Capparis sepiaria Linn - Pharmacognostical standardization and toxicity profile with chemical compounds identification (GC-MS)
Keywords:
C. sepiaria, Microscopical, Macroscopical standardizationAbstract
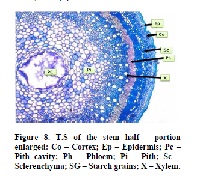
The present study was intended to evaluate the various pharmacognostical procedures in the leaves of Capparis sepiaria Linn., (Capparidaceae). The various pharmacognostical parameters were carried out as per WHO guidelines procedure i.e., bitterness, fineness, microscopical sections, loss on drying, water and alcoholic extractive values, water insoluble ash, acid soluble ash, total ash, swelling index, foaming index, heavy metal analysis, phytochemical analysis and toxicity studies (acute, subacute and chronic toxicity). The study was extended with analyzing the chemical compounds identification in the EECS (ethanolic extract of Capparis sepiaria by using GC-MS. The presence of various phytoconstituents such as glycosides, reducing sugars, flavonoids, saponins, starch and terpenoids is evidenced in EECS & AECS. The results showed that acid insoluble ash (1.70%), total ash (8.68%), water soluble ash (3.42%), water extractive (31.55%), alcohol extractive (5.06%), foaming index (105.26 Unit), loss on drying (9.84%), swelling index (4.16%), acute toxicity (nil), sub-acute toxicity (nil), chronic toxicity (nil). The study was concluded with the plant has standardized as per the World Health Organization procedures. The result of the pharmacognostical standardization of this plant serves as a reference piece and helps in future identification and authentication of this plant specimen. Might be the plant C. sepiaria has potential property by the standardization and it can be included in the normal flora of the plant kingdom.
References
Anonymous. Quality Control of Medicinal
Plant Materials. (An authorized publication of
World Health Organization, Geneva) New
Delhi: A.I.T.B.S. Publishers & Distributors
(Regd.); India: 2002. p. 1-122.
Harborne JB. Phytochemical Methods: A
Guide to Modern Techniques of Plant
Analysis. Champman and Hall, 3rd ed. New
York, USA: 1998.
Kokate CK. Practical Pharmacognosy,
Vallabh Prakashan, New Delhi, India: 1994.
Wagner JG, Roth RA. Neutrophil migration
during endotoxemia. J Leukoc Biol 1999; 66:
-13.
Harborne JB. Phytochemical Methods,
Champman and Hall, New York, USA: 1984.
Trease GE, Evans WC. Pharmacognosy.
Balliere Tindall Press London: 1983, p. 500-
Ikhiri K, Boureima D, Dan Kouloudo D.
Chemical screening of medical plants used in
traditional pharmacopoeia of Niger. Intern J
Pharmacogn 1992;30: 251-262.
Dahou N, Yamni K, Tahrouch S, Idrissi
Hassani LM, Badoc A, Gmira N. J Bulletin
De La Societe De Pharmacie De Bordeaux
;142: 61–78.
OECD/OCDE. Guidelines for the testing of
chemicals. Revised draft guidelines. 423:
Acute Oral Toxicity Acute Toxic Class
Method, Revised Document. 2000.
Evans WC. Trease and Evans
Pharmacognosy. 15th ed. Edinburgh: W.B.
Saunders: 2002.