HPLC Method for Determination of p-coumaric acid from the Medicinal Herb Leptadinia reticulata
Keywords:
Leptadinia reticulata, p-coumaric acid, HPLCAbstract
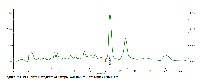
The aim of present study was to develop and validate a simple, precise and rapid HPLC method for the quantification of p-coumaric acid in Leptadinia reticulata extractst. The analysis was performed by reverse-phase chromatography on an phenomenex C18 columns with isocratic elution of Methanol and 0.8%-Formic acid in water (6:4) at a flow rate of 1.0mL/min, a column temperature of 35°C, photodiode array detector detection at 326 nm. The method validated in terms of linearity accuracy precision LOD, LOQ and stability. The herb Leptidinia reticulata contains 0.17% p-coumaric acid. The linear range of method was 0.25-50µg/ml with correlation coefficient of 0.9993, the recovery was 98-99.4% and the relative standard deviation is 0.98 % (n=6). The developed method was found to be a relatively simple, precise and reproducible for the quantification of p-coumaric acid. The method does not employ any derivatization procedure and can be used as a quality control tool for the routine analysis of p-coumaric acid from an herb Leptadinia reticulata.
References
. Daniel M. Medicinal plant chemistry and
properties. New Delhi Oxford and IBH
Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd 2006.
. Krishna PV, Venkata Rao E, Venkata Rao
D. Crystalline principle from the
leaves and twigs of Leptidinia reticulata.
Plant Med. 1975;27:395-400.
. Sastry BS, Vijayalakshmi T, Venkata RE,
Venkata RD. Chemical constituent of the
bark of Leptidinia reticulata. Indian drugs.
;22:611-612.
. Srivastav S, Deepak D, Khare A. Three
novel pregnane glycoside from
Leptadinia reticulata W & A.
Tetrahedron. 1994;50:789-798.
. Habla A, Sitaratna A. Leptidina A clinical
trials of its value as a galactogue.
The Antiseptic. 1972;9:331-333.
. Nikolova M and Gevrenova R.
Simultaneous determination of four
components in the herbs of Sumbucus
chinensis lindl. Asian J. Trad. Med.
;43:289-291.
. Ke Liu, Linqi Yan, Guocan Yao, Xinjie
Guo. Estimation of p-coumaric acid as
its application to a pharmacokinetic study
Journal of Chromatography B.
;831:303-306.
. Tianhong Zhang, Dan Yang, Yuanguo
Wang, Xiaohun Chen, Kaishun
BiSimultaneous. Determination of four
components in the herbs of Sumbucus
chinensis lindl. By HPLC. Asian Journal
of Traditional Medicines. 2010;5(2):70-74
. Meng Z, Wang W, Xing DM, Lei F, Lan
JQ, Du LJ. Pharmacokinetic study of pcoumaric acid in mouse after oral
administration of extract of Ananas
comosus L. leaves. Biomed Chromatogr.
;20(9):951-5.
. Jaytilak PG, Pardanani DS, Murthy B and
Sheth AR. Effect of an indigenous drug
(Speman) on accessory reproductive
function of mice. Indian J. Expt. Biol.
;2:170-173.
. Milena Nikolova and Reneta Gevrenova.
Simultaneous determination of four
components in the herbs of Sumbucus
chinensis lindl. by HPLC./ Asian Journal
of Traditional Medicines. 2010;43:289–
. ICH-Q2 (R1). Validation of Analytical
Procedures: Text and Methodology.
International Conference on
Harmonization: Geneva 2005.