400
. Nasir E, Ali SI. Flora of West Pakistan
and Kashmir. Pakistan Agriculture
Research Council, Islamabad 1970-1995
. Ali SI and Qaisar M: Flora of Pakistan.
Botany Department, University of Karachi,
Karachi 1995-2005
. Sher H and Hussain F: Ethnobotanical
Evaluation of Some Plant Resources in
Northern part of Pakistan. African journal
of Biotechnology 2007; 817: 4066-4076.
. Jan GK, Gul GM, Ahmad F, Jan M
and Zafar M: Ethnobotanical Studyof
Common Weeds of Dir Kohistan Valley,
Khyber Pakhtoonkhwa, Pakistan. 2010
Pak J Weed Sci Res;