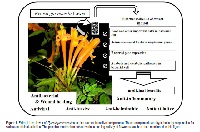
Phytochemistry and pharmacology of Pyrostegia venusta: a plant of Family Bignoniaceae
Keywords:
Pyrostegia venusta, phytomedicine, phytoconstituent, phytotherapyAbstract
Worldwide over 80% population have dependence on natural resources (esp. plants) for treatment of disease, either due to drug resistance diseases or side effects of synthetic drugs. Hence, in recent years, ethano-medicinal studies have been acknowledged to evaluate plants products in modern scientific lines of phytochemical analysis, pharmacological screening and clinical trials. This review provides information on the botanical description, traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology of one such important plant, Pyrostegia venusta. That has folkare tradition of medicinal use.
References
Blatt CTT, Santos MD, Salatino A (1998). Flavonoids of Bignoniaceae from "cerrado" and their possible taxonomic significance. Plant Syst Evol, 210: 289-292.
URL: http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00985673
Dantzer R (2009). Cytokine, Sickness Behavior and Depression. Immunol Allergy Clin, 29:247-264.
URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2740752/
De Paiva VN, Lima SNP, Fernandes MM, Soncini R, Andrade CA, Giusti-Paiva, A (2010). Prostaglandins mediate depressive-like behaviour induced by endotoxin in mice. Behav Brain Res, 215: 46-151
URL: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166432810005164
Dubey R, Misra KJ (1976). Chemical components of Pyrostegia venusta flowers. J Indian Chem Soc, 53: 378-381.
Ferreira DT, Alvares PS, Houghton PJ, Braz-Filho R (2000). Chemical constituents from roots of Pyrostegia venusta and considerations about its medicinal importance. Química Nova, 23:42-46.
URL: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?pid=S0100-40422000000100010&script=sci_arttext
Gupta MB, Nath R, Srivastava N, Shanker K, Kishor K, Bhargava KP (1980). Anti-inflammatory and antipyretic activities of beta-sitosterol. Planta Med, 39: 157-163
URL: https://www.thieme-connect.com/DOI/DOI?10.1055/s-2008-1074919
Harbone JB (1967). Comparative biochemistry of the flavonoids VI Flavonoid patterns in the Bignoniaceae and Gesneriaceae. Phytochemistry, 6: 1646-1651
URL: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031942200828976
Lima LA, Siani AC, Brito FA, Sampaio ALF, Henriques MGMO, Riehl CAS (2007). Correlation of anti-inflammatory activity with phenolic content in the leaves of Syzygium cumini (L) Skeels (Myrtaceae). Quim Nova, 30:860-864
URL: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?pid=s0100-40422007000400019&script=sci_arttext
Magalhães EA, Silva Jr GJ, de Campos TA, Silva LP, Silva RMG (2010). The Evaluation of the genotoxic potency of the Pyrostegia venusta (Ker Gawl) Miers, Bignoneaceae, crude extract on bone marrow of mice. Rev bras farmacogn 20(1): 65-69
URL: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?pid=S0102-695X2010000100014&script=sci_abstract
Mertz PM, Ovington LG (1993). Wound healing microbiology. Dermatol Clin 11(4):739-747.
URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8222357
Moreira CG, Horinouchi CD, Souza-Filho CS, Campos FR, Barison A, Cabrini DA, Otuki MF (2012). Hyperpigmentant activity of leaves and flowers extracts of Pyrostegia venusta on murine B16F10 melanoma. J Ethnopharmacol 141(3):1005-1011.
URL: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378874112002097
Ndayisenga I (2011). Pyrostegia venusta ker Gwal Miers. In Thesis: Butare city ornamental plant taxonomy and phytogeography; Submitted for the award of Bachelor’s degree in Biology in University of Rwanda
URL: http://www.biology.nur.ac.rw/IMG/pdf/Ndayisenga_I_2011.pdf
Nisha PV, Shruti N, Sweta Swamy K, Kumari M, Vedamurthy A B, Krishna V, Hoskeri JH (2012). Anthelmintic activity of Pyrostegia venusta using Pheretima posthuma. Int J Pharma Sci Drug Res 4(3): 205-208.
URL: http://www.ijpsdr.com/pdf/vol4-issue3/7.pdf
Pan MH, Hsieh MC, Hsu PC, Ho SY, Lai CS, Wu H, Sang S, Ho CT (2008). 6-Shogaol suppressed lipopolysaccharide-induced up-expression of iNOS and COX-2 in murine macrophages. Mol Nutr Food Res 52(12):1467-77.
Pan MH, Lai CS, Wang YJ, Ho CT (2006). Acacetin suppressed LPS-induced up expression of iNOS and COX-2 in murine macrophages and TPA-induced tumor promotion in mice. Biochem Pharmacol 72: 1293-1303.
URL: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006295206004795
Roy P, Amdekar S, Kumar A, and Singh V (2011). Preliminary study of the antioxidant properties of flowers and roots of Pyrostegia venusta (Ker Gawl) Miers. BMC Complement Altern Med 11: article 69, 2011.
URL: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6882/11/69
Roy P, Amdekar S, Kumar A, Singh R, Sharma P, Singh V (2012). In vivo antioxidative property, antimicrobial and wound healing activity of flower extracts of Pyrostegia venusta (Ker Gawl) Miers. J Ethnopharmacol 140(1):186-92
URL: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378874112000098
Scalon SP, Vieira MC, Lima AA, Souza CM, Mussury RM (2008). Pregerminative treatments and incubation temperatures on the germination of “cipóde- São-João” (Pyrostegia venusta (Ker Gawl) Miers)-Bignoniaceae. Rev bras plantas med 10:37-42.
Shen KH, Hung SH, Yin LT, Huang CS, Chao CH, Liu CL, Shih YW (2010). Acacetin, a flavonoid, inhibits thein vasion and migration of human prostate cancer DU145 cells via inactivation of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 333: 279-291.
URL: http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11010-009-0229-8
Silva RMG , Rodrigues DTM, Augustos FS, Valadares F, Neto PO, dos Santos L, Silva LP (2012). Antitumor and cytotoxic activity of Kielmeyera coriacea mart Zucc and Pyrostegia venusta (ker-gawl) Miers extracts. J Med Plants Res, 6(24):4142-4148.
http://www.academicjournals.org/jmpr/pdf/pdf2012/28June/Silva%20et%20al.pdf
Singh S, Rana A and Chauhan SVS (2009). Impact of environmental changes on the reproductive biology in Pyrostegia venusta Presl. J Environ Biol 30(2): 271-273.
URL: http://www.jeb.co.in/journal_issues/200903_mar09/paper_19.pdf
Veloso CC, Bitencourta AD, Cabral LD, Franqui LS, Dias DF, dos Santos MH, Soncini R, Giusti-Paiva A (2010). Pyrostegia venusta attenuate the sickness behavior induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 132:355-358.
URL: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378874110005465