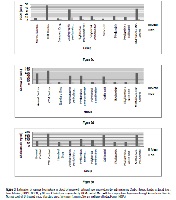
Varying influence on different biomarkers related to hepato-recovery events in liver-injured rats when treated with extracts of Andrographis paniculata, Phyllanthus amarus or their active principles individually and in combination.
Keywords:
Hepatoprotective, phytochemicals, Andrographis, Phyllanthus, liverAbstract
Water extracts of Phyllanthus amarus and Andrographis paniculata were used individually and in combination to investigate their hepato-recovery potential using carbon tetrachloride-treated, liver injured albino wistar rats. Toxicity study performed in female swiss albino mice was found to be satisfactory. HTPLC analysis revealed presence of andrographolide in A. paniculata and phyllanthin as well as gallic acid in P. amarus extracts. Histology analysis indicated extensive injury to liver tissue in experimental rats. Efficacy of polyherbal combination was less compared to individual extracts in reducing bilirubin concentration. SGPT and SGOT reduction by polyherbal combination was found to be similar to that of individual extracts. Co administration of extracts from both plants exhibited maximum reduction in γ GT concentration. However, polyherbal combination was not found to have any significant effect in reducing blood cholesterol when compared to individual extracts. Gallic acid, a component of P. amarus when used in pure form, was found to play significant role in reducing most liver biomarkers when compared to phyllanthin, the other active component of P. amarus. However, the latter was found to be more effective in reducing blood cholesterol compared to gallic acid. We concluded that polyherbal combination of A. paniculata and P. amarus does not always present a uniform, beneficial effect in cases of liver injury when monitored by several biomarkers. Further, gallic acid was found to be an equally important constituent of P. amarus extract along with phyllanthin in affecting hepato-protective activity in albino wistar rats.
References
harma A., Chakraborti KK., Handa SS. Anti-hepatotoxic activity of some Indian herbal formulations as compared to silymarin. Fitoterapia. 1991;62:229-235.
Subramonium A, Pushpangadan P. Development of Phytomedicines for liver diseases. Indian J Pharmacology. 1999;31:166-175.
Teoh NC, Chittun S, Farrell GC. Drug-induced hepatitis. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. Saunders Elsevier. 2010:chap 86.
Wedemeyer H, Pawlotsky JM. Acute viral hepatitis. Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Cecil Medicine. 24th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier; 2011:chap 150.
O'Shea RS, Dasarathy S, McCullough AJ. "Alcoholic liver disease." AASLD Practice Guidelines. 2010;51(1):307–28.
Lefkowitch JH. Morphology of alcoholic liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2005;9:37-53.
Mathurin P, Beuzin F, Louvet A, Carrie GN, Balian A, Trinchet JC, et al. Fibrosis progression occurs in a subgroup of heavy drinkers with typical histological features. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;25:1047-1054.
Longstreth GF, Zieve David. "Alcoholic Liver Disease". MedLinePlus: Trusted Health Information for You. Bethesda, MD: US National Library of Medicine & National Institutes of Health. 2009
Menon KV, Gores GJ, Shah VH. "Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of alcoholic liver disease" (PDF). Mayo Clin. Proc.2001;76 (10):1021–9.
Christensen E. Alcoholic hepatitis—glucocorticosteroids or not? J Hepatol. 2002;36:547-548.
Raetsch C, Jia JD, Boigk G, Bauer M, Hahn EG, Riecken EO et al. Pentoxifylline downregulates profibrogenic cytokines and procollagen I expression in rat secondary biliary fibrosis. Gut. 2005;50:241-247.
Bruce JD, Paul JE, and Arthur BP. Phase I Trial of Escalating Pentoxifylline Dose with Constant Dose Thiotepa. Cancer Res, 1990;50:6806.
Lucena MI, Andrade RJ, Cruz JP, Rodriguez MM, Blanco E and Sanchez de la Cuesta F. Effects of silymarin MZ-80 on oxidative stress in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. Results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2002;40:2-8.
Pares A, Planas R, Torres M, Caballeria J, Viver JM, Acero D et al. Effects of silymarin in alcoholic patients with cirrhosis of the liver: results of a controlled, double-blind, randomized and multicenter trial. J Hepatol. 1998;28:615-621.
Lee TD, Sadda MR, Mendler MH, Bottiglieri T, Kanel, G, Mato JM. Abnormal hepatic methionine and glutathione metabolism in patients with alcoholic hepatitis. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2004;28:173-181.
Lieber CS. S-Adenosyl-L-methionine and alcoholic liver disease in animal models: implications for early intervention in human beings. Alcohol. 2005;27:173-177.
Rambaldi A, Jacobs BP and Gluud C. Milk thistle for alcoholic and/or hepatitis B or C virus liver diseases. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4: CD003620. 2007.
Purohit V, Abdelmalek MF, Barve S, Benevenga NJ, Halsted CH, Kaplowitz N. et al. Role of S-adenosylmethionine, folate, and betaine in the treatment of alcoholic liver disease: summary of a symposium. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:14-24.
Kharbanda KK. Alcoholic liver disease and methionine metabolism. Semin Liver Dis. 2009;29: 155-165.
Kim SJ, Jung YS, Kwon Y, Kim YC. Alleviation of acute ethanol-induced liver injury and impaired metabolomics of S-containing substances by betaine supplementation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;368:893-898.
Craig SS. Betaine in human nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;80(3):539-549.
Preedy VR, Gove CD, Panos MZ, Sherwood R, Portmann B, Williams R, Peters TJ. Liver histology, blood biochemistry and RNA, DNA and subcellular protein composition of various skeletal muscles of rats with experimental cirrhosis: implications for alcoholic muscle disease. Alcohol Alcohol. 1990;25(6):641-649.
Kathriarachchi H, Hoffmann P, Samuel R, Wurdack KJ, Chase MW. "Molecular phylogenetics of Phyllanthaceae inferred from five genes (plastid atpB, matK, 3'ndhF, rbcL, and nuclear PHYC)". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 2005;36(1):112–34.
Burgos RA., Hancke JL., Bertoglio JC., Aguirre V, Arriagada S., Calvo M, Cáceres DD. "Efficacy of an Andrographis paniculata composition for the relief of rheumatoid arthritis symptoms: A prospective randomized placebo-controlled trial" Clinical Rheumatology. 2009;28:8
Patel, Jay Ram; Tripathi, Priyanka; Sharma, Vikas; Chauhan, Nagendra Singh; Dixit, Vinod Kumar (2011). "Phyllanthus amarus: Ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology: A review". Journal of Ethnopharmacology 138 (2): 286–313.
Trivedi NP, Rawal UM. Effect of aqueous extract of Andrographis paniculata on liver tumor. Indian J Pharmacol 1998;30:318-22.
Handa SS, Sharma A. Hepatoprotective activity of andrographolide from Andrographis paniculata against carbontetrachloride. Indian J Med Res. 1990;92:276-283.
Trivedi NP, Rawal UM, Patel BP. Hepatoprotective effect of andrographolide against hexachlorocyclohexane-induced oxidative injury. Integr Cancer Ther. 2007;6(3):271-80.
Pramyothin P, Ngamtin C, Poungshompoo S, Chaichantipyuth C. Hepatoprotective activity of Phyllanthus amarus Schum. et. Thonn. extract in ethanol treated rats: in vitro and in vivo studies. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007;114(2):169-73.
Dhalwal K, Biradar YS, Rajani M. High-performance thin-layer chromatography densitometric method for simultaneous quantitation of phyllanthin, hypophyllanthin, gallic acid, and ellagic acid in Phyllanthus amarus. J AOAC Int. 2006;89(3):619-623.
Ogwal-Okeng JW, Celestino O and William WA. Acute toxicity effects of the methanolic extract of Fagara zanthoxyloides (Lam.) root-bark Afr Health Sci. 2003;3(3):124–126.
Srivastava A, Misra H, Verma RK, Gupta MM. Chemical fingerprinting of Andrographis paniculata using HPLC, HPTLC and densitometry. Phytochem Anal. 2004;15(5):280-5.
Das SK, Vasudevan DM. Protective effects of silymarin, a milk thistle (Silybium marianum) derivative on ethanol-induced oxidative stress in liver. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 2006;43(5):306-311.
Kamisako T, Yoshinao K, Keisuke T, Tomoaki I, Kunihiro H, Yuji T, Esteban CG, Yukihiko A. Recent advances in bilirubin metabolism research: the molecular mechanism of hepatocyte bilirubin transport and its clinical relevance. Journal of Gastroenterology. 2000;35(9):659-664.
Ghouri N, Preiss D, Sattar Naveed. "Liver enzymes, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and incident cardiovascular disease: a narrative review and clinical perspective of prospective data". Hepatology 2006;52(3):1156–1161.
Nyblom H, Berggren U, Balldin J, Olsson R. "High AST/ALT ratio may indicate advanced alcoholic liver disease rather than heavy drinking". Alcohol. 2004;39(4):336–339.
Barouki R, Chobert MN, Finidori J, Aggerbeck M, Nalpas B, Hanoune J "Ethanol effects in a rat hepatoma cell line: induction of gamma-glutamyltransferase". Hepatology. 1983;3(3): 323–329.
You M, David WC. Molecular mechanisms of alcoholic fatty liver: role of sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. Alcohol. 2004;34(1):39-43.
Achliya GS, Wadodkar SG, Dorle AK. Evaluation of hepatoprotective effect of Amalkadi Ghrita against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic damage in rats. J Ethanopharmacol. 2004;90:1–4.
Anil UT, Sanjay JS, Manisha PS, and Nehal HG. Hepatoprotective effect of poly herbal formulation against various hepatotoxic agents in rats. Pharmacognosy Res. 2012; 4(1): 50–56.
Priya OS, Viswanathan MB, Balakrishna K, Venkatesan M. Chemical constituents and in vitro antioxidant activity of Phyllanthus wightianus. Nat Prod Res. 2011(10):949-58.
Londhe JS, Devasagayam TP, Foo LY, Ghaskadbi SS. Antioxidant activity of some polyphenol constituents of the medicinal plant Phyllanthus amarus Linn Redox Rep. 2008;13(5):199-207.
Trivedi NP, Rawa UM. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant property of Andrographis paniculata (Nees) in BHC induced liver damage in mice. Indian J Exp Biol. 2001;39:41–6.
Tang HR, Covington AD, Hancock RA. Structure–activity relationships in the hydrophobic interactions of polyphenols with cellulose and collagen. Biopolymers. 2003;70:403–413.
Niho N, Shibutani M, Tamura T, Toyoda K, Uneyama C, Takahashi N, Hirose M. Subchronic toxicity study of gallic acid by oral administration in F344 rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2001;39:1063–1070.
Chen C, Tang HR, Sutcliffe L, Belton PS. Green tea polyphenols react with 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picryhydrazyl free radicals in the bilayer of liposomes: direct evidence from electron spin resonance studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003;48:5710–5714.
Krishnamurthi GV, Seshadri TR. Phyllanthin from plant Phyllanthus. Proc Indian Acad Sci 1946;24:357– 362.
Row LR, Srinivasulu C, Smith M, SubbaRao GSR. New lignans from Phyllanthus niruri Linn—The constitution of phyllanthin. Tetrahedron. 1966;22(8):2899–2908.
Joy KL, Kuttan R. Inhibition by Phyllanthus amarus of hepatocarcinogenesis induced by N-nitrosodiethyl amine. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 1998;24:133–139.
Gowrishanker B, Vivekanandan OS. In vivo studies of a crude extract of Phyllanthus amarus L in modifying the genotoxicity induced in Vicia faba L by tannery effluents. Mutat Res. 1994;322:185– 192.
Anthony YHW, Mary Y W, Stephen KWT, Sandy TWY and Christopher KC. Andrographolide Up-Regulates Cellular-Reduced Glutathione Level and Protects Cardiomyocytes against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury. JPET. 2008;325:226-235.