Neuroprotective effect of Vinpocetine against 3- NP Induced reduction of body weight and oxidative stress in Rats
Keywords:
3- Nitropropionic acid, Vinpocetine, Huntington DiseaseAbstract
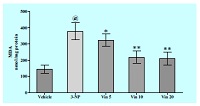
Huntington’s disease is a progressive, degenerative disease characterized by abnormal body movements symptoms like chorea and a reduction of body weight. Recently, it has been reported that oxidative stress, which is one of the pathological hallmarks of various neurodegenerative disorders, also plays an important role in the pathogenesis of Huntington’s disease. 3- Nitropropionic acid, a neurotoxin treatment significantly reduction in body weight. Intraperitoneal administration of 3-nitropropionic acid (10 mg/kg for 14 days) caused significant loss of body weight and poor rentention of memory. Biochemical analysis revealed that 3-NP administration significantly increase in lipid peroxidation in the brains of rats. The present study demonstrated that inhibition of type 1 phosphodiesterase (PDE1) by vinpocetine (5, 10 & 20mg\kg) significantly reversed behavioral and biochemical dysfunction in 3-NP treated group. The result of the present study suggests facilitatory role of PDE1 enzyme in loss in body weight and oxidative stress following 3-NP injection.
References
. Vonsattel JP, DiFiglia M. Huntington
disease, J. Neuropathol Exp Neurol
;57:369-384.
. Martin JB. and Gusella JF. Huntington’s
disease: pathogenesis and management. N
Engl J. Med 1986; 315: 1267-1276.
. Cruz, V and Santamaria, A. Integrative
Hypothesis for Huntington’s disease: A
Brief Review of Experimental Evidence.
Physiol. Res 2007; 56: 513-526.
. La Fontaine MA, Geddes JW, Banks A
and Butterfield DA. Effect of exogenous
and endogenous antioxidants on 3-
nitropropionic acid – induced in vivo
oxidative stress and striatal lesions:
insights into Huntington’s disease. J
Neurochem 2000; 75: 1709- 1715.
. Kumar P, Padi SSV, Naidu PS and Kumar
A. Possible Neuroprotective of Curcumin
in Attenuating 3-Nitropropionic Acid –
Induced Neurotoxicity. Methods Find.
Exp. Clin. Pharmacol 2006; 17: 485- 92.
. KimYJ ,Yi ,Y Sapp, Wang Y, Cuiffo B,
Kegel, Qin ZH, Aronin, DiFiglia M.
Capase3- cleaved N- terminal fragments
of wild type and mutant huntingtin are
present in normal and Huntington’s
disease brains , associate with
membranes, undergo calpain – dependent
proteolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci . U.S.A.
; 98: 12784- 12789.
. Vis JC, Van Huizen RT, Veerbeek MM,
de Waal RM, ten Donkelaar HJ and
Kremer B. Creatine protects against 3-
nitropropionic acid-induced cell death in
murine corticostriatal slice cultures. Brain
Res 2004; 1024: 16-24.
. Beal MF. Mitochondrial dysfunction in
neurodegenerative disease. Biochem
Biophy Acta 1998; 1366: 211-223.
. Nagakura M, Oosumi K, Hirano H,
Onishi Y. Pharmcogenomics and
therapeutics trategies for Dementia .
Science direct 2002; 34:357- 379.
. Puzzo D, Vitolo O , Trinchese F, Joel P,
Jacob AP, Arancio . Neurobiology of
Disease Amyloid β Peptide Inhibits
Activation of the Nitric
Oxide/cGMP/cAMP-Responsive
Element-Binding Protein Pathway during
Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity. J
Neuroscience 2005; 25: 6887– 6897.
. Fujita SS, Zghb J, Hong . Species
differences in Brain phosphodiesterase
levels . J Neural Transm 2008; 41:185.
. Nibuya M , Nestler EJ, Duman RS.
Chronic antidepressant administration
increases the expression of cAMP
response element binding protein (CREB)
in rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 1996; 16:
–2372.
. Chun YJ, Kim MY, Guengerich FP.
Resveratrol is a selective human
cytochrome P450 1A1 inihibitor.
Biochem Biophys Rest Commun 1999;
:20-24.
. Song, Perides, Liu and YF .Expression of
full length polyglutamine expanded
Huntington distrupt growth factor
receptor signaling in rat. J Biolchem
; 277:6703-6707.
. Bishop VS, DM Farrell. The role of
cGMP and cAMP in active
thermoregulatory vasodilation. Neurobiol
Dis 1997; 272: R975- R981.
. O’Donnell JM and Zhang HT.
Antidepressant effects of inhibitors of
cAMP phosphodiesterase. Trends
Pharmacol. Sci 2004; 25: 158–163.
. K Tarnok, E Kiss, PGM Luiten, C
Nyakas, K Tihanyi, K Schlett ,and ULM
Eisel. Effects of Vinpocetine on
mitochondrial function and
neuroprotection in primary cortical
neurons. Curr Pharm Des 2008; 66: 63-
. Lugnier C: Cyclic nucleotide
phosphodiesterase superfamily.
Pharmacol Ther 2006; 109:366-398.
. Wills ED. Mechanism of lipid peroxide
formation in animal. Biochems J. 1966;
: 667-676.
. Kumar P, Padi SSV, Naidu PS and
Kumar A. Effect of resveratrol on 3-
nitropropionic acid- induced biochemical
and behavioural changes: possible
neuroprotective mechanisms. Behav.
Pharmacol, 2006 ; 17: 485- 492.
. Rose GM, Hopper A, De Vivo M and
Tehim A. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors
for cognitive enhancement. Curr Pharm
Des 2005; 11(26): 3329-3334.
. Vas A and Gulyas D. Eburnamine
derivatives and the brain. Med Res Ev
; 25: 737-57.
. Kaudac D and Mittlemon A , Serpico R,
Sinha AA, Natale C, Pani P, Simone S
and Farber E. Cell death: apoptosis versus
necrosis. Int J on col 2002; 21: 165- 70.
. Koutouzis TK , Borlongan, Scorcia and
Creese PR , Systemic 3-NP : long term
effects on locomotor behavior. Brain Res
; 646:242- 46.
. Tunez I, Montilla P, Munoz and Tariq
MC. Treatment with
dehydroepiandrosterone prevents
oxidative stress induced by 3-
nitropropionic acid in synaptosomes.
Pharmacology 2005; 74:113-118.
. Borlongan CV , Freeman TK, DW Cahill.
Behavioral pathology induced by repeated
injection of 3-NP mimic the symptoms of
HD . Brain Res 1995; 697: 254-257.
. Borlongan CV, Kanning K ,Freeman.
Free radical damage and oxidative stress
in Huntington’s disease. JFLA Med Assoc
; 83: 335-41.
. Haik KL, Haik, DA,Shear Sabel, Dunbar
GL, Quinolinic acid released from
polymeric brain implants causes
behavioral and neuroanatomical
alterations in a rodent model of HD. Exp
Neurol 2000; 163: 430- 439.
. Kodsi, Swerdlow. Mitochondrial 3-NP
produce abnormalities in rats that model
of HD. Depart Psych 1997; 231 : 103-07.
. Sun Y. Free radicals and antioxidant
enzymes. Free Radic Biol Med 1990; 8:
-99.
. Stolc S. Indole derivatives as
neuroprotectants .Life Sci 1950; 65:
-50.
. Santos MS, Durate AL, Oliveria.
Synaptosomal response to oxidative
stress: effects of Vinpocetine. Free Radic
Res 2000; 32: 57-66.