Flavones composition and therapeutic potential of Dodonaea viscosa against liver fibrosis
Keywords:
Dodonaea viscosa, flavones, phytochemical constituents, liver fibrosis,, antioxidants, histopathologyAbstract
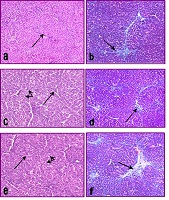
Dodonaea viscosa (L.) Jaeq (Sapindaceae) is used in traditional medicine for the treatment of hemorrhoids, ulcer, and pains of hepatic or stomach origin. The current study was designed to investigate the phytochemical constituents of the plant and evaluate its activity against liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) in rats. The phytochemical analysis has afforded one flavanone; 5,7-dihydroxy flavanone (pinocembrin) (1) and eight flavones. The compounds were isolated and elucidated as; 5,7-dihydroxy-3,6,4'-trimethoxyflavone (santin) (2), 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-3-methoxy flavone (kaempferol 3-O-methyl ether) (3), 3,4',5-trihydroxy-7-methoxy flavone (kaempferol 7-O-methyl ether) (4), 3',4',5,7-tetrahydroxy-3-methoxy-flavone (quercetin 3'-O-methyl ether) (5), 3,3',4',5,7- pentahydroxyflavone (quercetin) (6), 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-3,6-dimethoxy flavone (7), 5,7-dihydroxy 3,6,3',4'- tetramethoxy flavone (8), and isorhamnetin-3-O-robinobioside (9).. In vitro screening of ethanol extract, fractions of toluene and ethyl acetate, the flavanone and major flavone compounds as antioxidants was carried out. In addition, D. viscosa ethanol extract and two fractions were examined in vivo against liver fibrosis induced by CCl4 in rats. The evaluation was done through measuring hepatic oxidative stress markers; malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH) and superoxide dismutase (SOD). The work was extended to measure serum protein content and liver function enzymes; aspartate and alanine aminotransferases (AST and ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT). Liver histopathological analysis was done for results confirmation. In conclusion, among the isolated flavones, compounds 3, 4, and 8 were isolated for the first time. The ethanol extract and compound of 6, 5 followed by 7 exhibited the strongest antioxidant activities. Treatment with D. viscosa extract and its fractions attenuates the increments of MDA, AST, ALT, ALP, GGT, total protein and increased GSH and SOD levels. The ethanol extract showed the most potent effect. The data confirmed the rationale for the traditional use of D. viscosa extracts to hepatic disorders. Further studies are needed in order to evaluate the isolated flavones as protective agents against liver injury and for their clinical application.
References
. van-Heerden FR, Viljoen AM, van-Wyk
BE. The major flavonoid of Dodonaea
angustifolia. Fitoterapia 2000;71:602–
. Niu HM, Zeng DQ, Long CL, Peng YH,
Wang YH, Luo JF, Wang HS, Shi YN,
Tang GH, Zhao FW. Clerodane
diterpenoids and prenylated flavonoids
from Dodonaea viscosa. J Asian Nat
Prod Res 2010;12:7–14.
. Shanmugavasana A, Ramachandran
T. Investigation of the extraction
process and phytochemical
composition of preparations of
Dodonaea viscosa (L.) Jacq. J
Ethnopharmacol 2011;137:1172-1176.
. Pengelly A. Medicinal activity of
Dodonaea viscosa—A preliminary
study. Regional Industries Research
and Development Corporation,
Australia, 2008.
. Anilreddy B: Preparation,
characterization and biological
evaluation of some overview of
Dodonaea viscosa Linn. J Pharmaceut
Sci Tech 2009;1:1–9.
. Rani MS, Rao, SP, Mohan K.
Dodonaea viscosa Linn—an overview.
J Pharmaceut Res Health Care
;1:97–112.
. Khalil MN, Sperotto SJ, Manfron PM:
Anti-inflammatory activity and acute
toxicity of Dodonaea viscosa.
Fitoterapia 2006;77:478 – 480.
. Meenu J, Sunil S, Manoj K. Evaluation
of antihyperglycemic activity of
Dodonaea viscosa leaves in normal
and STZ-diabetic rats. Int J Pharm
Pharmaceut Sci 2011;3:69-74.
. Veerapur VP, Prabhakar KR, Parihar
VK, Bansal P, Srinivasan KK,
Priyadarsini KI, Unnikrishnan MK:
Antidiabetic, hypolipidaemic and
antioxidant activity of Dodonaea
viscosa aerial parts in streptozotocininduced diabetic rats. Int J Phytomed
;2:59–70.
. Kanter M, Coskun O, Budancamanak
M. Hepatoprotective effects of Nigella
sativa L. and Urtica dioica L. on lipid
peroxidation, antioxidant enzyme
systems and liver enzymes in carbon
tetrachloride-treated rats. World J
Gastroenterol 2005;11:6684–6688.
. Nevin KG, Vijayamma L. Effect of
Aerva lanata against hepatotoxicity of
carbon tetrachloride in rats. Environ
Toxicol Pharmacol 2005;20:471-477.
. Shankar GNL, Manavalan R,
Venkappayya D, Raj CD.
Hepatoprotective and antioxidant
effects of Commiphora berryi (Arn)
Engl bark extract against CCl4-induced
oxidative damage in rats. Food Chem
Toxicol 2008;46:3182–3185.
. Mitra SK, Venkataranganna MV,
Sundaram R, Gopumadhavan S. Effect
of HD-03, an herbal formulation, on the
antioxidant defense system in rats.
Phytother Res 1998;12:114–117.
. Abu-Gabal NS, Abd-Alla HI, Ahmed
HH, Al-Saigh SM, Shalaby NMM.
Efficacy of Aloe vera extracts in
attenuating neurological
endangerment-induced by
dexamethasone in adult male rats. J
Arab Soc Med Res 2007;2:59-73.
. Wyk VEB. A broad review of
commercially important southern
African medicinal plants. J
Ethnopharmacol 2008;119:342–355.
. Agrawal PK, Bansal MC. Flavonoid
glycosides. In: studies in organic
chemistry 39, 13C-NMR of flavonoids,
Agrawal PK (Ed.), Elsevier science,
New York, U.S.A., 1989.
. Mabry TJ, Markham KR, Thomas MB.
The systematic identification of
flavonoids. Springer-Verlag, Berlin,
;pp. 41–164.
. Markham KR. Techniques of flavonoid
identification. Academic Press Inc, Ltd,
London, 1982;pp. 84.
. Harborne JB, Mabry TJ. The
Flavonoid: Advances in research,
Chapman and Hall Ltd, London,
;pp. 1-18.
. Chen HY, Lin YC, Hsiech CL.
Evaluation of antioxidants activity of
aqueous extract of some selected
nutraceutical herbs. Food Chem
;104:1418-1424.
. Marsillach J, Camps J, Ferré N,
Beltran R, Rul A, Mackness B, Michael
MM, Joven J. Paraoxonase-1 is related
to inflammation, fibrosis and PPAR
delta in experimental liver disease.
BMC Gastroenterol 2009;9:3.
. Yuvaraj P, Subramoniam A.
Hepatoprotective property of
Thespesia populnea against carbon
tetrachloride induced liver damage in
rats. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol
;20:169-177.
. Buege JA, Aust SD. Microsomal lipid
peroxidation. Meth Enzymol
;52:302-310.
. Moron MS, Depierre JW, Mannervik B.
Level of glutathione, glutathione
reductase and glutathone-Stransferase activities in rat lung and
liver. Biochimica Biophysica Acta
;582:67-78.
. Nishikimi M, Rae NA, Yagi K. The
occurrence of superoxide anion in the
action of reduced phenazine
methosulphate and molecular oxygen.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun
;46:849-853.
. Gella FJ, Olivella T, Cruz PM, Arenas
J, Moreno R, Durban R, Gomez JA. A
simple procedure for routine
determination of aspartate
aminotransferase and alanine
aminotransferase with pyridoxal
phosphate. Clin Chem Acta
;153:241-247.
. Rosalki SB, Foo AY, Burlina A.
Multicenter evaluation of iso-ALP test
kit for measurement of bone alkaline
phosphatase activity in serum and
plasma. Clin Chem 1993;39:648-652.
. Szasz G. A kinetic photometric method
for serum γ-glutamyl transpeptidase.
Clin Chem 1969;15:124-136.
. Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive
method for the quantitation of
microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding.
Anal Biochem 1976;72:248-254.
. Suzuki H, Suzuki K. Rat hypoplastic
kidney (hpk/hpk) induces renal
anemia, hyperparathyroidism, and
osteodystrophy at the end stage of
renal failure. J Vet Med Sci
;60:1051-1058.
. Leenhouts PW. Notes on the extraAustralian species of Dodonaea
(Sapindaceae). Blumea 1983;28:271-
. Horie T, Ohtsurs Y, Shibata K,
Yamashita K, Tsukayama M,
Kawamura Y. 13C NMR special
assignment of the a-ring of
polyoxgenated flavones.
Phytochemistry 1998;47:865–874.
. Rashid MA, Armstrong JA, Gray AI,
Waterman PG. Alkaloids, flavonoids
and coumarins from Drummondita
hassellil and D. calida. Phytochemistry
;31:1265–1269.
. Salah NAM, Mansour RMA, Markham
KR. An acylated isorhamnetin
glycoside from Aerva javanica.
Phytochemistry 1990;29:1344-1345.
. Halim AF, Saad HEA, Hashish NE.
Flavonol glycosides from Nitraria
retusa. Phytochemistry 1995;40:349-
. Sachdev K, Kulshreshtha DK.
Flavonoids from Dodonaea viscosa.
Phytochemistry 1983;22:1253–1256.
. Getie MG, Gebre-Miriam T, Rietz R,
Neubert R. Distribution of quercetin,
kaempferol and isorhamnetin in some
Ethiopian medicinal plants used for
treatment of dermatological disorders.
Ethiopian Pharmacol J 2000;18:25–34.
. Abdel-Mogib M, Basaif SA, Asiri AM,
Sobahi TR, Batterjee SM. New
clerodane diterpenoid and flavonol-3-
methyl ethers from Dodonaea viscosa.
Pharmazie 2001;56:830-831.
. Fukumoto LR, Mazz G. Assessing
antioxidant and prooxidant activities of
phenolic compounds. J Agric Food
Chem 2000;48:3597–3604.
. Jeong JM, Choi CH, Kang SK, Lee
IH, Lee JY, Jung H. Antioxidant and
chemosensitizing effects of flavonoids
with hydroxy and/or methoxy groups
and structure-activity relationship. J
Pharm Pharm Sci 2007;10:537-546.
. Rice-Evans CA, Miller NJ, Paganga G.
Structure-antioxidant relationships of
flavonoids and phenolic acids. Free
Radic Biol Med 1996;20:933–956.
. Saskia ABE, Acker V, Van-Den Berg
DJ, Bast A: Structural aspects of
antioxidant activity of flavonoids. Free
Radic Biol Med 1996;20:331–342.
. Teffo LS, Aderogba MA, Eloff JN.
Antibacterial and antioxidant activities
of four kaempferol methyl ethers
isolated from Dodonaea viscosa Jacq.
var. angustifolia leaf extracts. S Afr J
Bot 2010;76:25-29.
. Manna P, Sinha M, Sil PC. Aqueous
extract of Terminalia arjuna prevents
carbon tetrachloride induced hepatic
and renal disorders. BMC Comp Alt
Med 2006;6:33-42.
. April JE, Michael PR, Gwendolyn LK,
Edward JN, Evan BS. Experimental
diabetes attenuates cerebral cortical –
evoked forelimb motor responses.
Diabetes 2005;54:2764-2771.
. Gharib B, Abd-Allah OM, Dessein H,
De-Reggi M. Development of
eosinophil peroxidase activity and
concomitant alteration of antioxidant
defenses in the liver of mice infected
with Schistosoma mansoni. J Hepatol
;30:594-602.
. Mansour HH, Hafez HF, Fahmy, NM.
Silymarin modulates cisplatin-induced
oxidative stress and hepatotoxicity in
rats. J Biochem Mol Biol 2006;39:656-
. Yadav NP, Pal A, Shanker K,
Bawankule DU, Gupta AK, Darokar
MP, Khanuja SPS. Synergistic effect of
silymarin and standardized extract of
Phyllanthus amarus against CCl4-
induced hepatotoxicityin Rattus
norvegicus. Phytomed 2008;15:1053–
. Opoku AR, Ndlovu IM, Terblanche SE,
Hutchings AH. In vivo
hepatoprotective effects of Rhoicissus
tridentata subsp. cuneifolia, a
traditional Zulu medicinal plant, against
CCl4-induced acute liver injury in rats.
South African J Botany 2007;73:372–
. Romero FJ, Bosch-Morell F, Romero
MJ, Jareńo EJ, Romero B, Marίn N,
Romá J. Lipid peroxidation products
and antioxidants in human disease.
Environ Health Perspectives
;106:1229–1234.
. Sharma N, Shukla S. Hepatoprotective
potential of aqueous extract of Butea
monosperma against CCl4 induced
damage in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol
;63:671-676.
. Reyes-Gordillo K, Segovia J,
Shibayama M, Vergara P, Moreno MG,
Muriel P. Curcumin protects against
acute liver damage in the rat by
inhibiting NF-kappa B, proinflammatory
cytokines production and oxidative
stress. Biochim Biophys Acta
;1770:989-996.
. Hamed MA. Metabolic profile of rats
after one hour of intoxication with a
single oral dose of ethanol. J
Pharmacol Toxicol 2011;6:158-165.
. Wagner H. Trends and challenge:
phytomedicine: research in the new
millennium. In: Yaniv Z, Bachrach U
(Eds.), Handbook of Medicinal Plants.
Haworth press, New York, 2005;pp. 3–
. Sivanesan D, Selvi VAVT, Bhakyaraj
R, Arunachalam T. Protective effect of
Dodonaea viscosa (L) against lead
acetate induced altered glycoprotein
profiles in rats. E J Chem 2009;6:725-