Antifungal Activity of Essential Oils against Fluconazole Resistant Fungi
Keywords:
Essential oils, antifungal drug, drug resistance, synergistic actionAbstract
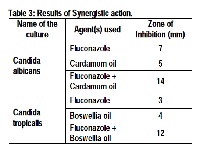
Pathogenic fungi like Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis and Trichophyton mentagrophytes are commonly encountered strains associated with a wide range of conditions including scalp infection, oral thrush, skin infection, and vaginal thrush. Unlike bacterial pathogens, fungal pathogens are difficult to control. Fluconazole is a commonly administered antifungal drug. The medical fraternity has been reporting an alarming increase in the development of resistance observed amongst fungal strains to Fluconazole. The present study involves screening of essential oils for their antifungal activity against Fluconazole resistant fungi. Essential oils of Black pepper, Cardamom, Cumin, Boswellia and Patcholi were selected for the study. The results indicated that all the oils inhibited fungal strains in varying degrees of dilutions. Essential oil of Boswellia was found to be the most effective in antifungal activity against Candida tropicalis and essential oil of Cardamom against Trichophyton mentagrophytes. To assess the effect of combination of essential oils with Fluconazole, synergistic action was also studied. The results indicated that essential oil of Boswellia and Fluconazole in combination acted as the most powerful antifungal agent against Candida tropicalis even at 1:10 dilution and 100μg/ml respectively. These results lead us to believe that active components present in essential oils should be a focus area of future in vivo research, especially in conjunction with existing antifungal drugs. The molecular mechanisms, mode of action, stability, toxicity, and efficacy of the active components isolated from essential oils need to be further studied and evaluated.
References
Lixandru BE, Dracea NO, Dragomirescu CC,
Dragulescu EC, Coldea IL, Anton L, Dobre E,
Rovinaru C, Codita I. Antimicrobial activity of
plant essential oils against bacterial and fungal
species involved in food poisoining and/or food
decay. Roum Arch Microbiol Immunol.
;69(4):224-230.
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21462837
Bansod S, Rai M. Antifungal Activity of Essential
Oils from Indian Medicinal Plants Against Human
Pathogenic Aspergillus fumigatus and A. niger.
World J of Medical Sciences. 2008;3(2):81-88.
http://idosi.org/wjms/3(2)08/7.pdf
Gibbons S. Plants as a source of bacterial
resistance modulators and anti-infective agents.
Phytochem Rev. 2005;4:63-78.
http://210.27.80.89/2005/zhihua/file/2005pdf/51Pl
ants%20as%20a%20source%20of%20bacterial%
resistance%20modulators.pdf
Prabuseenivasan S, Jayakumar M, Ignacimuthu
S. In vitro antibacterial activity of some plant
essential oils. BMC Complementary and
Alternative Medicine. 2006;6:39.
http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6882/6/39
Coutinho HDM, Matias EFF, Santos KKA, Tintino
SR, Souza CES, Guedes GMM, Santos FAD,
Costa JGM, Falcao-Silva VS, Siqueira-Junior JP.
Enhancement of the norfloxacin antibiotic activity
by gaseous Contact with the essential oil of
Croton zehntneri. Pharmacognosy.
;2(4):362-364.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC301
/
Burt S. Essential oils: their antibacterial properties
and potential applications in foods – a review.
Int.J. Food Microbiol. 2004;94(3):223-253.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15246235
Rex JH, Rinaldi MG, Pfaller MA. Resistance of
Candida Species to Fluconazole. Antimicrob.
Agents Chemother. 1995;39(1):1-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC162
/
Hemaiswarya S, Kruthiventi AK, Doble M.
Synergism between natural products and
antibiotics against infectious diseases.
Phytomedicine. 2008;15:639-652.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S
Shiota S, Shimizu M, Mizushima M, Ito H, Hatano
T, Yoshida T, Tsuchiya T. Restoration of
effectiveness of beta-lactams on methicillin
resistant Staphylococcus aureus by
tellimagrandin I from rose red. FEMS Microbiol.
Lett. 2000;185:135-138.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10754237
Mitscher LA, Drake S, Gollapudi SR, Okwute SK.
A modern Look at folkloric use of anti-infective
agents. J of Natural Products. 1987;50:1025-
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3443855
Janssen AM, Scheffer JJC, Baerheim Svendsen
A. Antimicrobial activity of essential oils: a 1976-
literature review. Aspects of the test methods.
Planta Medica. 1987;53:395-398.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3324126
Sivropoulou A, Kokkini S, Lanaras T, Arsenakis
M. Antimicrobial activity of mint essential oils. J of
Agriculture and Food Chemistry. 1995;43:2384-
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jf00057a013
Den Hollander JG, Mouton JW, Verbrugh HA.
Use of pharmacodynamics parameters to predict
efficacy of combination therapy by using fractional
inhibitory concentration kinetics. Antimicrob.
Agents Chemother. 1998;42:744-748.