Antimicrobial activity of Saraca indica against clinical pathogens
Keywords:
Saraca indica, antimicrobial activity, alkaloids, Rf valueAbstract
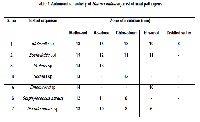
The antimicrobial activity of flowers of the medicinal plant Saraca indica collected from from the regions of Ambalathara, Kerala, South India was checked against the clinical pathogens by well diffusion method. Saraca i1ndica showed highest antimicrobial activity on methanolic extracts. The phytochemical evaluation showed the presence of alkaloids, tannins, proteins and reducing sugars. With the help of column chromatography the methanolic extract was purified and highest antimicrobial activity was observed in the concentration 2:8. By thin layer chromatography the compounds are separated and the Rf value obtained was 0.6. The compound responsible for the antimicrobial activity was partially identified as alkaloids
References
. Arora DS, Kaur JK. Antibacterial
activity of some Indian, medicinal
plants. Journal of natural medicines.
; 61:313-319.Prusti A, Mishra
SR, Sahoo S, Mishra SK.
Antibacterial activity of some Indian
medicinal plants. Ethnobotanical
Leaflets. 2008; 12:227-230.
. Pradhan P, Joseph L, Gupta V,
Chulet R, Arya H, Verma R, Bajpai
A. Journal of chemical and
pharmaceutical research. 2009;
(1): 62-71.
. Duraipandiyan V, Muniappan A,
Savarimuthu I. Antibacterial activity
of some ethnomedicinal plants used
by Paliyar tribe from Tamil Nadu,
India. Complementary and
alternative medicine. 2006; 10:6-35.
. Sainath R, Prathiba J Malathi R.
Antimicrobial properties of the stem
bark of Saraca indica
(Caesalpiniaceae). European
Review for Medical and
Pharmacological Sciences. 2009;
: 371-374.
. Unni BG, Borah A, Singh HR.
Phytochemical and antibacterial
study of North East India on
Escherichia coli. Asian J. Exp. Sci.
; 23(1):103-108.
. Solanki,R. Some medicinal plants
with antibacterial activity.
International journal of
comprehensive pharmacy. 2010;
(10):1-4.
. Raman S, Sultana N, Anwar MN.
Invitro Antimicrobial activity of
Holarrifine-24ol isolated from the
stem bark of Holarrhena
antidysenterica. International journal
of agriculture and biology. 2004;
:698-700.
. Bauer AW, Kirby WMM, Sherris JC
and Truck M. Antibiotic susceptibility
testing by standard single disk
diffusion method. Am. J. Clin. Path.
;45:493-496.
. Kepm W. Qualitative Organic
Analysis: Spectrochemical
Techniques. 2nd Edn., McGraw- Hill,
London and New York, ISBN
1986;pp: 197.
. Dabur R, Gupta A, Mandal TK,
Singh DD, Bajpai V, Gurav AM,
Lavekar GS. Antimicrobial activity
of some Indian medicinal plants.Afr.
J. Trad. Comp. Alt. Med. 2007; 4:
-318.
. Narang GD, Nayar S, Mcndiratta
DK. Antibacterial activity of some
indigenous drugs, J. Vet. Animal
husb. Res. 1962; 6(1): 22-25.
. Cibin TR, Gayathri DD, Abraham A.
Chemoprevention of skin cancer by
the flavonoid fraction of Saraca
asoka. Phytotherapy Research .
; 24:666–672.
. Cai L, Wu CD. Compounds of
Syzygium aromaticum possessing
growth inhibitory activity against oral
pathogens. J of Nat. Prod. 1996;
(9): 987–990.